When speaking about a recession, investing might not be the first activity that comes to mind, however, during these testing times, investors and traders can still source out industries that with or without a recession have to keep the wheel rolling. Being able to sift through the thousands of options available, the key essential service providers are what you should be looking at during these dire times we are experiencing now.
Another great way to seek out those investment opportunities during a recession is to look back at the most recent recession and find out which industries managed to stay afloat, or even strive during that period. Below are the top five industries that managed to plow on during the tough times.
Healthcare
Although the financial situation of civilians may be negatively impacted by a recession, there are certain products and services that we really cannot do without, the first on that list is healthcare. During this COVID-19 pandemic, populations all around the world are investing in healthcare products as well as medical equipment to help prepare the people and their respective healthcare systems to combat this new virus.

This is not to say that all health care companies will make it out successfully as there are companies with large debts and less cash flow that will, unfortunately, suffer too during this time. It would also be best to stay away from new and upcoming biotech startups which are still in their early phases which makes them riskier. Therefore, it would be best to source out companies that have a low debt-to-equity ratio as these are the ones more likely to perform better.
Food
Like healthcare, food is a basic necessity that cannot be spared. Looking at the recession that took the world by storm back in 2008, it seems like although populations tend to take a step back from dining out and purchasing expensive food to cut down on their monthly cost, they shift their purchasing to cheaper, pre-packaged food options. Again, looking back to 2008, we can see that popular brands such as Walmart, McDonald’s and other large food chains did relatively well during that tough period.
Freight and Logistics
The COVID-19 pandemic brought a halt to most air and sea transportation for people, however, goods are still being shipped and flown across the globe. Freight companies or companies that help to move freight from one country to the other are quite safe options when looking for trading opportunities during recessions such as the one we are currently experiencing.

Do it Yourself
By looking back at 2008, one can notice that although people are unlikely to go out looking to purchase new cars, furniture or properties, during tough times people tend to focus their time and effort on fixing/DIY projects around their household. Taking into consideration that this pandemic has put millions of people on lockdown inside their homes, home projects are definitely on the rise. Any large home and garden improvement centers, as well as auto retailers that focus on parts, might do better during these times
Discount Shops
The high unemployment rates currently plaguing countries all over the world, similar to 2008, people are shifting to more affordable and cheap essential items. When a person’s income is drastically decreased, they have 2 options, either to stop purchasing or to purchase cheaper options. When it comes to essential items, stopping purchasing is not an option, so discount stores such as Dollar General or Walmart are a safe option to invest in. Back in 2008, Dollar general rose by a whopping 60% in that year alone.
Needless to say, it is not only the above-mentioned industries that will most probably come out of this recession without too many scratches, however, but this list can also put you in the right frame of mind of what to look out for. Keep in mind, even from your own experience during recessions, what goods and services do you still require, what services are deemed as non-essential during these times and what would you prioritize if your income suddenly decreased?


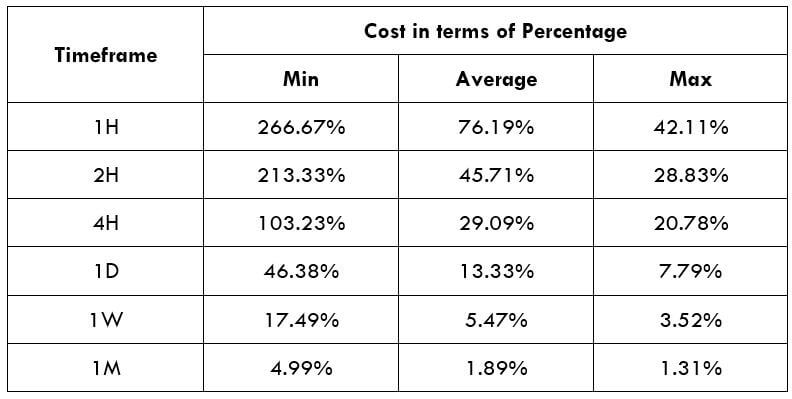
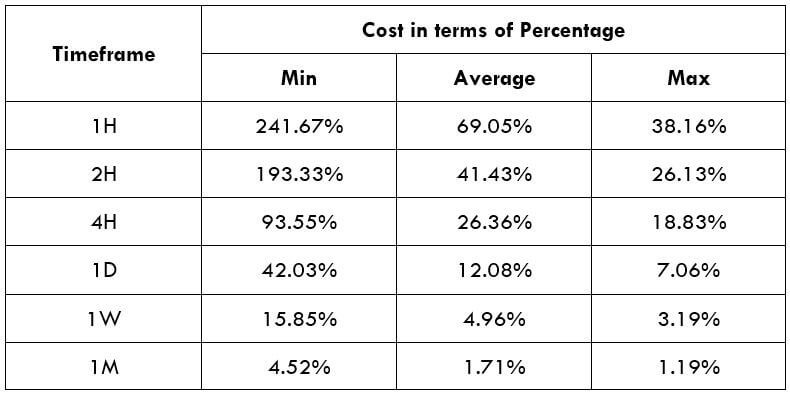


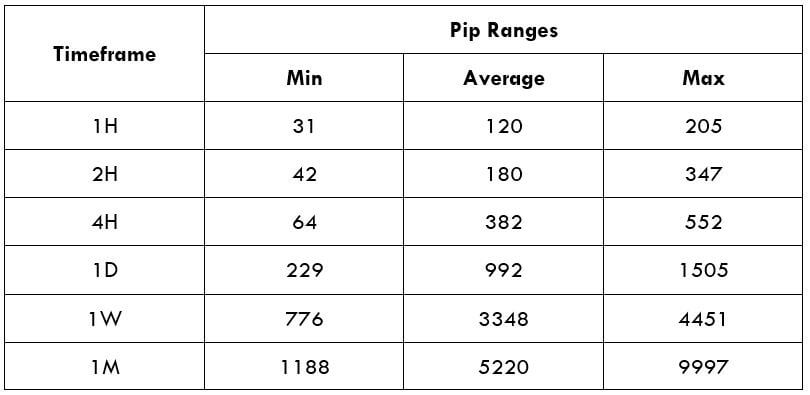
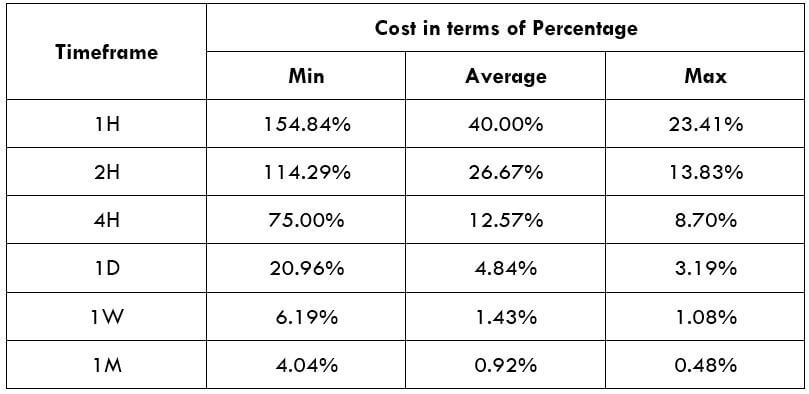
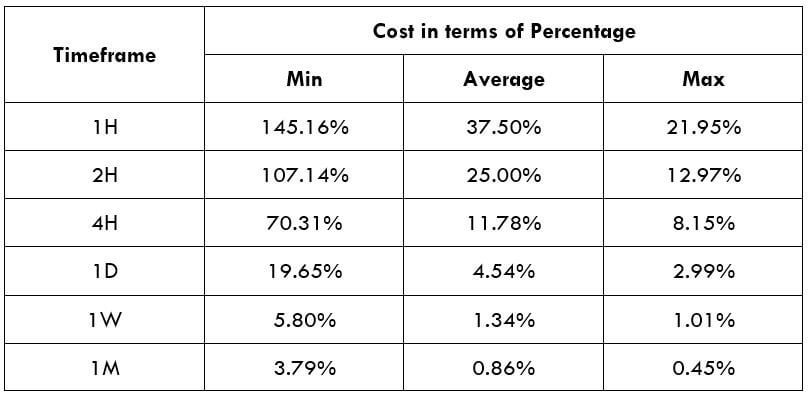
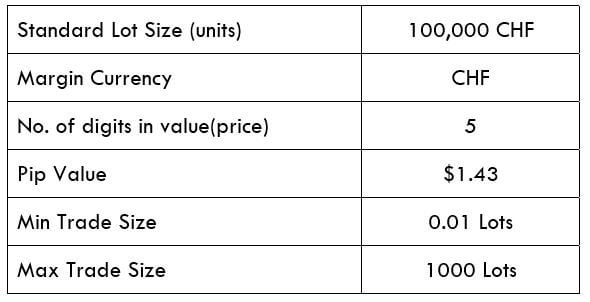
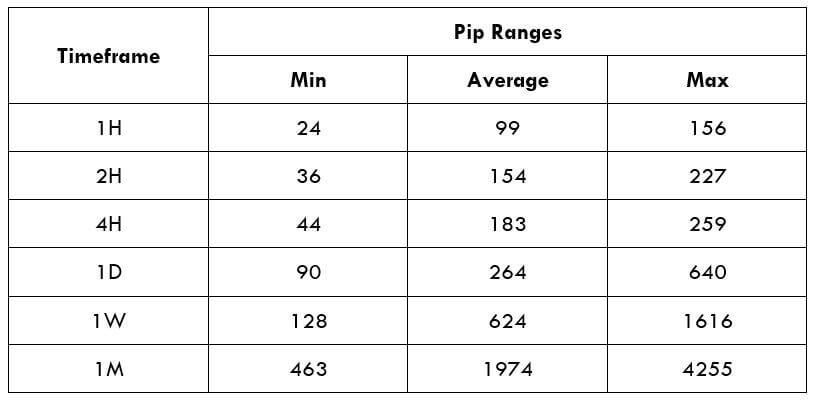
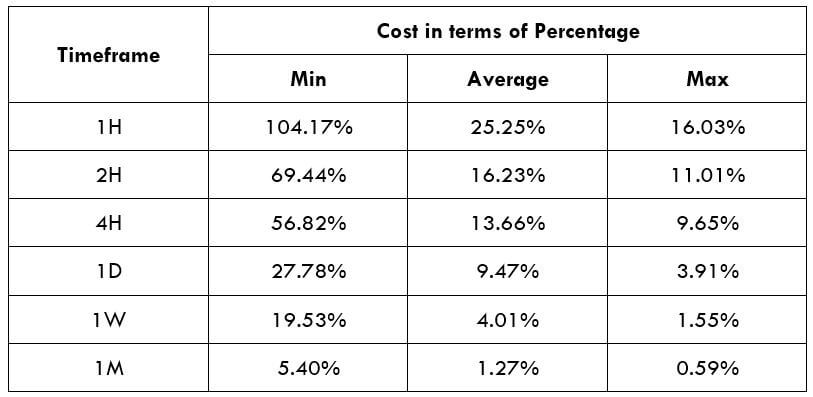


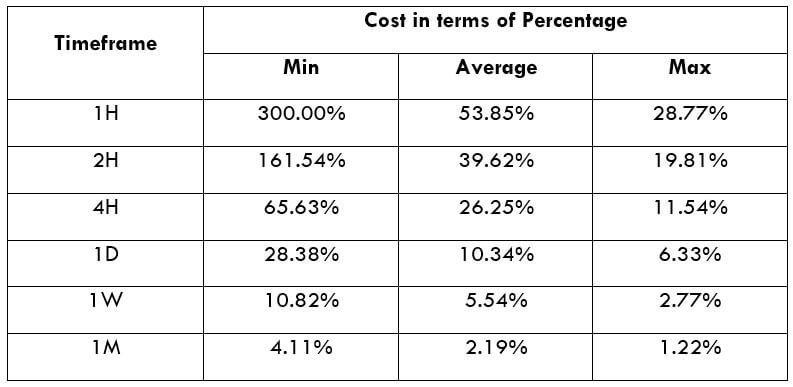

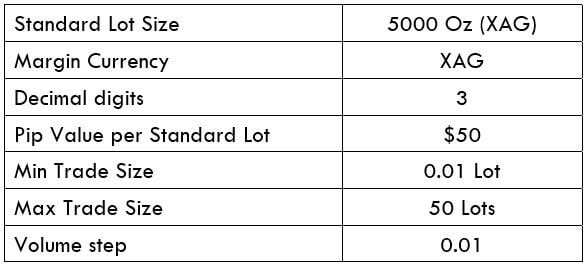
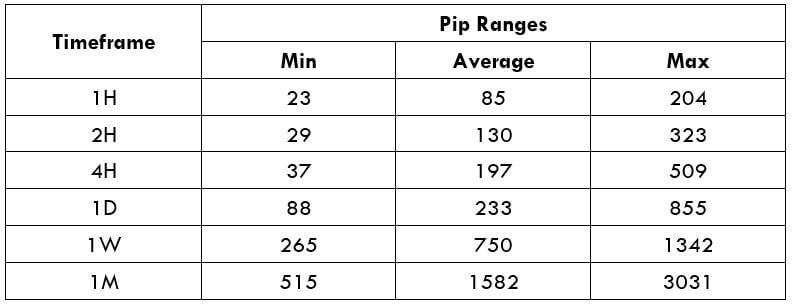
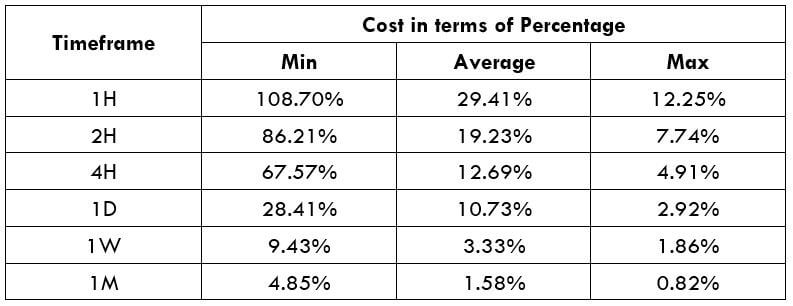

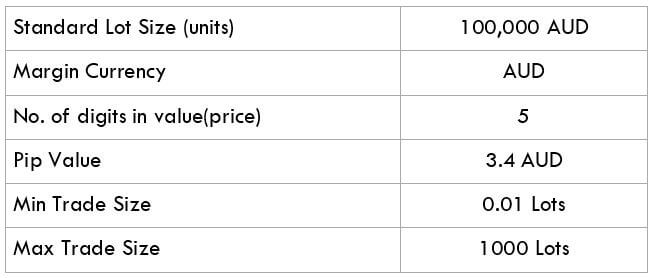
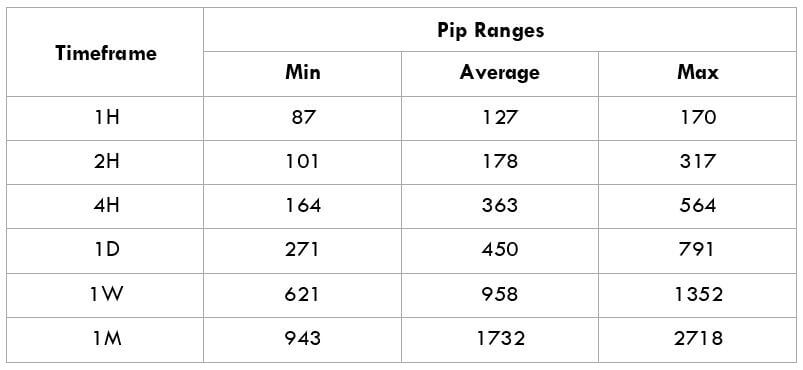
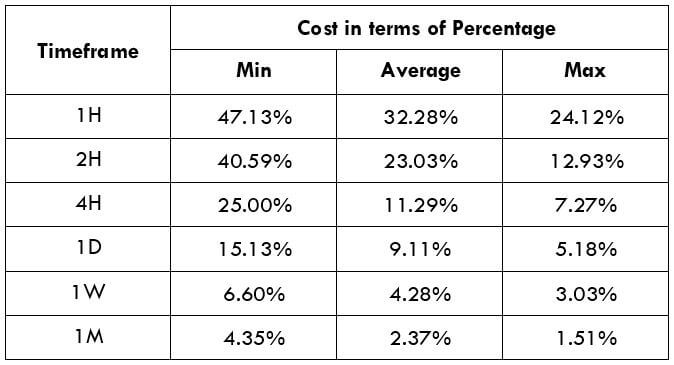

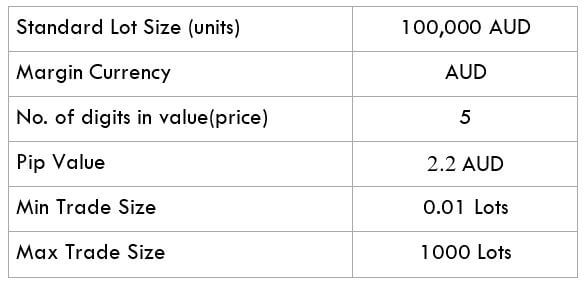
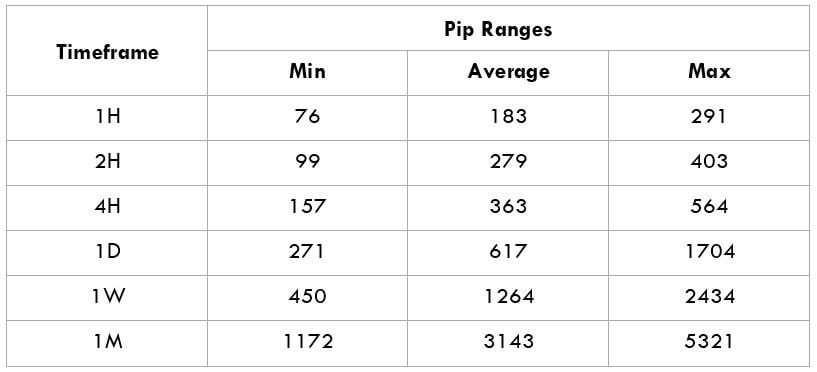
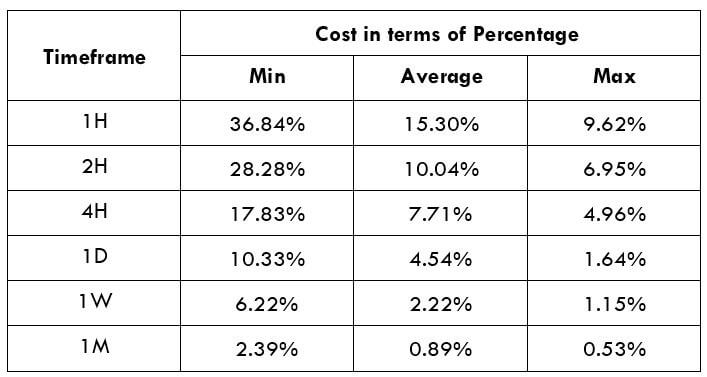
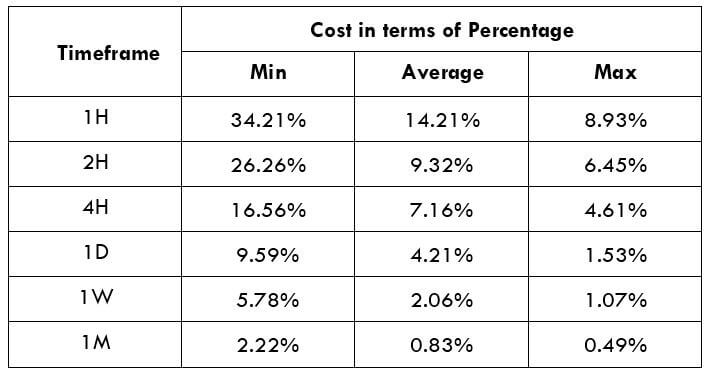
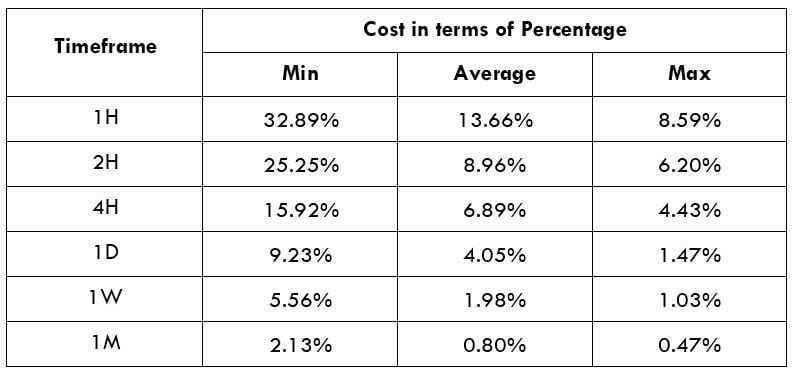

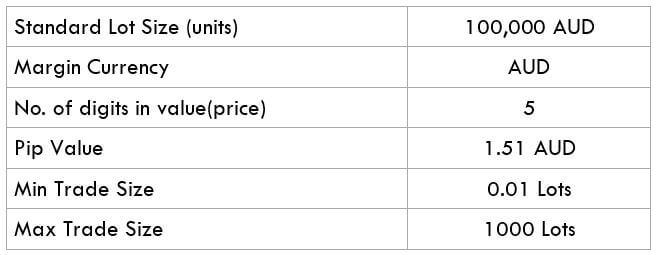
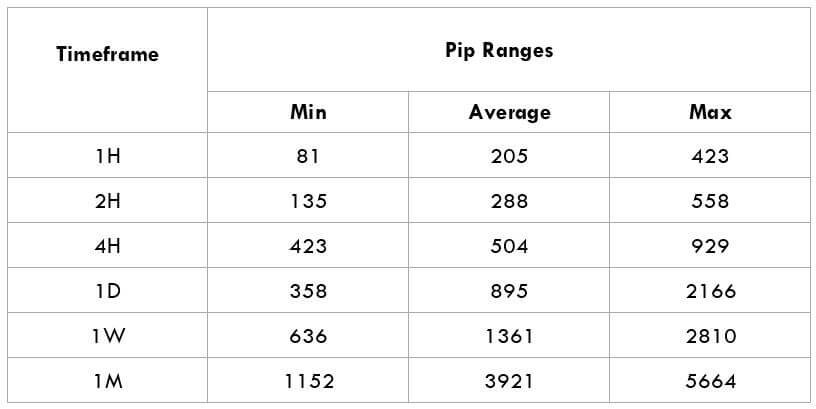
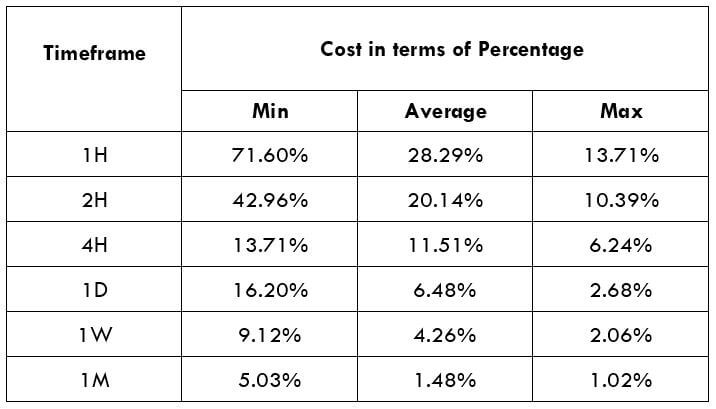


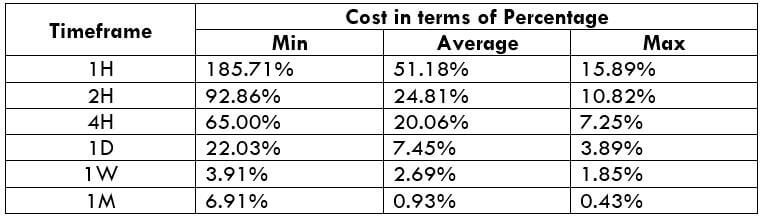
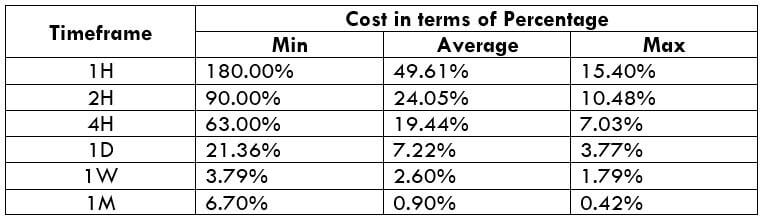

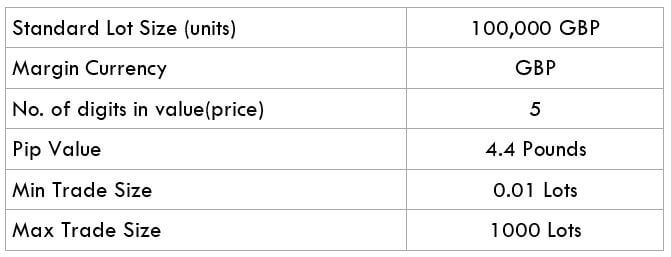
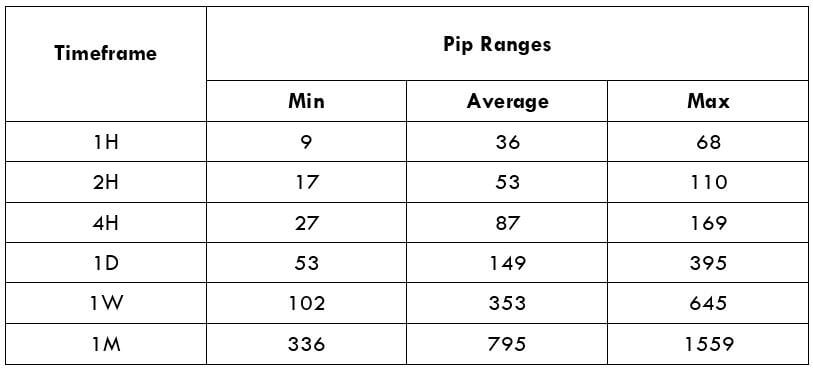
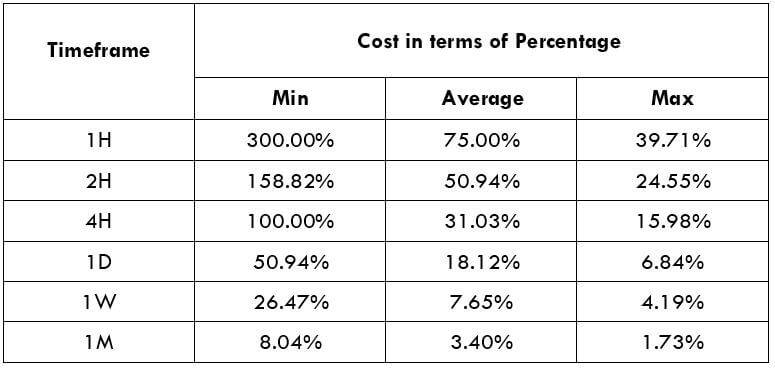

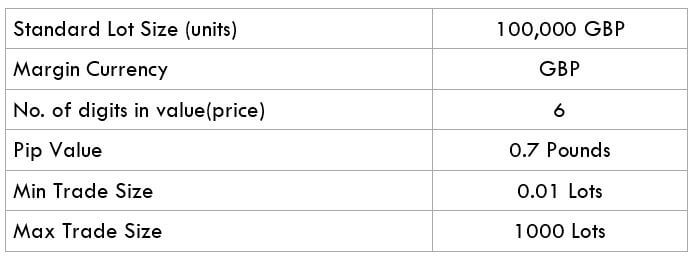
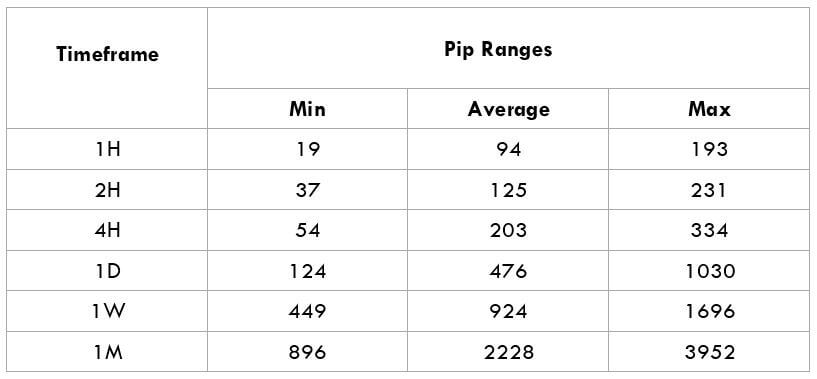
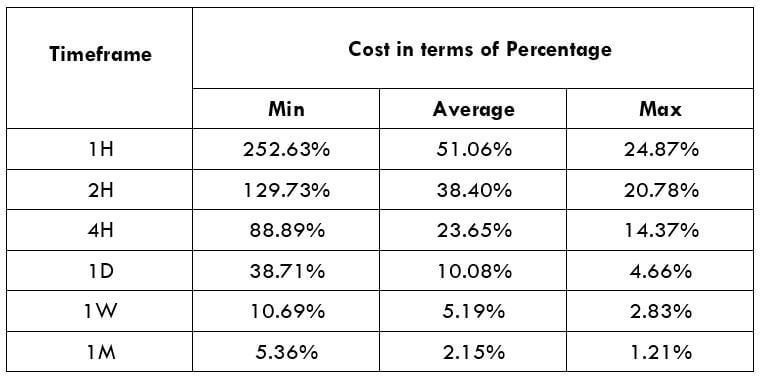


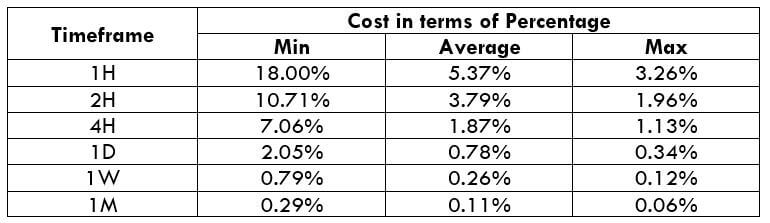
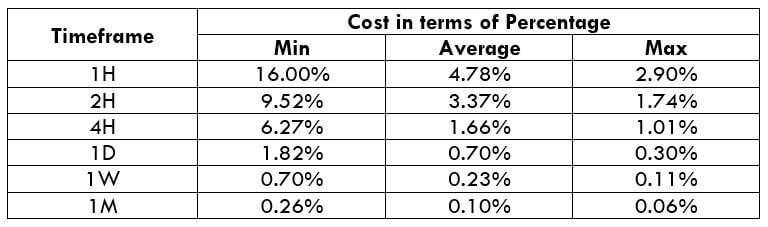

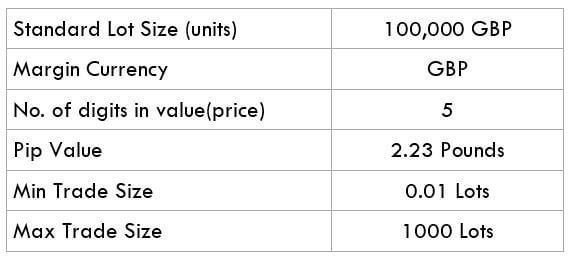
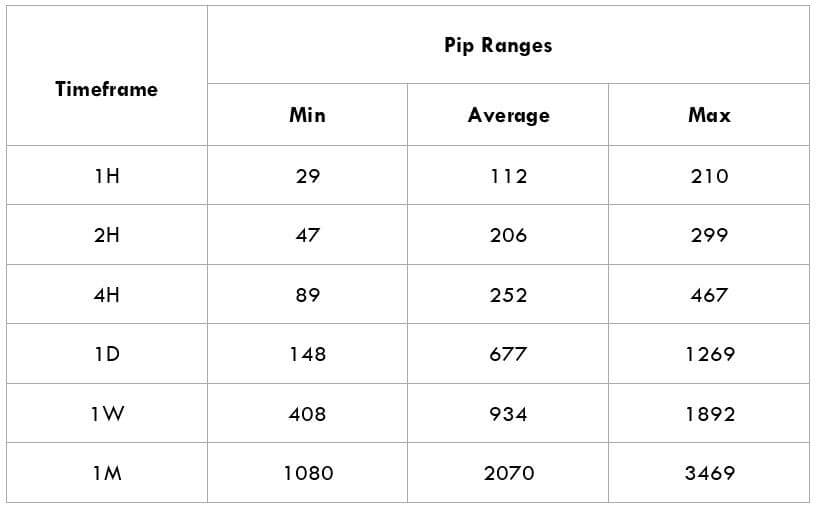
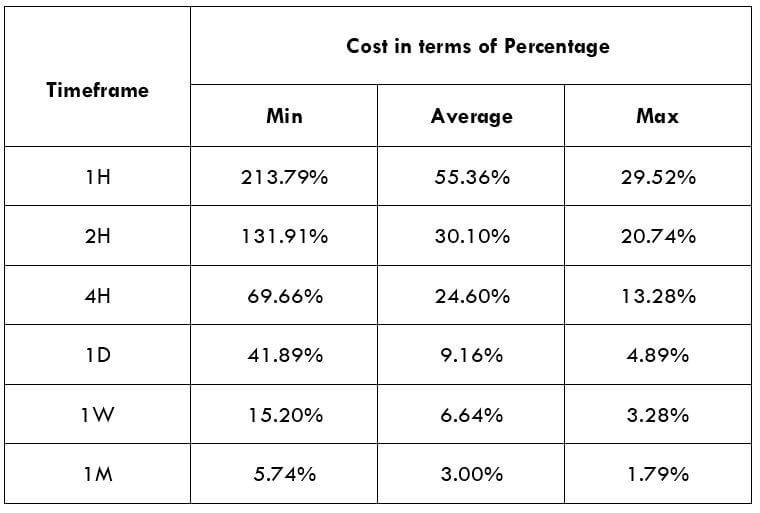


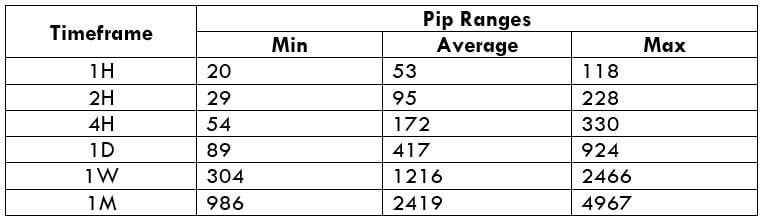
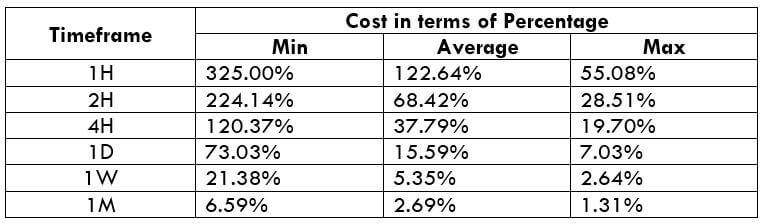

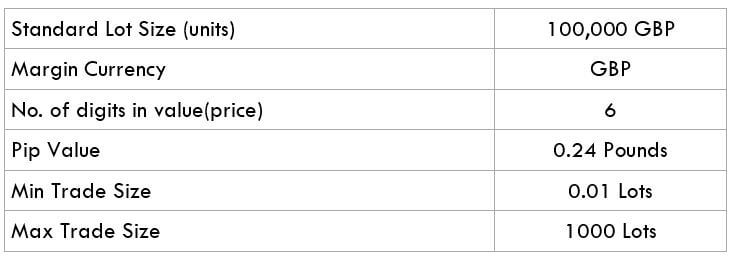
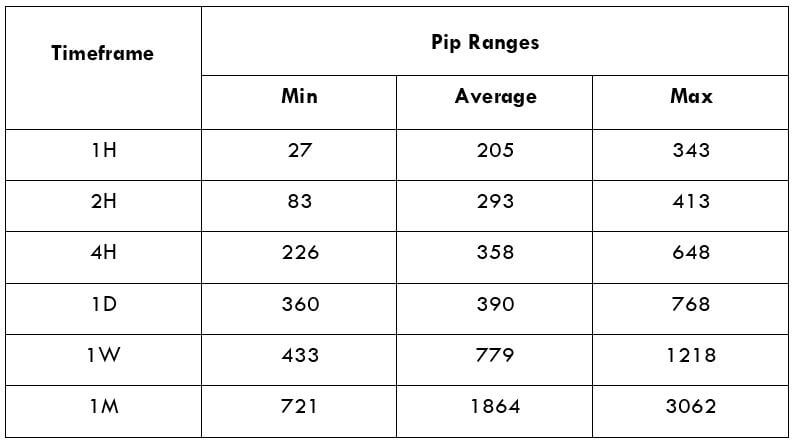
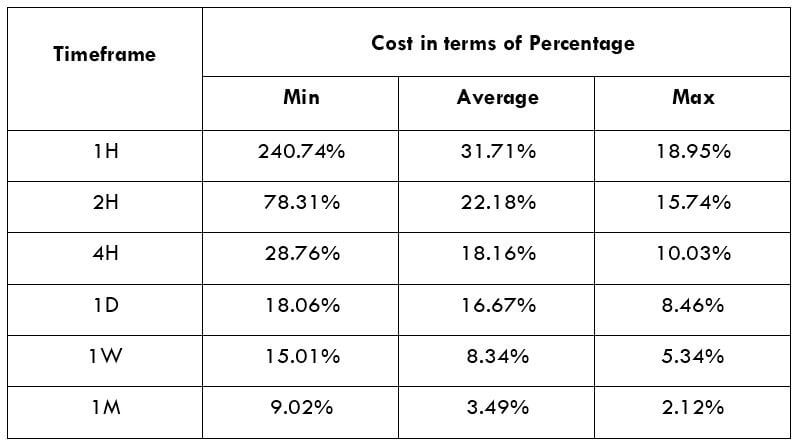
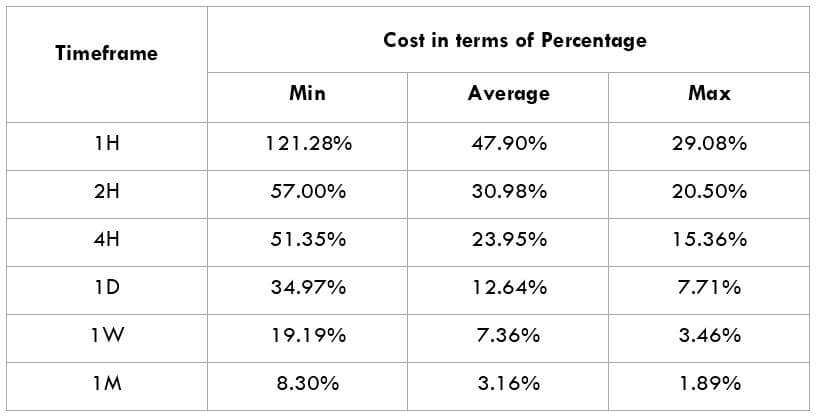

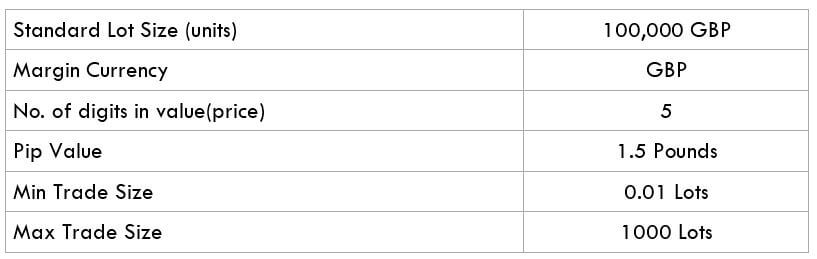
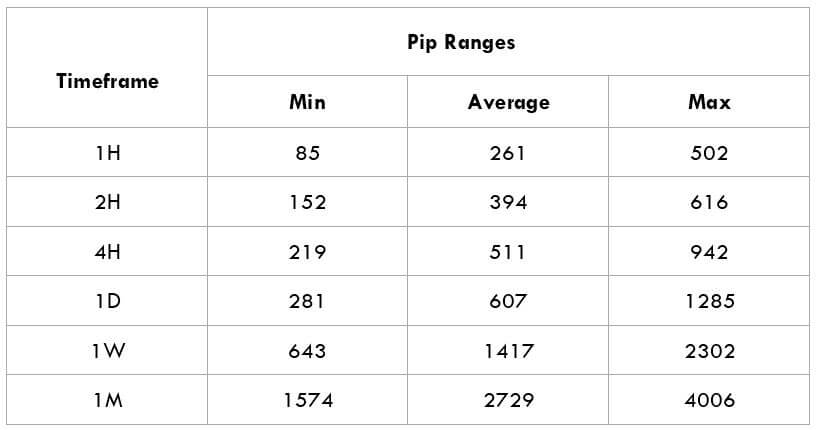
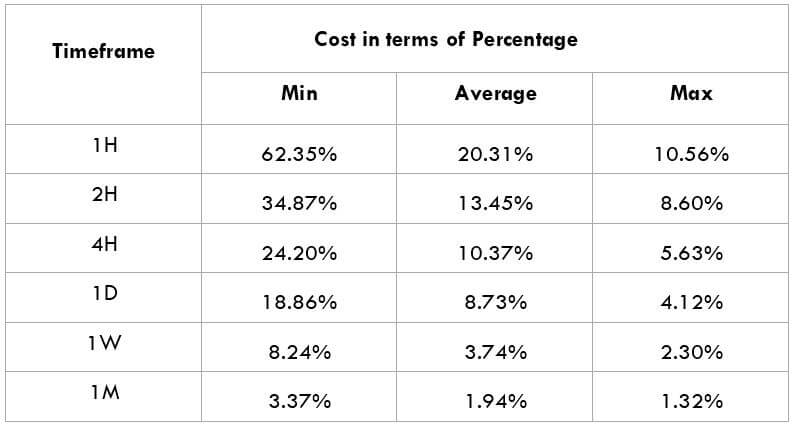
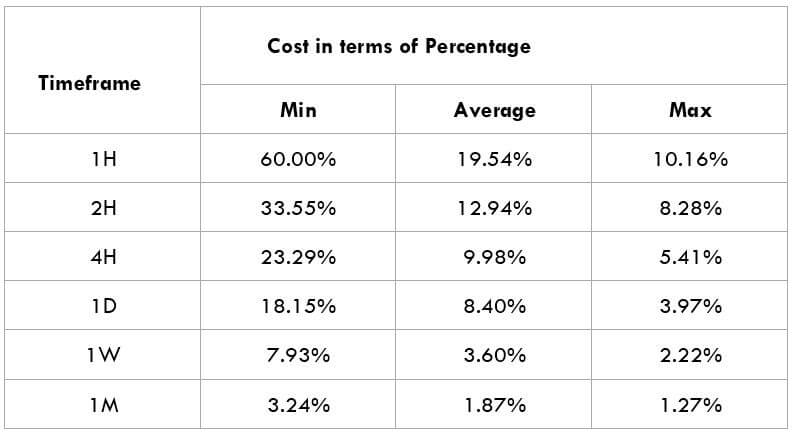

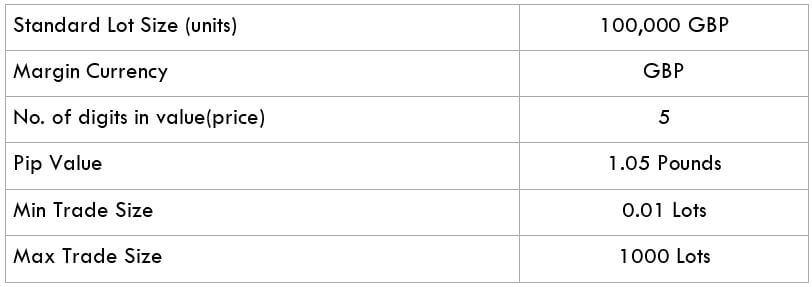
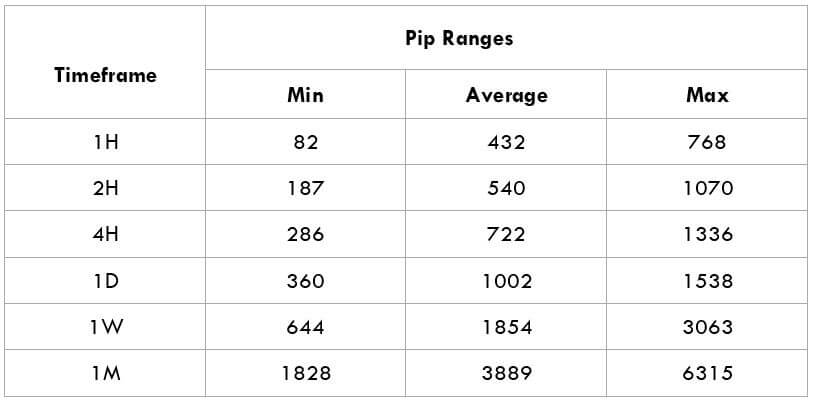
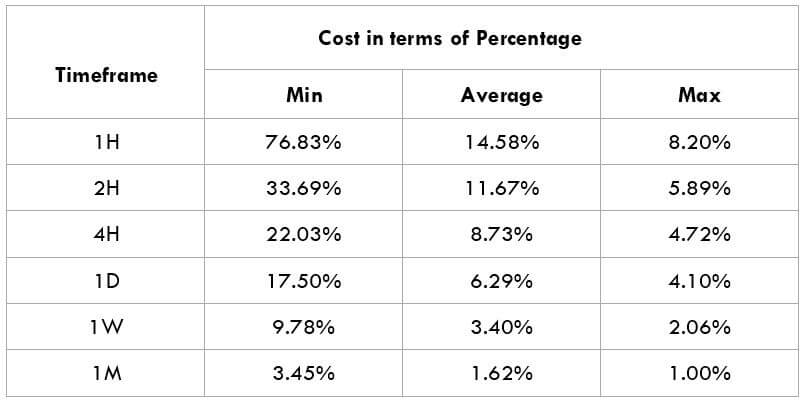


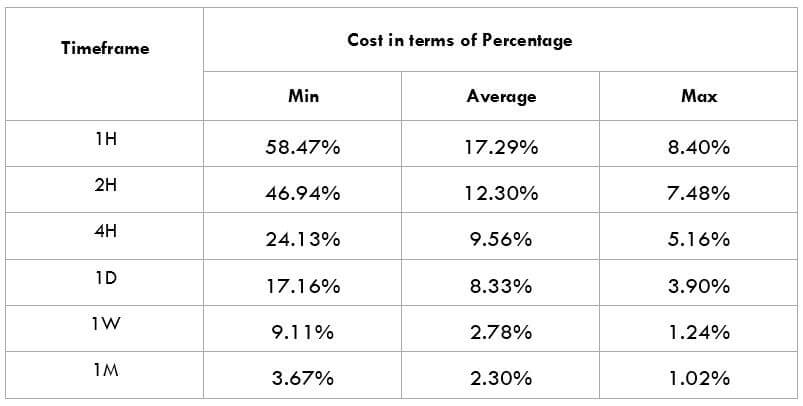
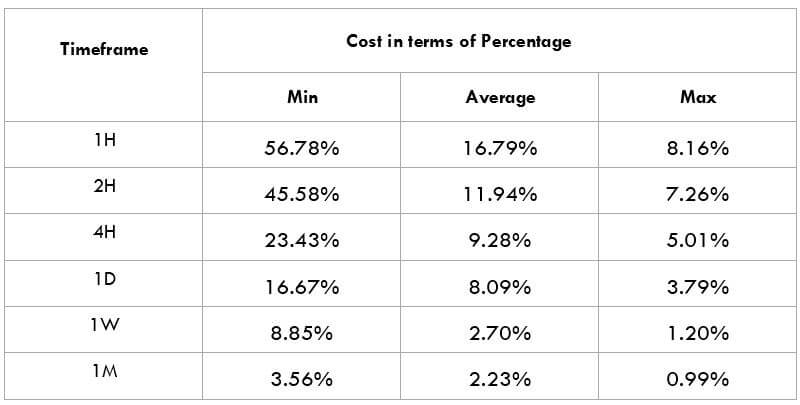
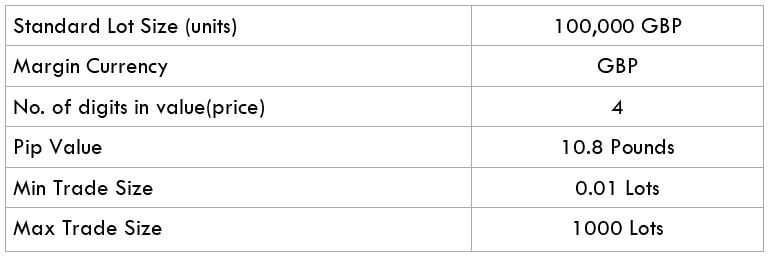

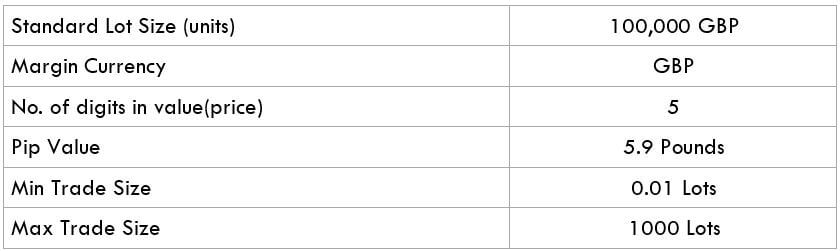
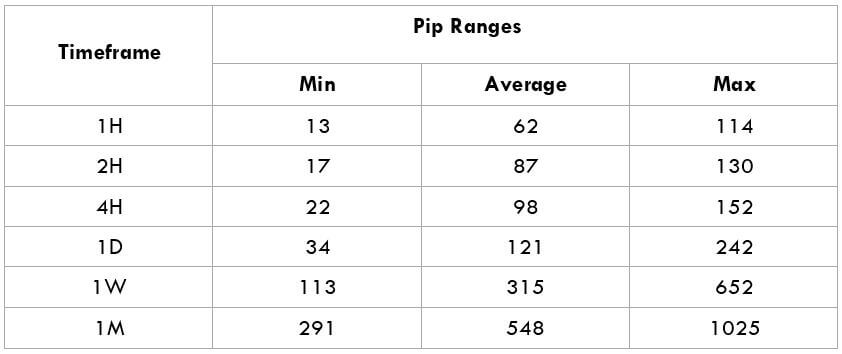
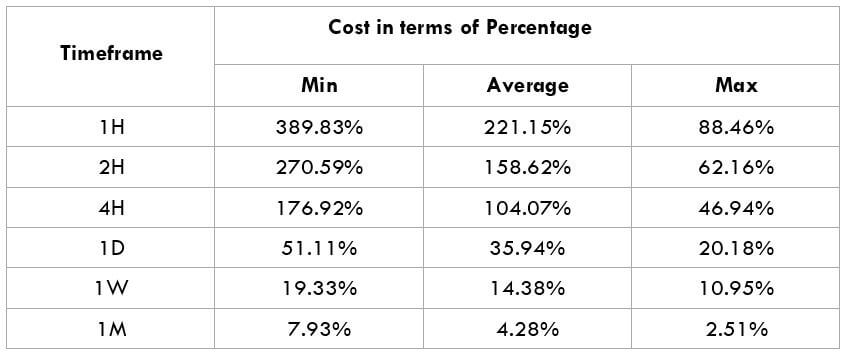
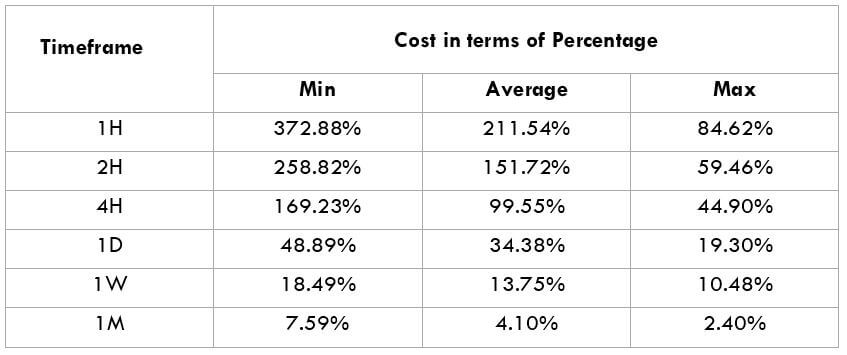

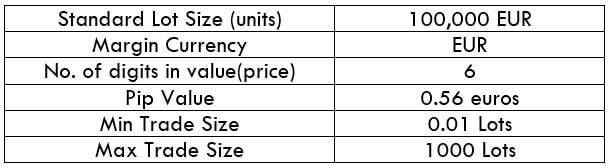
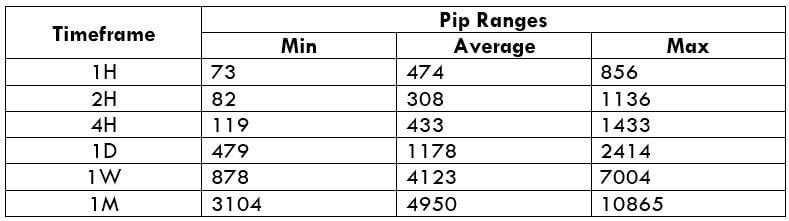
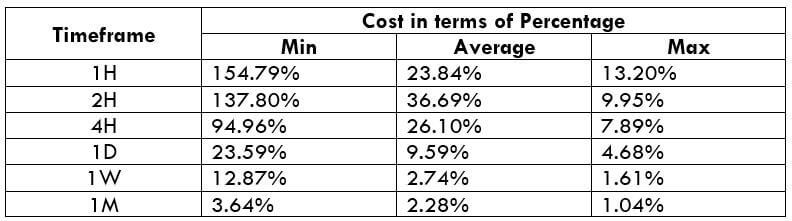
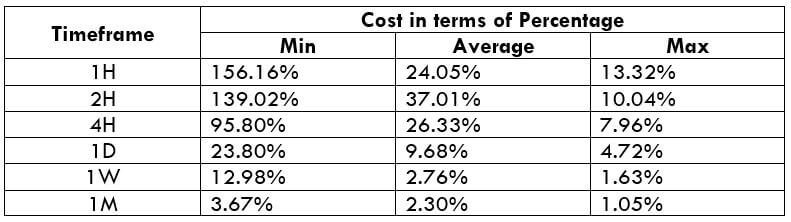

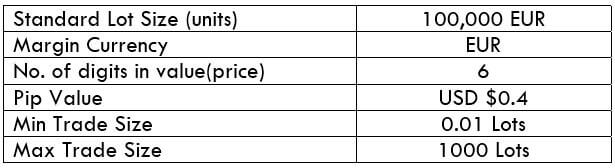
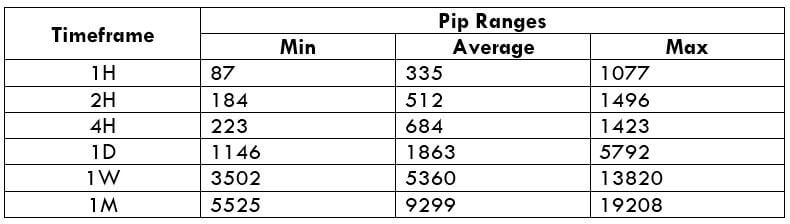
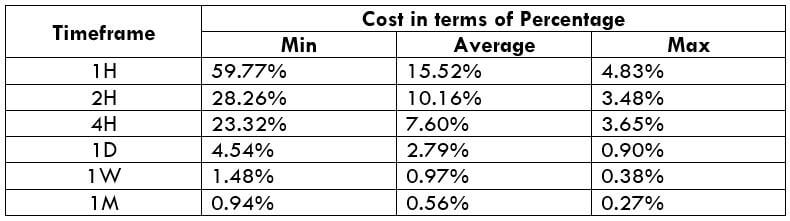
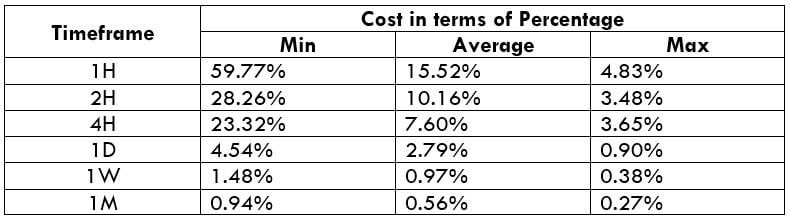

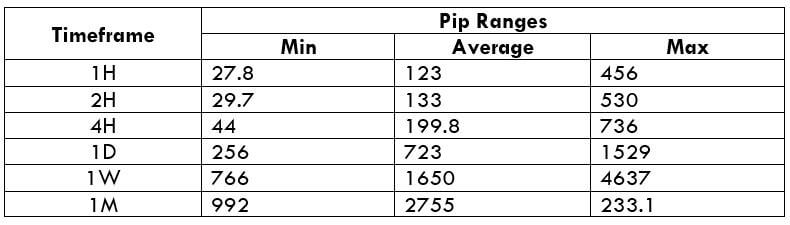
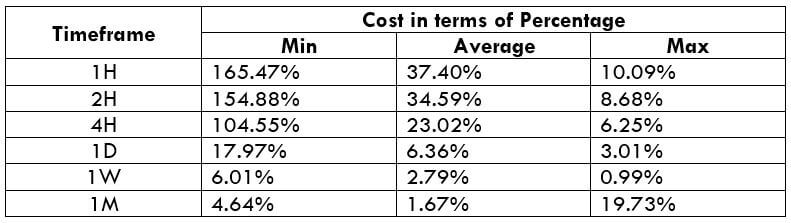
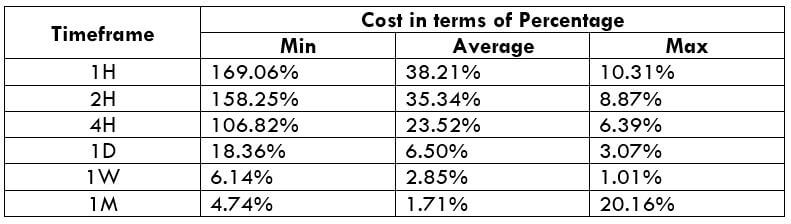

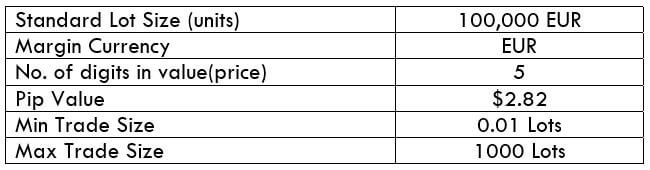
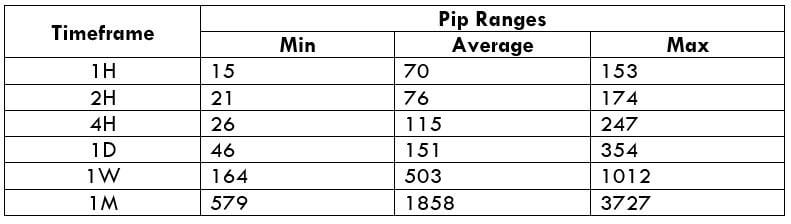
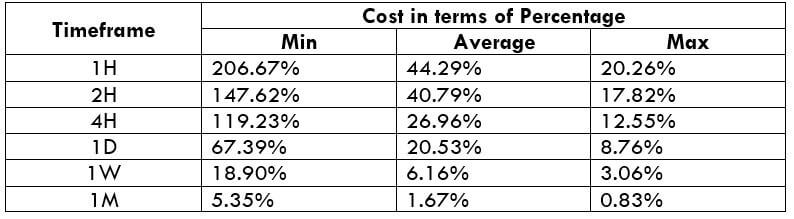

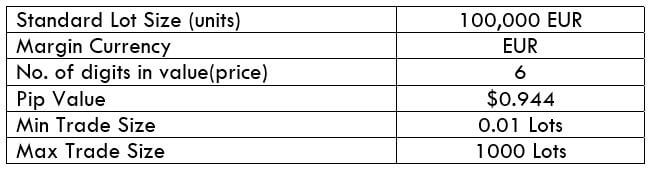
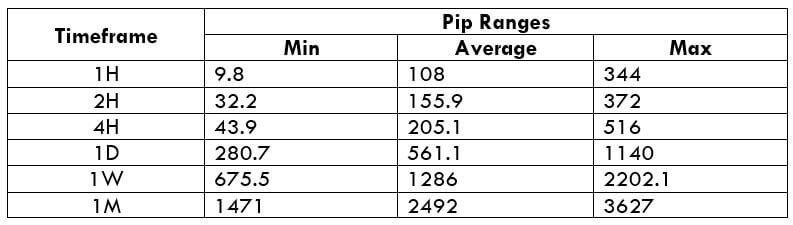
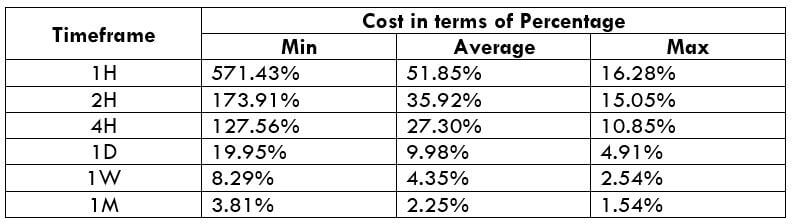

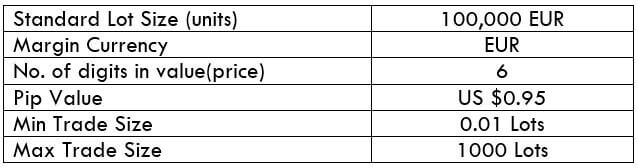
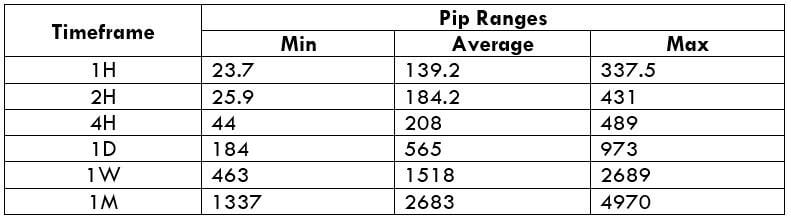
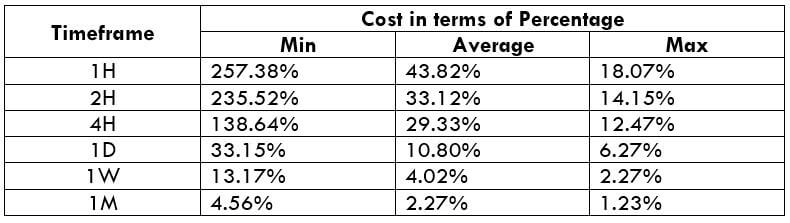
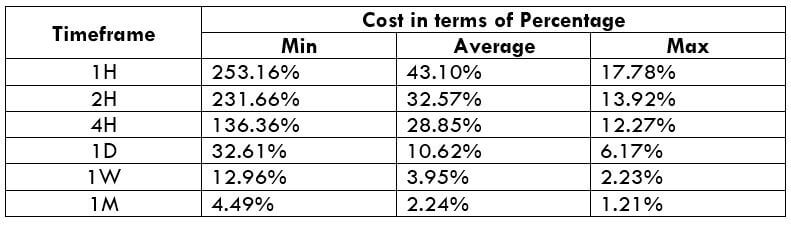
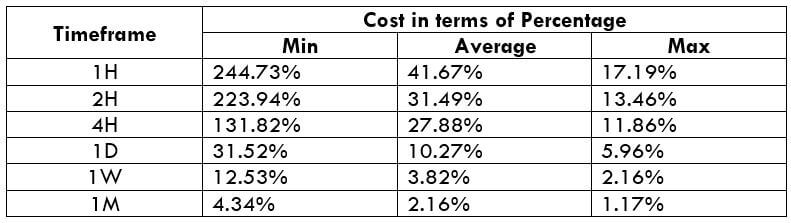

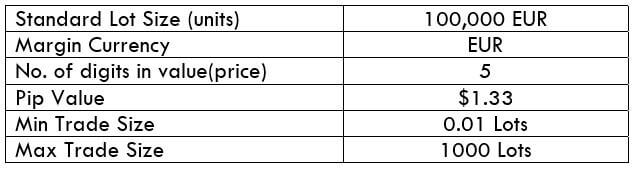
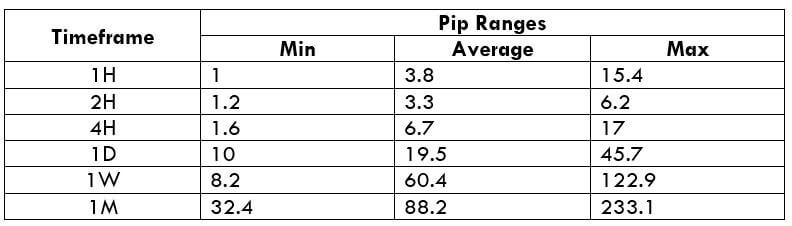
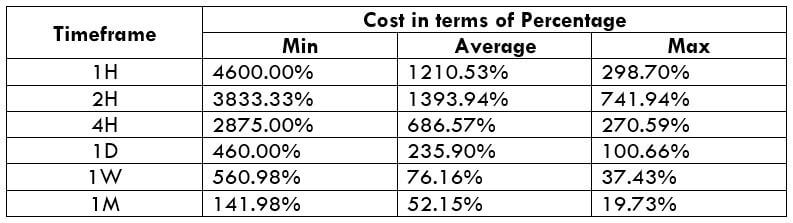

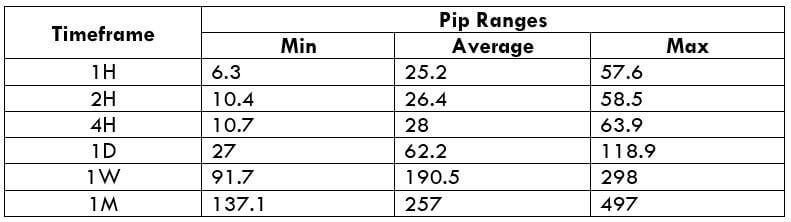
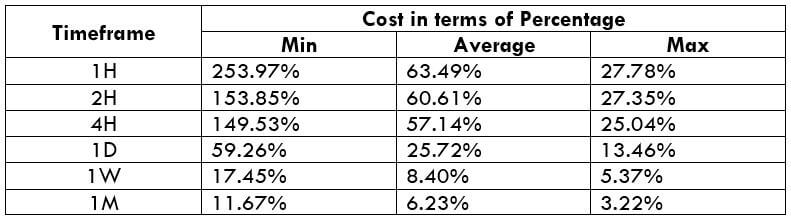
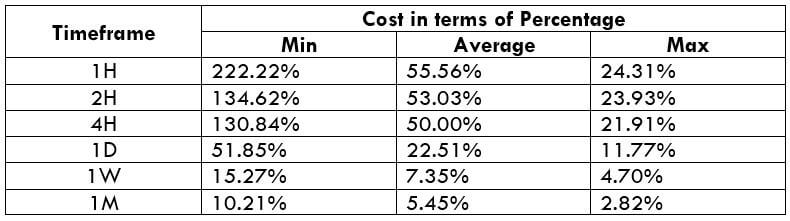

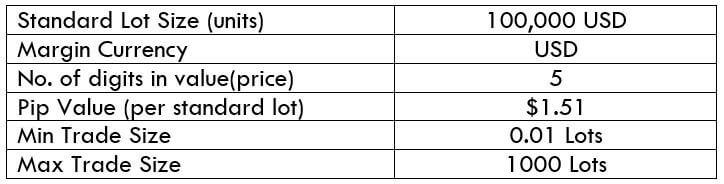
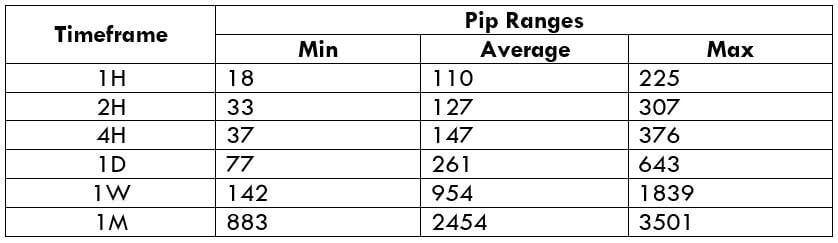
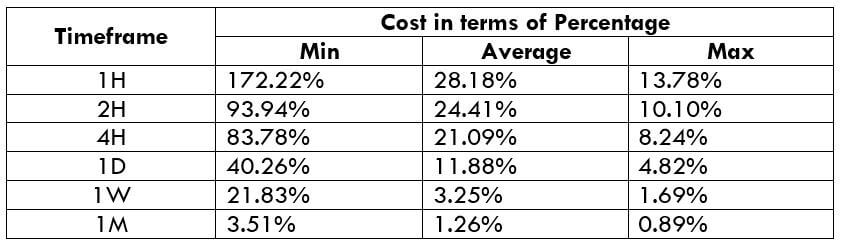

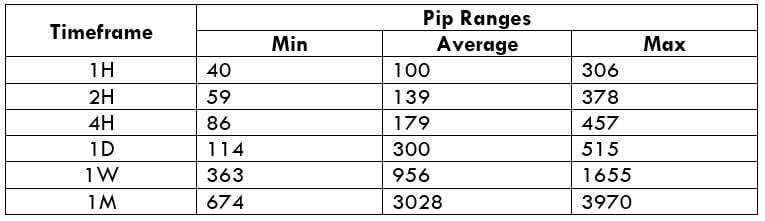
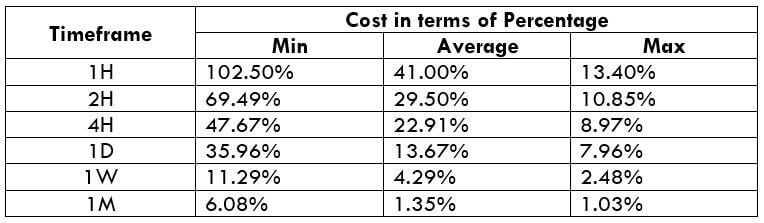
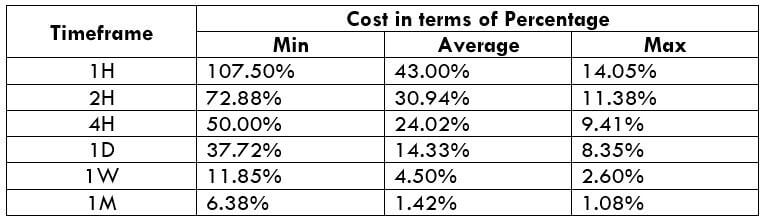

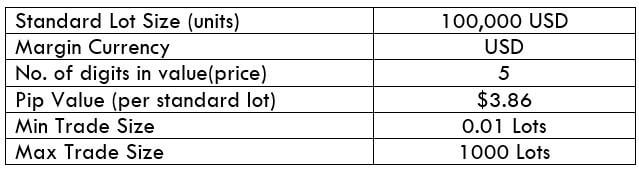
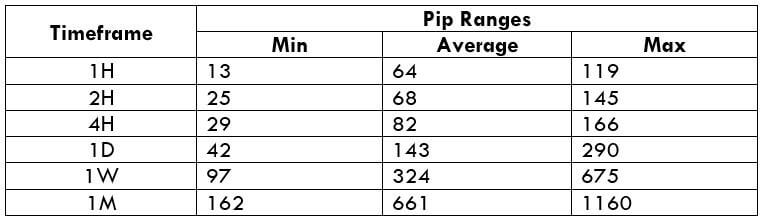
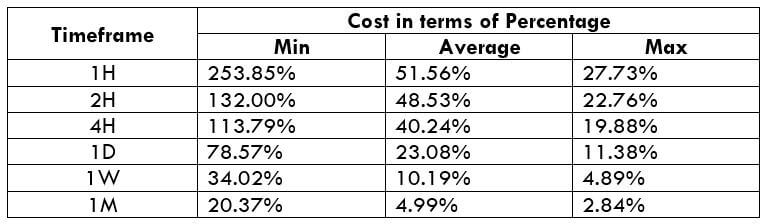

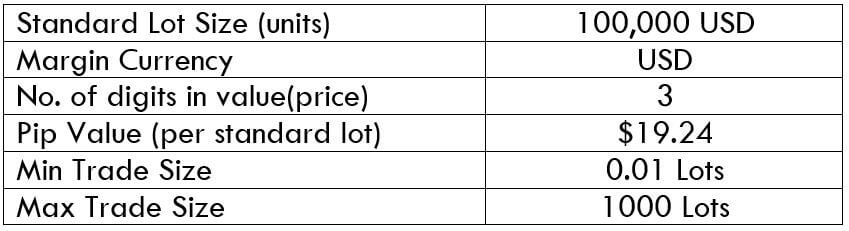
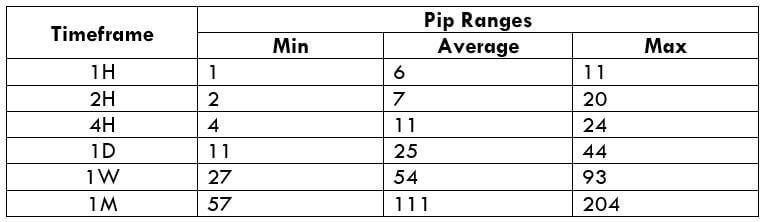
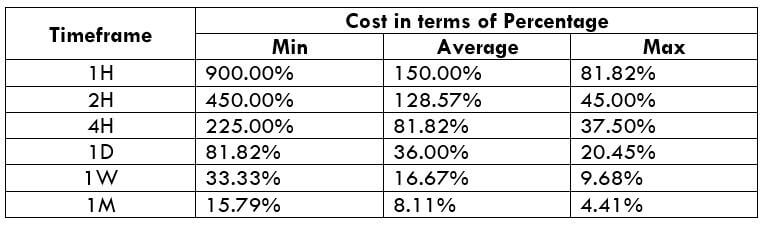
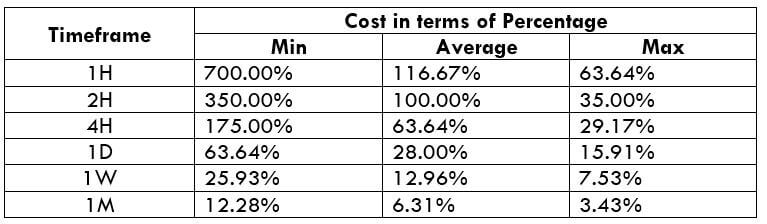

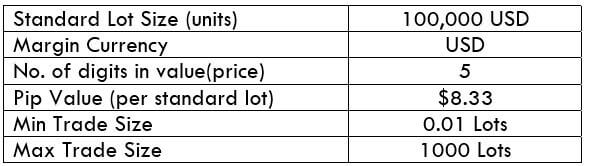
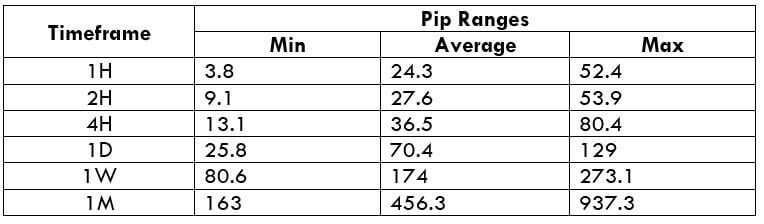
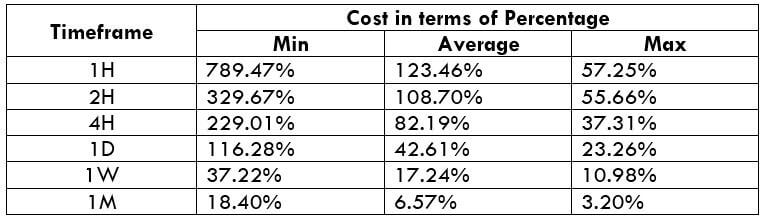
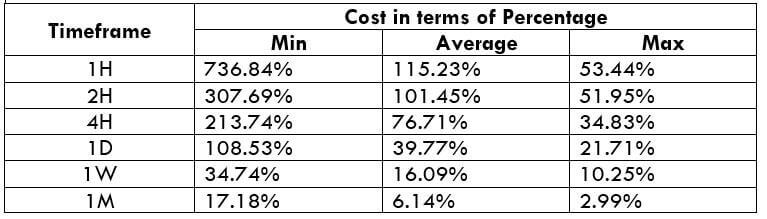

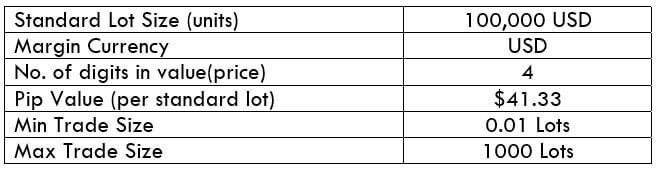
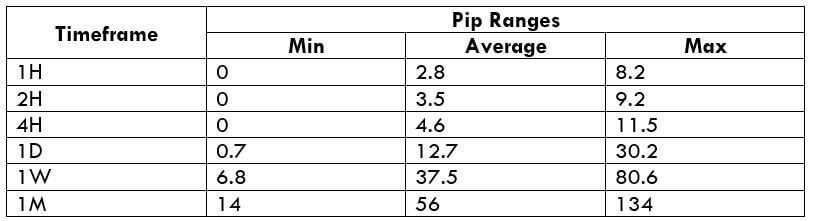
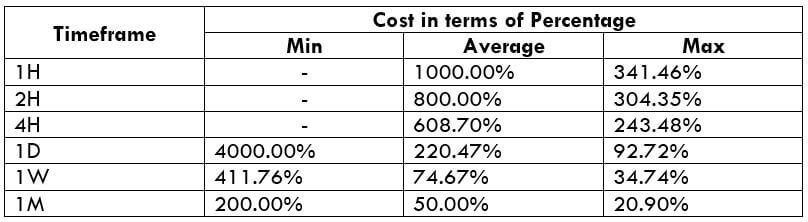
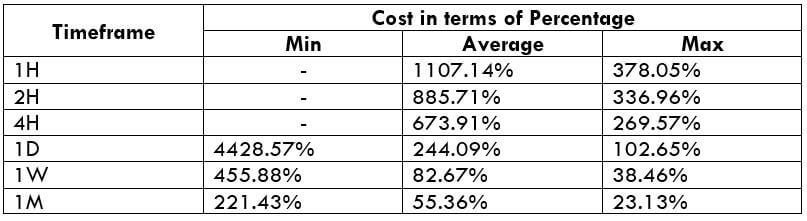

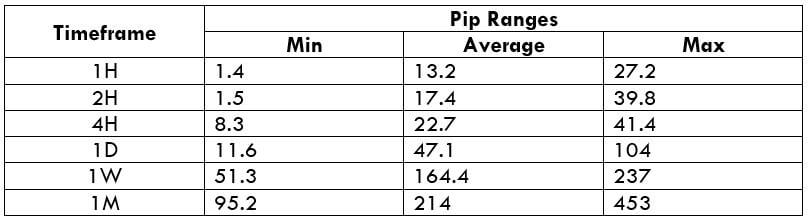
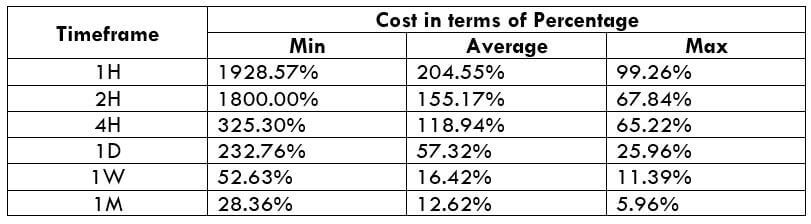
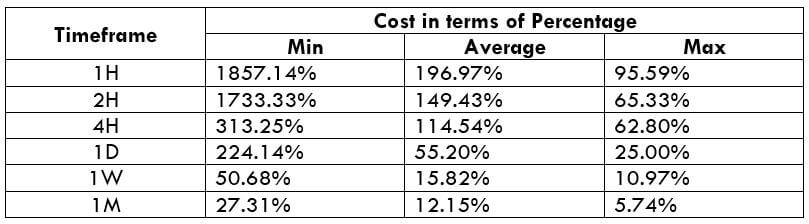
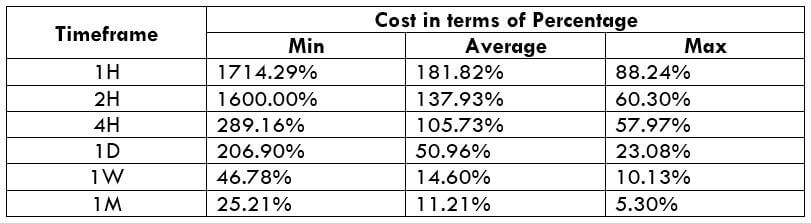

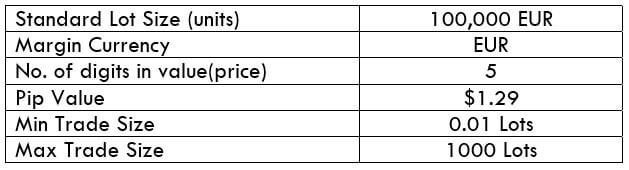
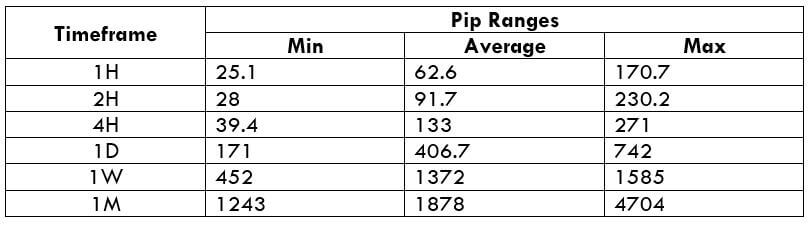
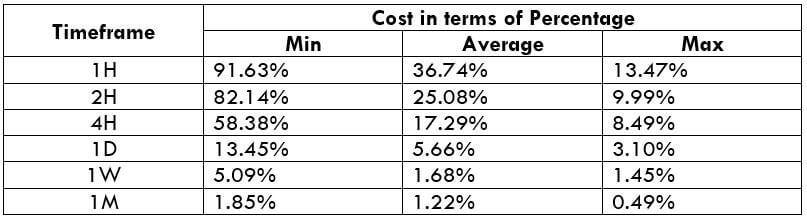
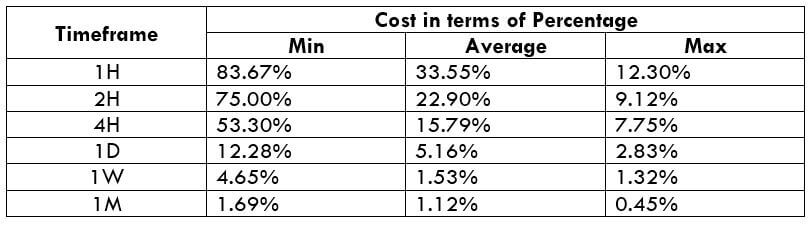

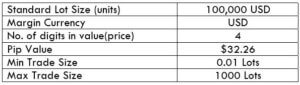
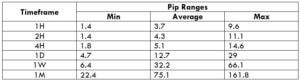
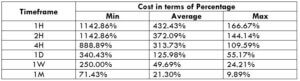
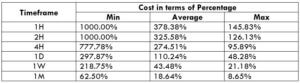
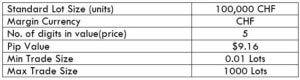
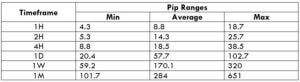
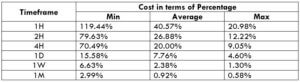
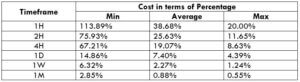

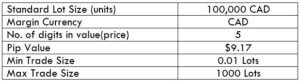
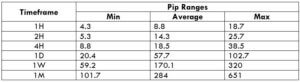
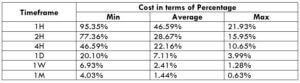
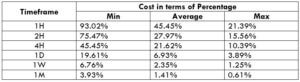
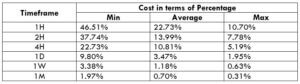

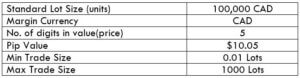
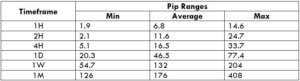
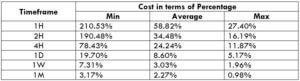
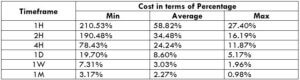

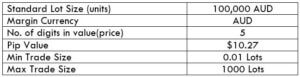
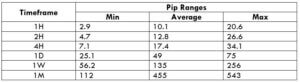
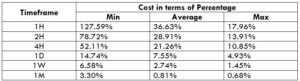
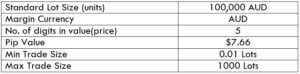
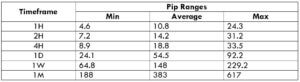
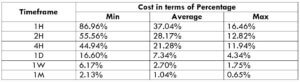
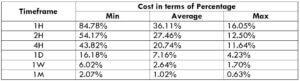 The Ideal way to trade the AUD/CAD
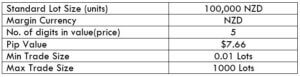
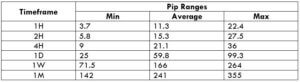
The Ideal way to trade the AUD/CAD
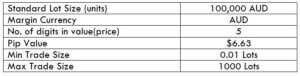
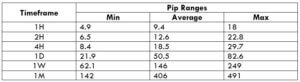
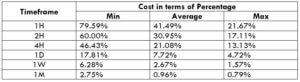
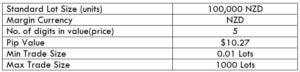
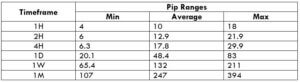
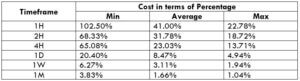
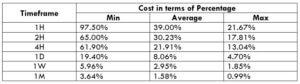
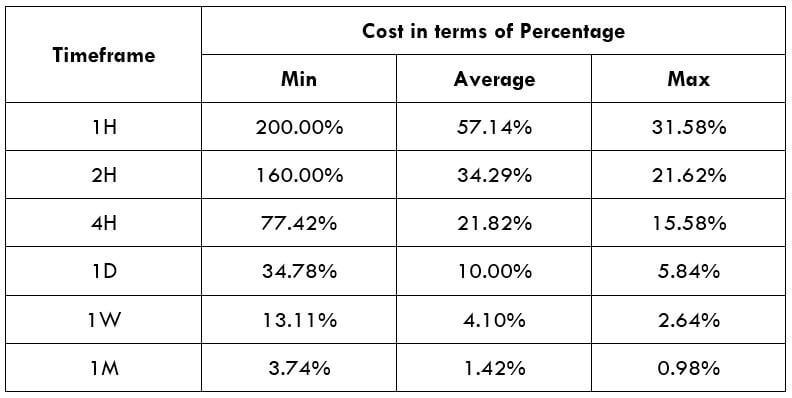
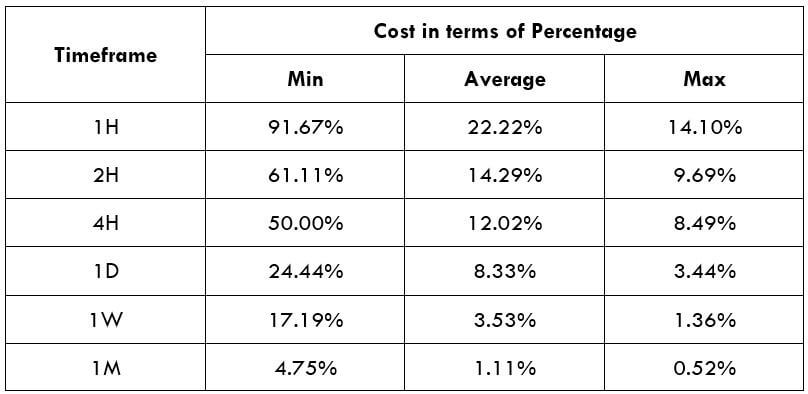
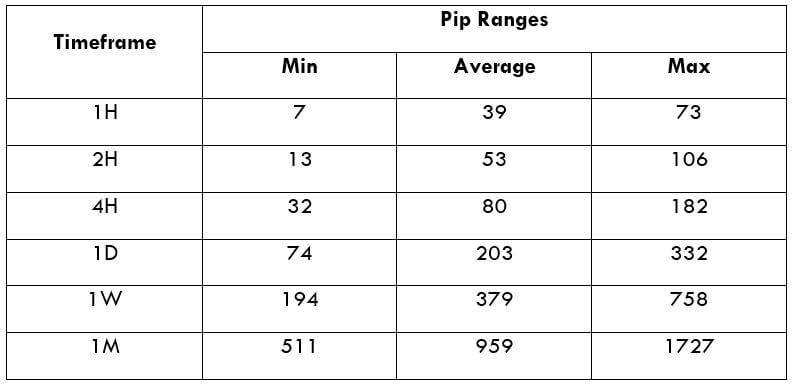
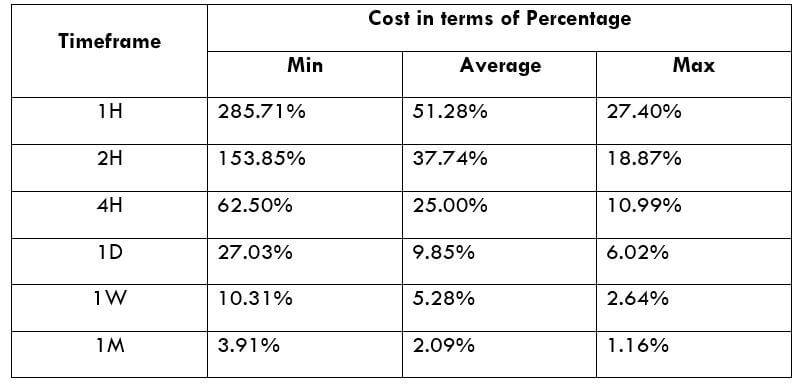
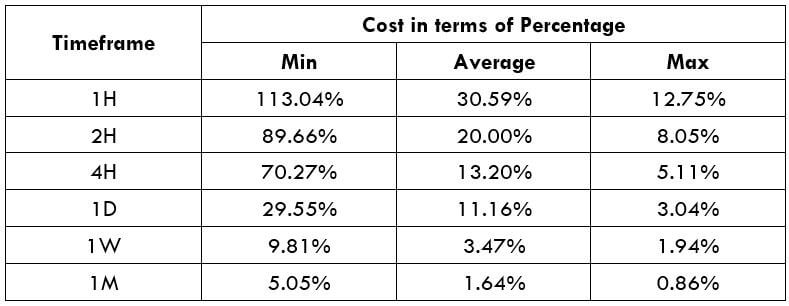
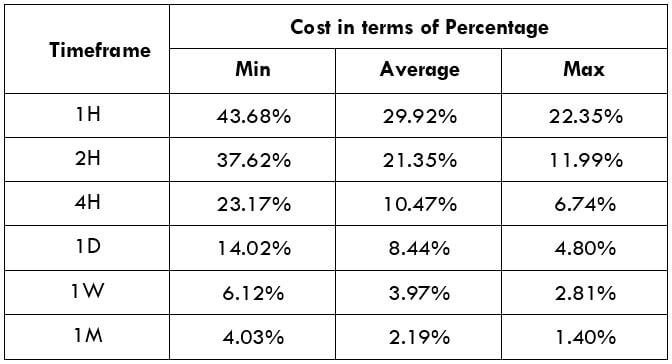
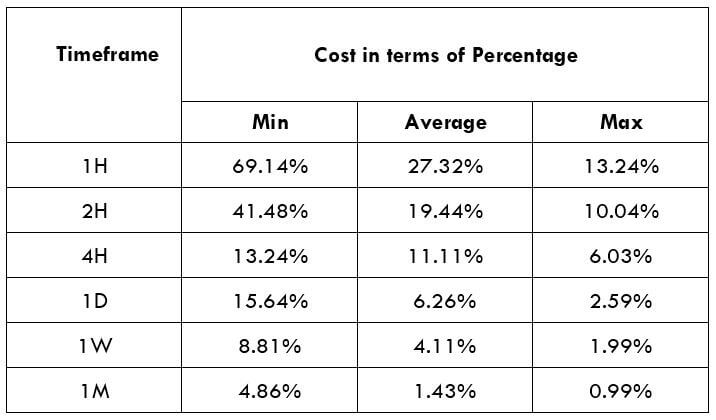
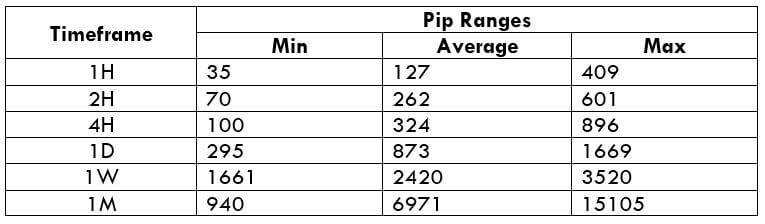
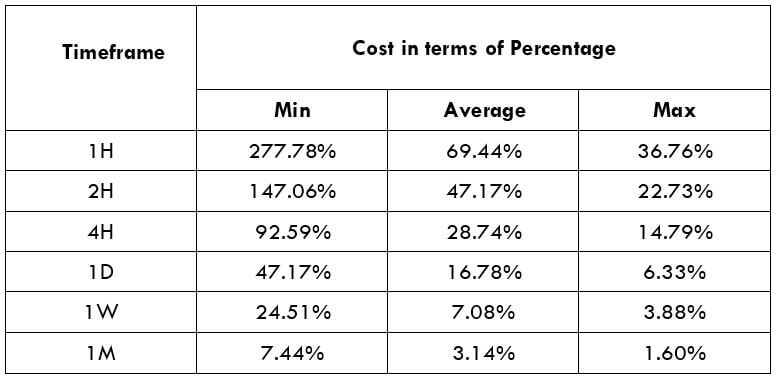
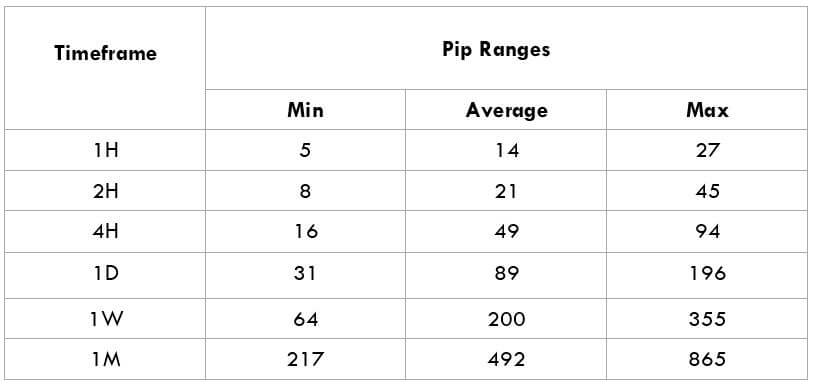
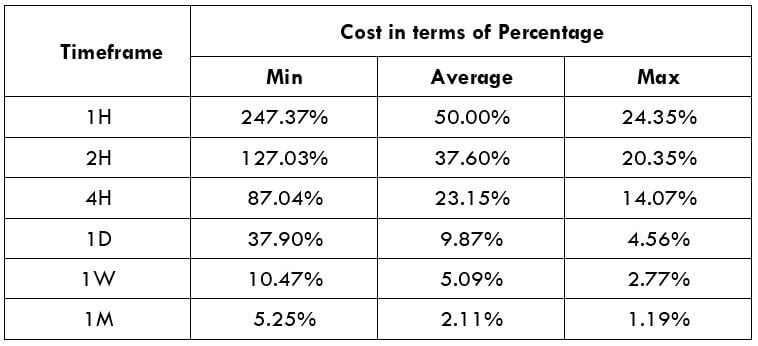
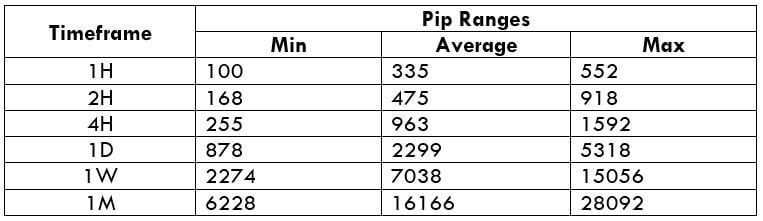
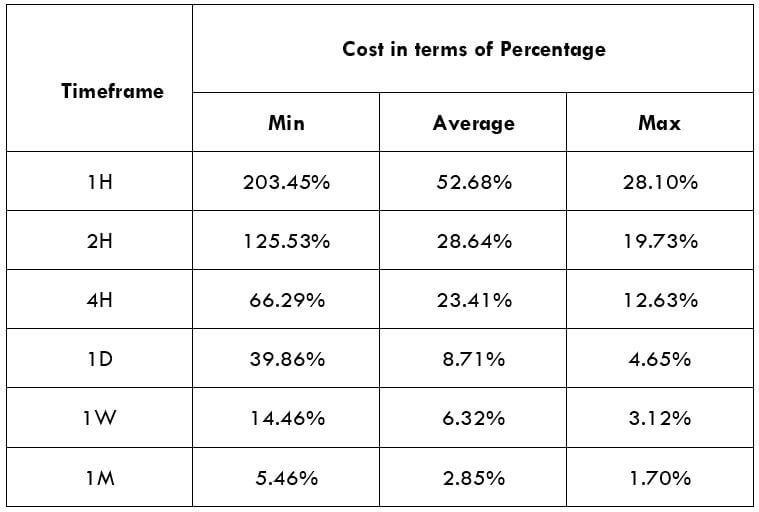
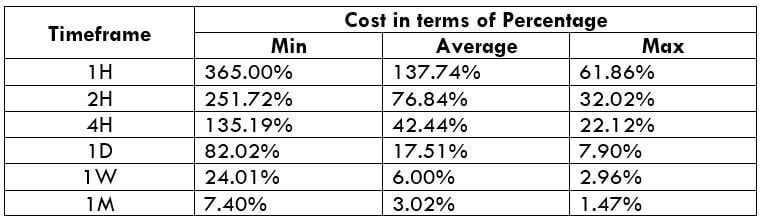
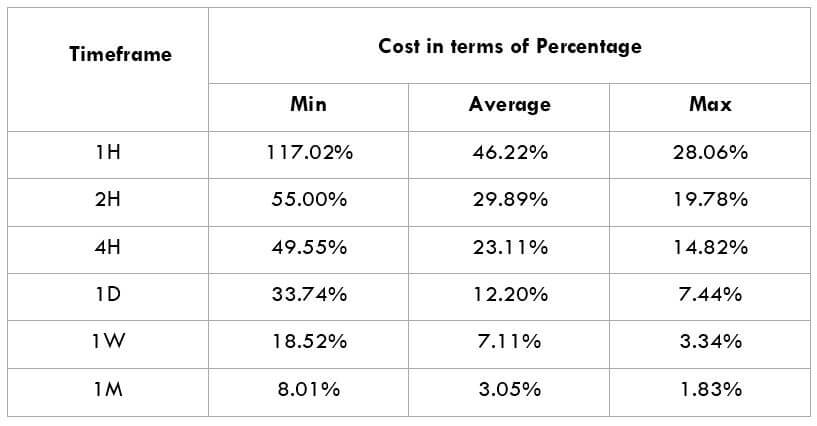
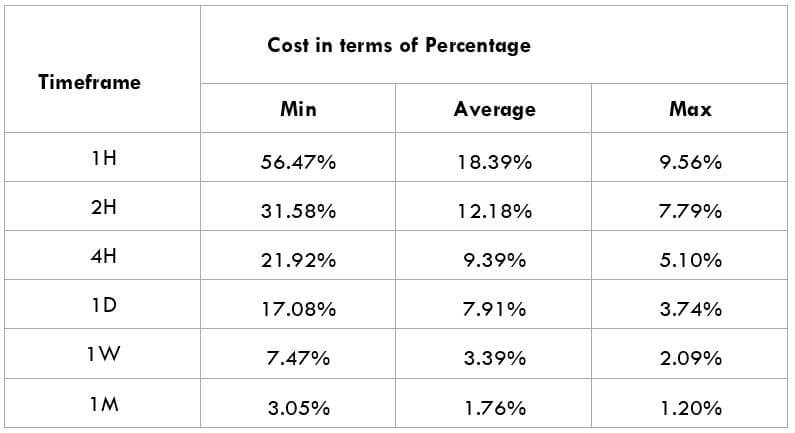
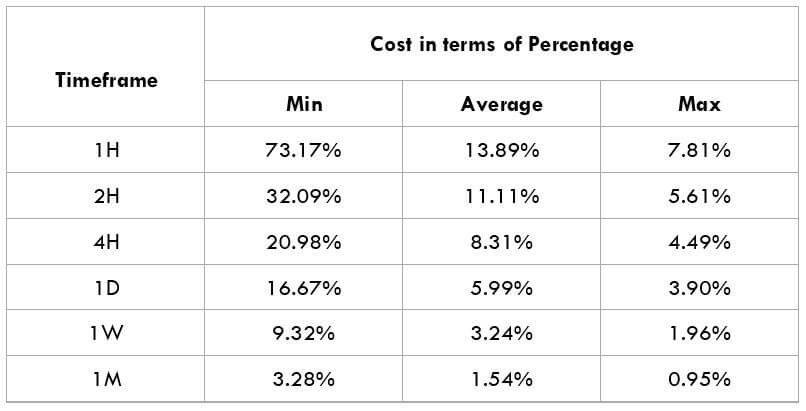
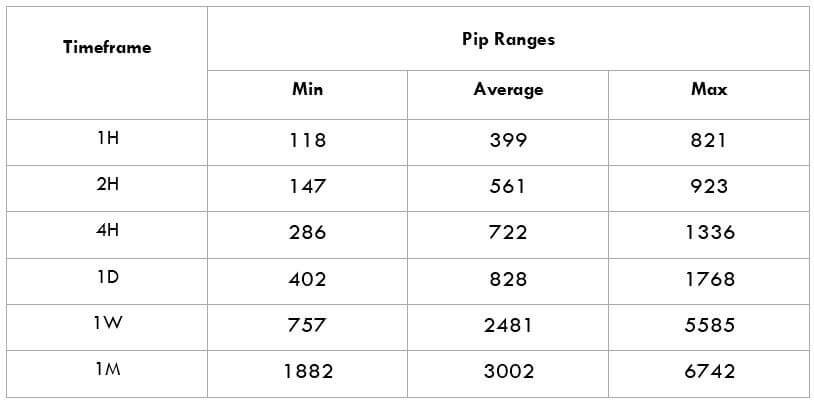
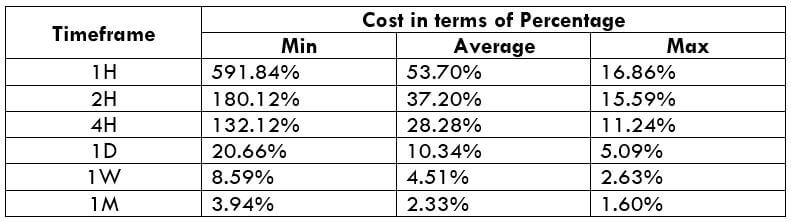
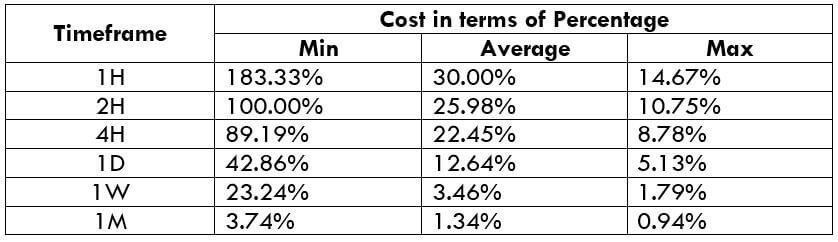
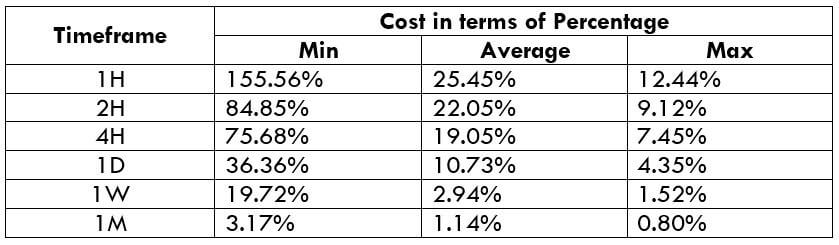
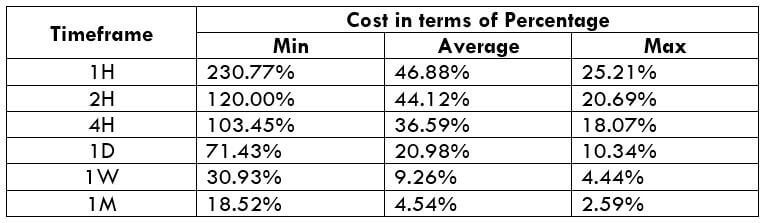
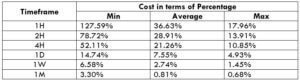
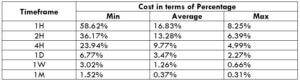
 The Ideal way to trade the AUD/NZD
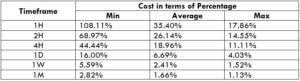
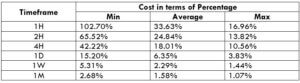
The Ideal way to trade the AUD/NZD