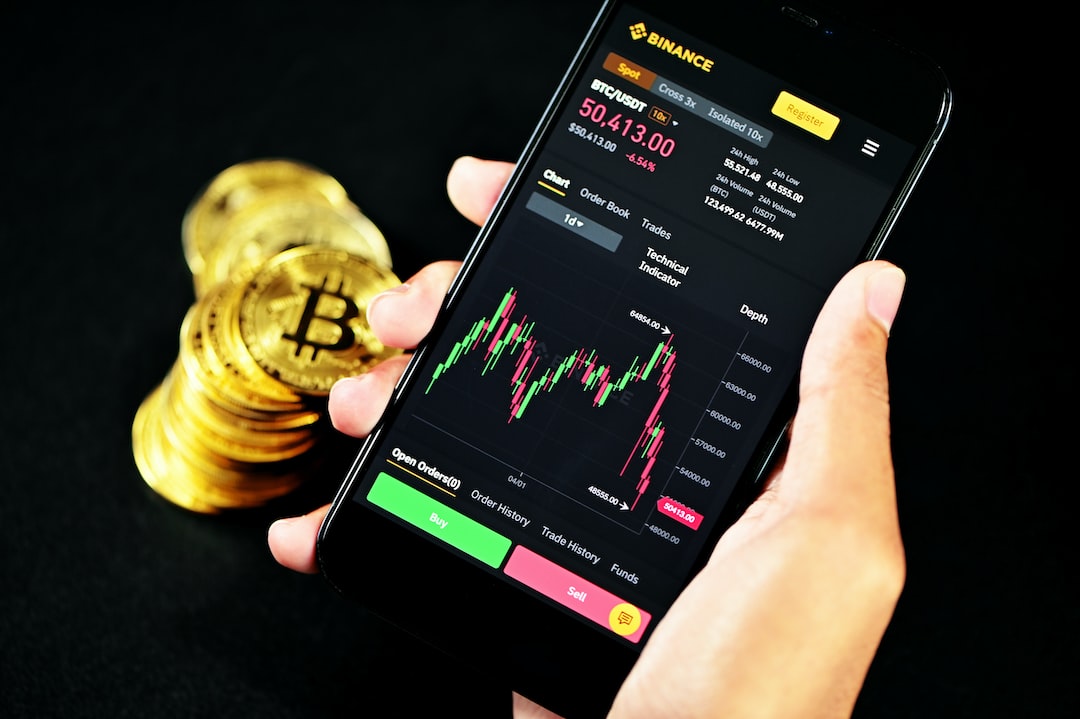
The foreign exchange market, or forex, is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world. It involves trading currency pairs, with the aim of profiting from fluctuations in their exchange rates. In forex trading, it is important to understand the correlation between currency pairs. Some forex pairs move together, either in the same direction or in opposite directions, while others have no correlation at all. Understanding these correlations can help traders make informed decisions and manage their risk more effectively.
Currency correlation is the measure of how one currency pair moves in relation to another. It is measured on a scale of -1 to +1, where -1 represents a perfect negative correlation, +1 represents a perfect positive correlation, and 0 represents no correlation at all. A positive correlation means that the pairs move together in the same direction, while a negative correlation means that they move in opposite directions.
So, which forex pairs move together? Some of the most closely correlated pairs include:
1. EUR/USD and GBP/USD: These two pairs are highly correlated because both currencies are affected by the same economic and political factors in Europe. They both tend to move in the same direction, although the correlation is not always perfect.
2. USD/JPY and Nikkei Index: The Japanese yen is often used as a funding currency for carry trades, which involves borrowing in low-yielding currencies and investing in higher-yielding assets. The Nikkei Index is a barometer of the Japanese economy and stock market. When the Nikkei Index rises, the yen tends to weaken and USD/JPY tends to rise.
3. AUD/USD and Gold: The Australian dollar is often seen as a commodity currency because of Australia’s significant natural resources, including gold. When the price of gold rises, the Australian dollar tends to rise along with it.
4. USD/CAD and Oil: Canada is a major producer and exporter of oil, so the Canadian dollar tends to be closely correlated with the price of oil. When the price of oil rises, the Canadian dollar tends to rise along with it, and USD/CAD tends to fall.
5. EUR/USD and USD/CHF: These two pairs are negatively correlated because the Swiss franc is often used as a safe haven currency in times of uncertainty. When investors are risk-averse, they tend to buy Swiss francs, causing USD/CHF to fall and EUR/USD to rise.
It is important to note that correlations can change over time, and they are not always consistent. Economic and political events can cause correlations to break down, or new correlations to emerge. Traders should always monitor the correlation between currency pairs and adjust their trading strategies accordingly.
In addition to understanding currency correlations, traders should also be aware of the risks associated with trading multiple correlated pairs. Holding multiple positions in highly correlated pairs can increase risk and exposure to market volatility. Traders should diversify their portfolios and manage their risk carefully to avoid significant losses.
In conclusion, understanding which forex pairs move together can help traders make informed decisions and manage their risk more effectively. While correlations can change over time, knowing the historical relationships between currency pairs can provide valuable insights and help traders anticipate market movements. By monitoring currency correlations and diversifying their portfolios, traders can maximize their chances of success in the dynamic and ever-changing forex market.