Introduction
In the AUD/KES pair, the AUD represents the Australian Dollar while the KES is the Kenyan Shilling. When buying and selling this exotic currency pair, forex traders should expect instances of high volatility. In the AUD/KES pair, AUD is the base currency, and KES is the quote currency. The price attached to this pair is the amount of KES that 1 AUD can buy. For example, if the price of AUD/KES is 76.399, it means that if you have 1 Australian Dollar, you can buy 76.399 Kenyan Shillings.
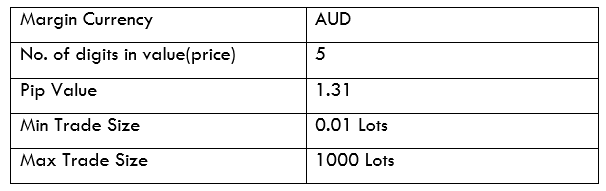
AUD/KES Specification
Spread
When you want to buy a currency pair in forex trading, you buy it from the broker. If you sell the pair, you sell it to the broker. The difference between these two prices is the spread. The spread for the AUD/KES pair is – ECN: 25 pips | STP: 30 pips
Fees
Most brokers charge a commission when you open a position. This commission varies from broker to broker and also depends on the size of your position. STP accounts are usually commission-free.
Slippage
In times of high volatility, or when your broker delays executing a trade, you will notice that the price at which you open a position is different from the exertion price. This is slippage in forex trading.
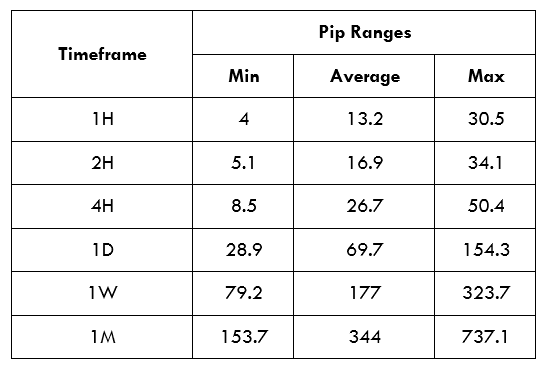
Trading Range in the AUD/KES Pair
In forex trading, trading range refers to the fluctuation in a currency pair’s price across different timeframes. Analysis of the trading range provides a powerful tool for deriving the volatility of a currency pair.
The Procedure to assess Pip Ranges
- Add the ATR indicator to your chart
- Set the period to 1
- Add a 200-period SMA to this indicator
- Shrink the chart so you can determine a larger period
- Select your desired timeframe
- Measure the floor level and set this value as the min
- Measure the level of the 200-period SMA and set this as the average
- Measure the peak levels and set this as Max.
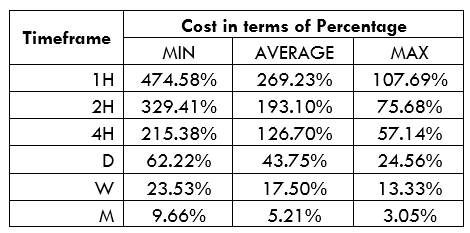
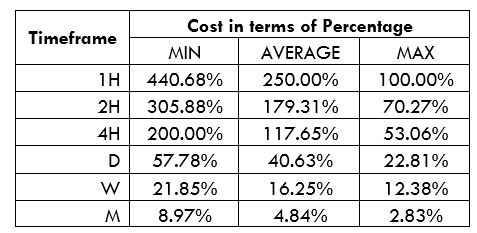
AUD/KES Cost as a Percentage of the Trading Range
The total trading cost involved in buying and selling a currency pair includes the spread, slippage costs, and brokers’ fees. Using the total trading costs, we can establish the percentage costs of a currency pair in pips.
ECN Model Account Cost
Spread = 25 | Slippage = 2 | Trading fee = 1 | Total = 28
STP Model Account Cost
Spread = 30 | Slippage = 2 | Trading fee = 0 | Total cost = 32
The Ideal Timeframe to Trade the AUD/KES
These analyses show that trading the AUD/KES pair on larger timeframes carries lower costs than smaller timeframes. Notice that on longer timeframes, volatility is higher. We can thus say that higher volatility corresponds to lower costs. For both the ECN and the STP accounts, costs are highest when volatility is at four pips and lowest when volatility is 737.1 pips.
To determine the ideal trading will depend on your trading style. Generally, longer-term traders enjoy low costs for both types of accounts. For the shorter-term traders, waiting for when volatility is at the ‘maximum’ will help lower the costs. Traders can also use forex limit orders to lower trading costs since using such orders eliminates slippage. Here’s one example using the ECN account.
Total cost = Slippage + Spread + Trading fee = 0 + 25+ 1 = 26
With no slippage costs, notice how costs have significantly dropped. The highest cost for the AUD/KES pair has dropped from 474.58% to 440.68%.