introduction
USDHKD is the abbreviation for the US dollar and the Hong Kong dollar. The USDHKD is an exotic currency pair. Exotics are pairs that are thinly traded in the foreign exchange markets and are not widely used in the global markets. One can expect high volatility and low volumes on this pair. Here, USD is referred to as base currency and HKD as the quote currency.
Understanding USD/HKD
The value of USDHKD represents the value of the Hong Kong dollar that is equivalent to one US dollar. It is quoted as 1USD per X HKD. For example, if the market price of USDHKD is 7.7684, then these many units of HKD are required to purchase one USD.
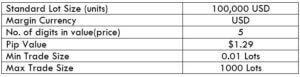
Spread
Spread is the difference between the bid price and the ask price of a currency pair. This value is set by the brokers, and it varies from different brokers. The type of execution model brings a variation in the spreads.
ECN: 5 | STP: 9
Fees
When you execute any trade through your brokers, there is a fee that has to be paid. The fee differs from brokers to brokers, as well as their execution type. Typically, there is no fee on STP accounts.
Slippage
Slippage is the difference between the trader’s intended price to execute a trade and the price he actually received from the broker. There is always this difference due to the volatility of the market and the broker’s execution speed. As a matter of fact, slippage is pretty high on exotic pairs.
Trading Range in USD/HKD
The trading range is the depiction of the minimum, average, and maximum pip movement of a currency pair. And these values help in assessing one’s risk on a trade. By finding the product of the volatility value with the pip value, you can determine the profit or loss that can be incurred in a specified timeframe.
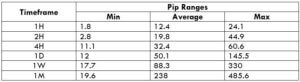
Procedure to assess Pip Ranges
- Add the ATR indicator to your chart
- Set the period to 1
- Add a 200-period SMA to this indicator
- Shrink the chart so you can determine a large time period
- Select your desired timeframe
- Measure the floor level and set this value as the min
- Measure the level of the 200-period SMA and set this as the average
- Measure the peak levels and set this as Max.
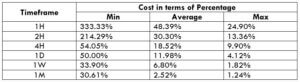
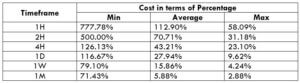
USD/HKD Cost as a Percent of the Trading Range
This calculation is an extremely helpful tool to analyze the cost variations in a trade. This table is basically a representation of the total cost variations in different timeframes and volatilities of the market. The costs are represented as a percentage of the range, and the magnitude of it depicts the cost of the trade.
ECN Model Account
Spread = 5 | Slippage = 5 |Trading fee = 1
Total cost = Slippage + Spread + Trading Fee = 5 + 5 + 1 = 11
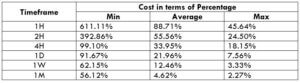
STP Model Account
Spread = 9 | Slippage = 5 | Trading fee = 0
Total cost = Slippage + Spread + Trading Fee = 9 + 5 + 0 = 14
The Ideal way to trade the USD/HKD
Exotic pairs are expensive to trade when compared to major and minor currency pairs. However, it does not mean that one must completely avoid it. There are a few ways by which one can minimize the costs on the trade and take positions on it.
The higher the magnitude of the percentage, the higher is the cost of the trade. It is evident that the values are significant on the min column and comparatively small on the max column. Hence, costs are high for low volatilities markets and vice versa.
When it comes to picking the right time to enter the market, it is ideal to take positions when the volatility of the market is around the average values. From this, one can be guaranteed with affordable costs and decent volatility.
Slippage has a significant weight on the total cost of a trade. However, slippage can be wiped out. Trading using limit orders instead of market orders will take away the slippage on the trade. The next table displays the costs using limit orders.
Spread = 5 | Slippage = 0 |Trading fee = 1
Total cost = Slippage + Spread + Trading Fee = 5 + 0 + 1 = 6