The role of the financial market in a modern civilized society is enormous. Its aim is to mobilize capital, distribute it among industries, control and maintain the reproduction process and improve the efficiency of the overall economic system.
The main functions of the financial market, performed by its participants, are as follows:
- Facilitate efficient relationships between all market participants, from individuals and individual investors to large institutional investors.
- To supervise and regulate the processes carried out in the financial system: regulation of the money supply, control of compliance with the rules established by market participants, licensing, development of legal provisions.
- Mobilize and allocate capital to be used more efficiently and generate added value.
- Minimise risks, including fraud prevention (combating money laundering). Ensure transparent prices and avoid price manipulation.
- Provide liquidity to the market.
- Guarantee the privacy and transparency of transactions made.
- Provide necessary information.
Financial market activities are based on the liabilities of national banks to control exchange rates and to set interest rates. Foreign exchange markets and stocks, as well as commercial banks, are directly related to the development of the financial asset market. The stock market is the most interesting segment of the financial market in terms of return on investment.
Financial Market Participants
Each investor is a participant in the financial market in some way. Each of us works somewhere, making our own contribution to the GDP rate, buying something, which indirectly affects inflation and the level of consumer prices. Someone becomes an investor, buys a foreign currency or collectible currencies, or invests in bank deposits, investment companies, using loans.
But still, economic science classifies financial market participants according to their segment. This means that the financial market, simplifying a lot, is a relationship between two categories of participants: buyers and sellers The third category includes intermediaries who are directly involved in transactions, providing assistance, facilitation, and guarantees. The same financial market actor can act simultaneously as the seller, the buyer, and the intermediary.
Foreign Exchange Market
Sellers – The main sellers are the state and the banks. The country that sells a currency does so through authorized agencies and then performs a regulatory function. Sellers may also be companies engaged in foreign economic activity (sale of profits in foreign currency) and individuals.
Buyers – All agents, even sellers, can interact as buyers.
Intermediaries – This category may include commercial banks, bureaux de change, etc.
The Credit Market
Borrowers – They work internationally, borrowers are States, and the ratio of GDP to external debt is considered one of the best statistical indicators of the state of a country’s economy. At the national level, borrowers are businesses and individuals, local governments, etc. A clear example of a multilevel credit market structure is the US mortgage system, where banks issued mortgage securities to accumulate new capital for later loans.
Lenders – These market participants have reserve capital and want to increase it: individuals, investing their funds in deposits that will then be used for loans, buyers of debt securities (insurance, pensions, investment funds). Certainly, any investor can be called a lender, since it gives extra money with the aim of obtaining a percentage that is destined for development. The state can also be called a lender, which creates liquidity and distributes the money to borrowers through the central bank.
Middlemen – They are all involved in the organization of the distribution of money: banks, brokers, concessionaires, investment management companies. Insurance and pension funds can also be attributed to intermediaries, accumulating and distributing capital.
The credit market is closely related to stock and investment markets. For example, corporate bonds are a tool to raise money and security at the same time. Government bonds are one of the favorite investment options with the lowest risk for investment funds.
The Insurance Market
Insurers – These are companies, duly authorized to provide insurance services. There are open-ended insurance companies (they provide services to all market participants), captive insurers (they are owned and controlled by their policyholders), and risk reinsurance companies.
Insured – Individuals, companies, institutions, who purchase insurance services to minimize risks.
Intermediaries – There are no intermediaries, the transactions are made directly between the insurer and the insured.
All markets are closely intertwined. As mentioned above, insurance companies also participate in the investment market. It also includes insurance instruments (for example, several swaps) used by securities market agents.

Investment Market
Every person who invests his capital in a particular asset is an investor. Intermediaries can be banks, stock exchanges, different types of funds, etc.
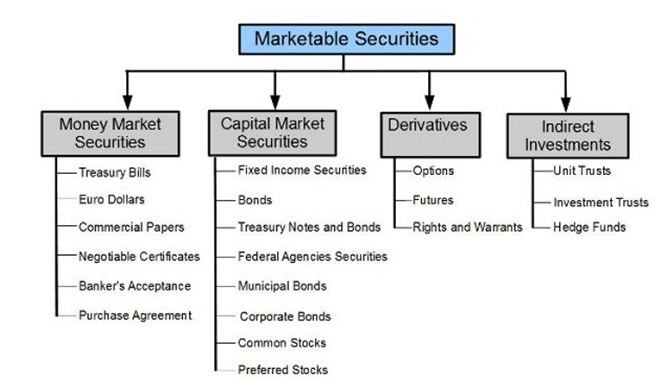
The Securities Market
Emitters – These include organizations and companies that issue certain securities: shares, bonds, etc. When issuing, issuers agree that they must comply with all specified (agreed) requirements at the time of issuance.
Investors – They are all those who buy securities to generate income. There are strategies (buying a majority stake) and minority (making up a portfolio, buying securities in order to generate revenue only).
Middlemen – Stock exchanges, banks, insurers, rating agencies, auditors, and other participants involved in the organisation of the issue and placement of securities.
The classification described above can be grouped as follows:
The state and central banks (regulatory and supervisory organisations). Managing the largest amount of capital, these agents mainly perform the supervisory and regulatory function.
Regulators (regulatory and supervisory institutions). Establishments that do not participate directly in transactions (that is why they cannot be referred to intermediaries), but perform a control function. The oversight function is also carried out by the central bank and the state government, but it can also be a separate institution, such as a self-regulatory organization (SRO).
Financial services companies (organisations providing services to the financial market and financial intermediaries). We are talking about institutions that are often involved in organisational work: currency exchanges, stocks and raw materials, brokers, insurers, auditors, depositors, registrars, compensation companies, and consulting.
Banks (financial intermediaries). They are intermediaries involved in the distribution of capital, market regulation, and supervision of compliance with established rules.
Legal entities (lenders, investors, borrowers). The largest group of participants: companies dedicated to the placement of clients’ pension savings, investment, insurance, hedge funds, trust management companies, brokers, concessionaires, individual loan organizations, companies involved in any type of financial activity, participating in the return of money.
Natural persons (lenders, borrowers, investors): traders, speculators, individual asset managers, long-term investors, and ordinary persons, as mentioned at the beginning.
Important Financial Market Indicators
As a general rule, experienced traders actively use the economic calendar, which is provided free of charge by the broker. I recommend making this a habit if you haven’t already. Here is a short summary of some of the most important indicators in the economic calendar and tips on how to analyze them:
Interest rate – One of the main economic tools that allow managing the volume of money supply, thus also adjusting inflation. The interest rate grants loans to commercial banks. A higher interest rate increases interest rates on loans and deposits and therefore encourages consumers to invest. This, in turn, reduces the inflation rate. Influence, when the interest rate is raised, is exclusively dependent on the economy of a given country. For developed countries (e.g., the US), a higher interest rate increases the exchange rate of the national currency. In the least developed countries, raising the interest rate can be seen as an attempt to curb stagnation and thus increase investor interest.
Non-agricultural payroll (Non-Farm Payrolls) – Report on changes in the number of jobs in the US non-agricultural sector. It is considered one of the most important reports, but its impact on the dollar price lasts a relatively short time (few hours). Goes public on the first Friday of every month at 12.30 (13.30) GMT. The statistics are based on data from more than 400 households and are published by the US Department of Labor. In theory, the factor that influences the rate of the US dollar will be the deviation of the fact of the forecast by more than 40 thousand. In practice, much depends on accompanying statistics and investor sentiment.
 Consumer price index – It is calculated for a specific group of goods and services that are part of the consumption basket of the average resident of the country. The index analysis for the current year is carried out in comparison with the base (baseline). The IMF, EBRD, and the United Nations recommend the statistical basis for the calculation, but there is no single approach, each country has its own calculation peculiarities. The calculation methodology can be based on the price indices of Lowe, Paasche, and Laspeyres. If the index decreases, it means that consumer purchasing power (real demand) also decreases and may partially suggest a higher rate of inflation growth.
Consumer price index – It is calculated for a specific group of goods and services that are part of the consumption basket of the average resident of the country. The index analysis for the current year is carried out in comparison with the base (baseline). The IMF, EBRD, and the United Nations recommend the statistical basis for the calculation, but there is no single approach, each country has its own calculation peculiarities. The calculation methodology can be based on the price indices of Lowe, Paasche, and Laspeyres. If the index decreases, it means that consumer purchasing power (real demand) also decreases and may partially suggest a higher rate of inflation growth.
With regard to indicators such as GDP, inflation rate, unemployment, I think everything is clear: the better the indicator, the more positive is the feeling of investors in the currency and stock markets.
Important point: the economic calendar is only a complementary information tool and in no way can it serve as the main tool to base trading strategies. At the time of news release, the market is especially volatile, therefore, the calendar is often used upside down to exit trading.
If you are still willing to try to negotiate with the economic calendar, here are some tips:
Compare the actual value with the forecast. If, for example, GDP growth was 2%, given a forecast of 2.5%, it will have a negative influence on the market. Please note that the data can be reviewed.
Evaluate the chances of an event and the expectations of investors. Let’s take an example, if what is anticipated is that the Federal Reserve increase the rate of federal funding at the next meeting, investors will consider it beforehand and will not undergo major changes at the time of the news release.
Compare the importance of news with other factors. For example, if in times of silence, the publication of statistics on US oil reserves has a significant impact on quotes, then during the peak of the US-China trade war, these data were hardly noticed.