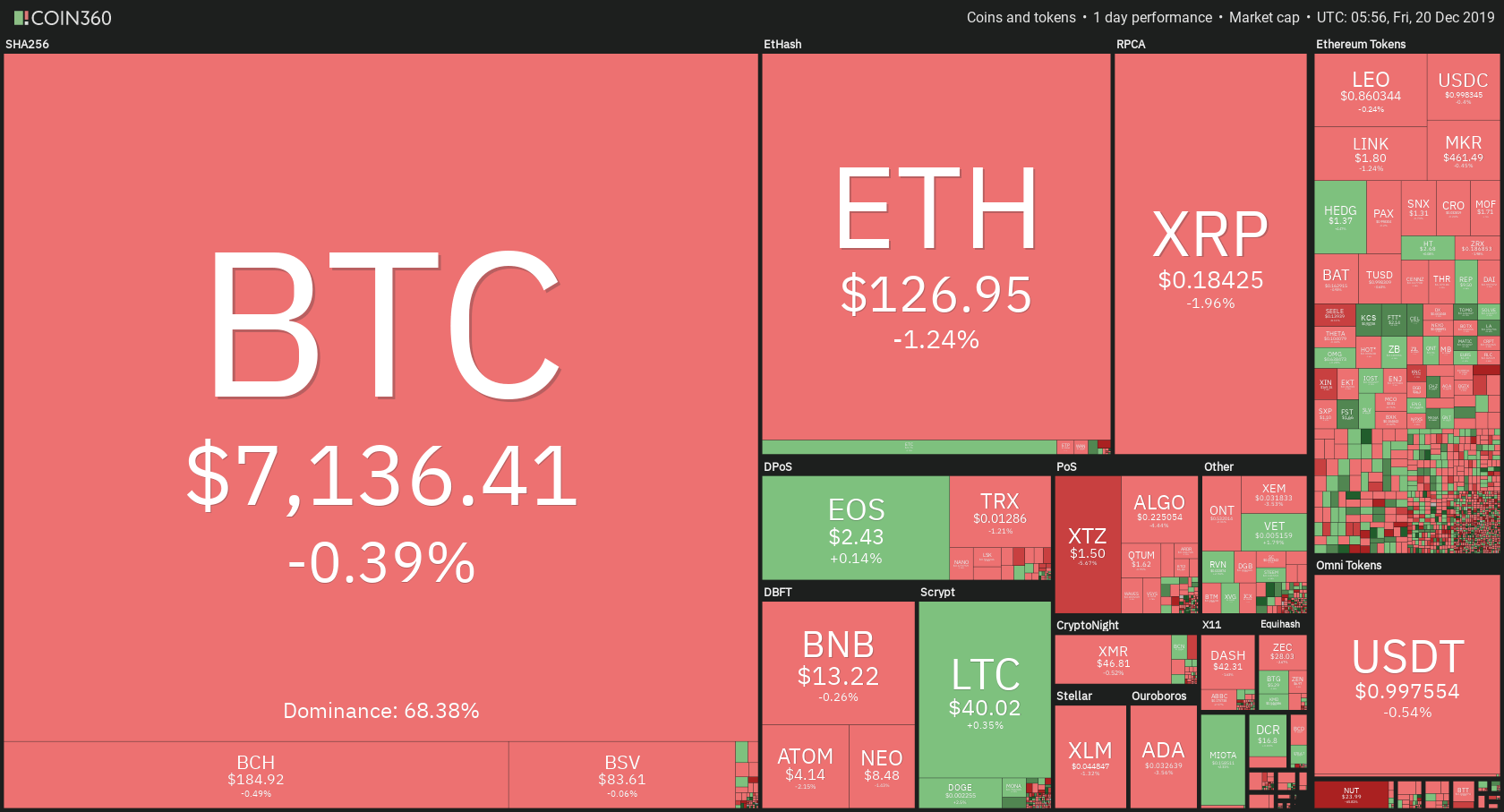
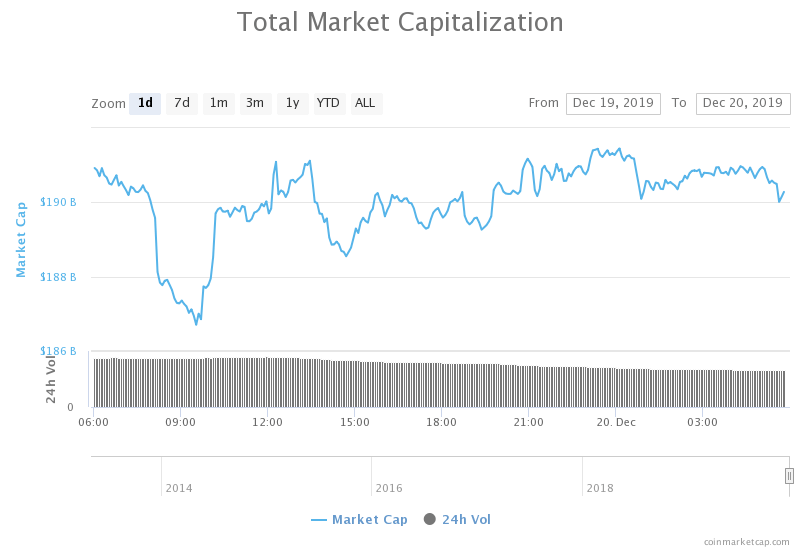
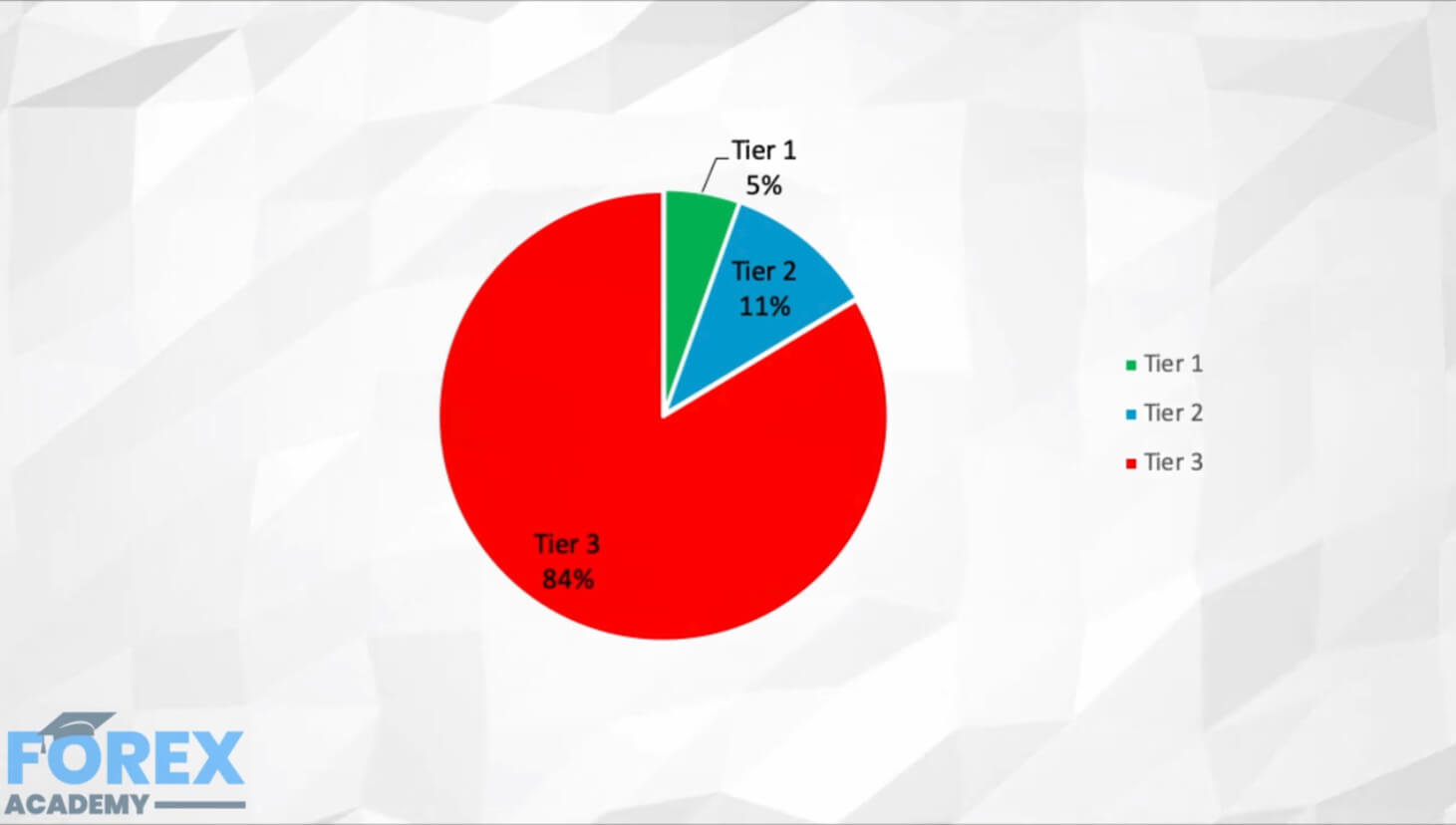
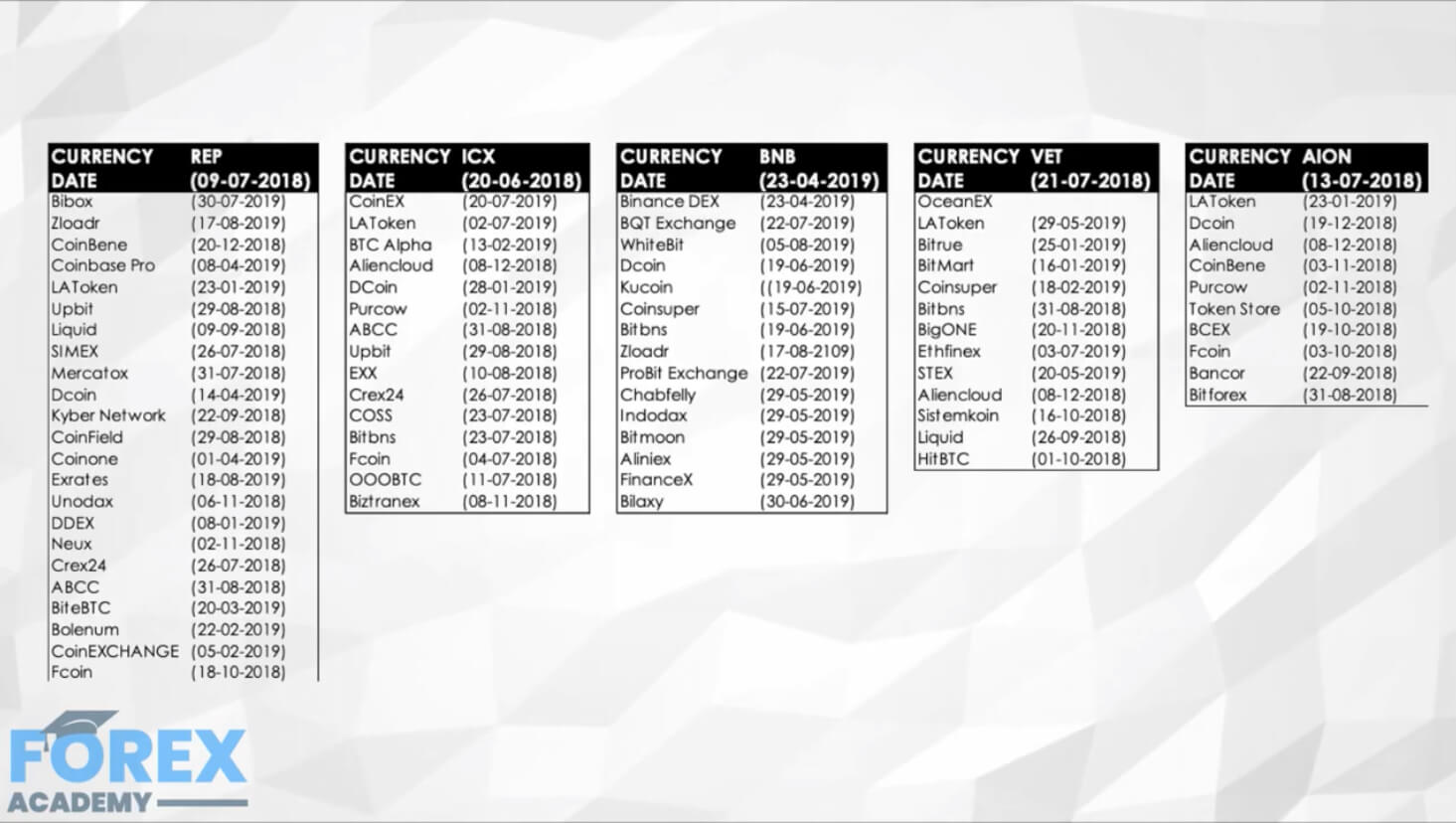
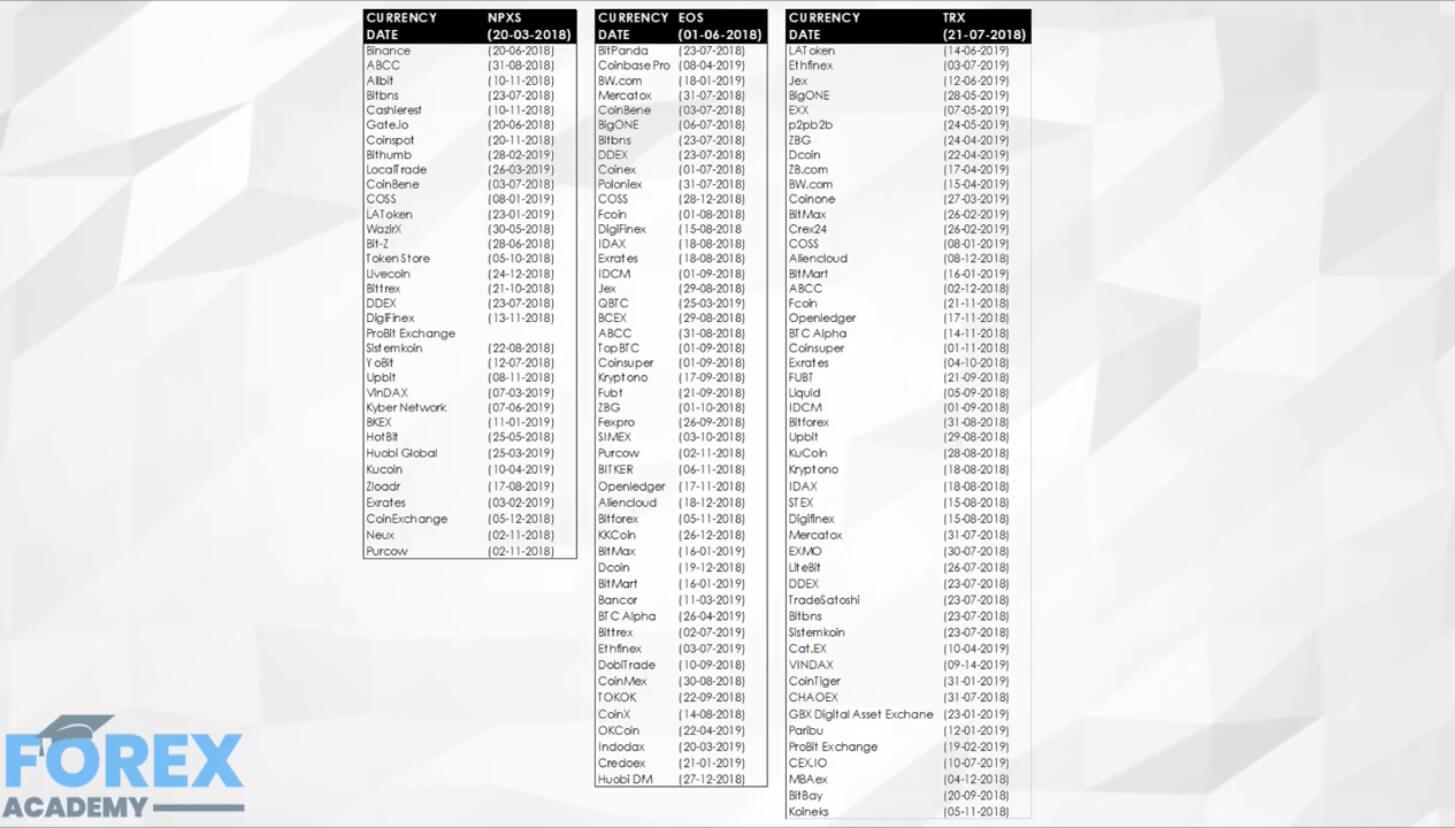
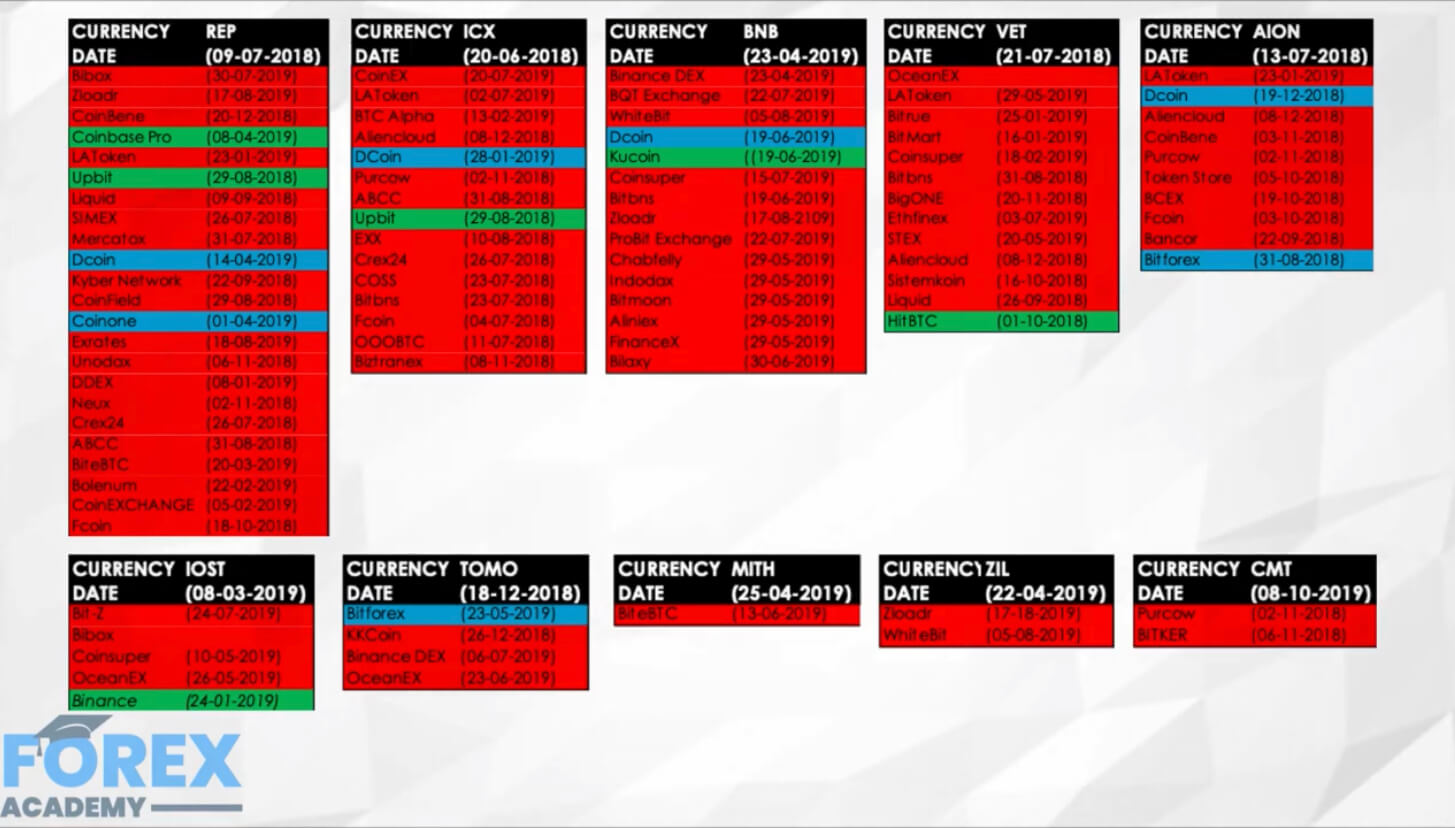
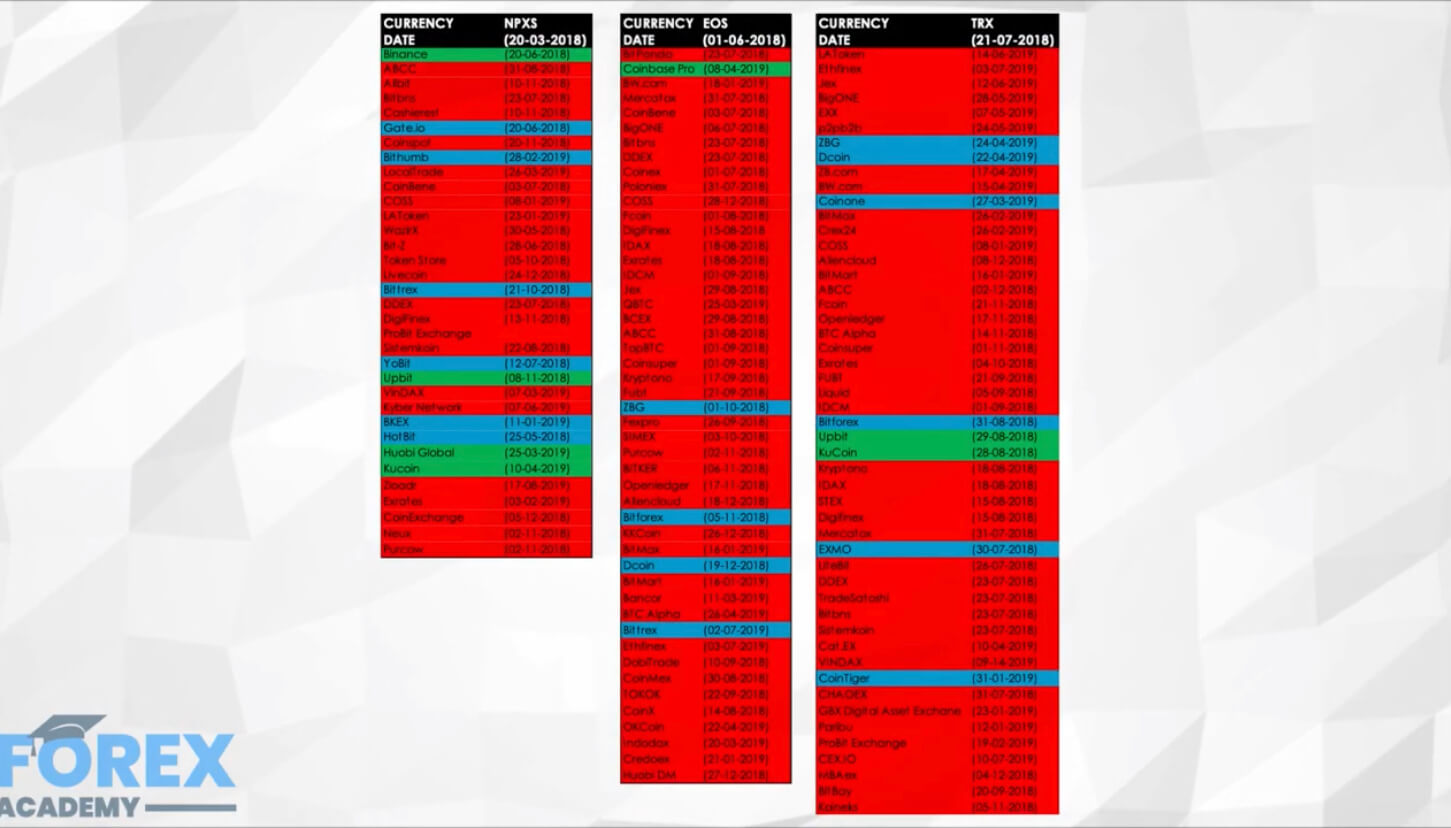
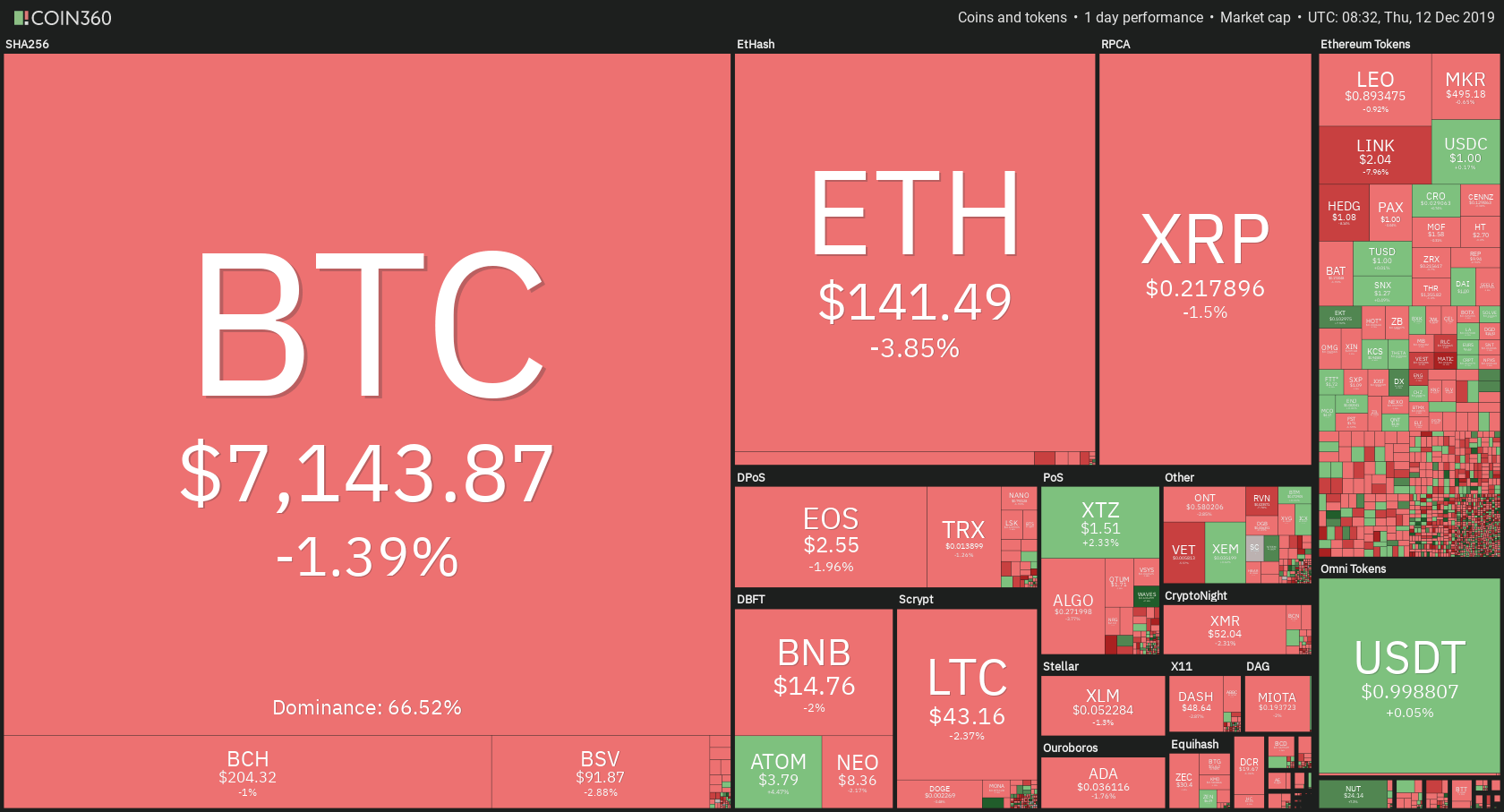
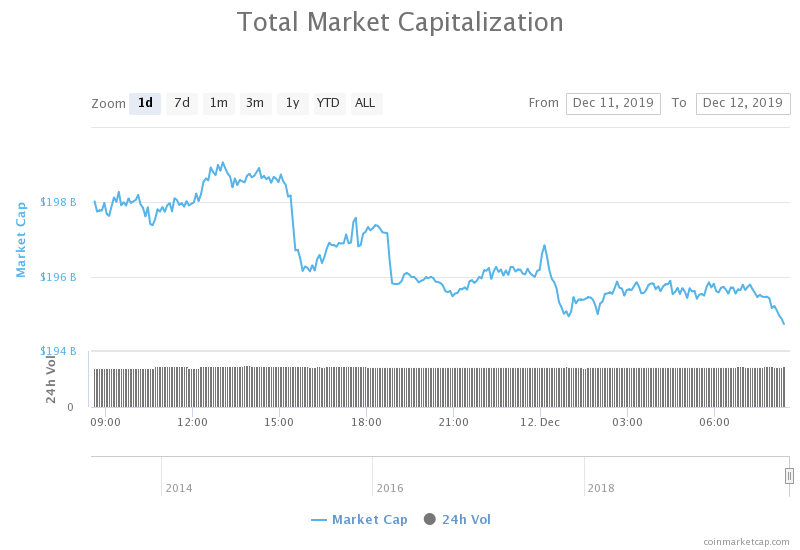
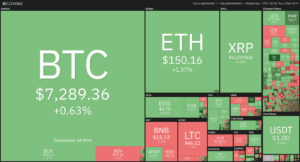
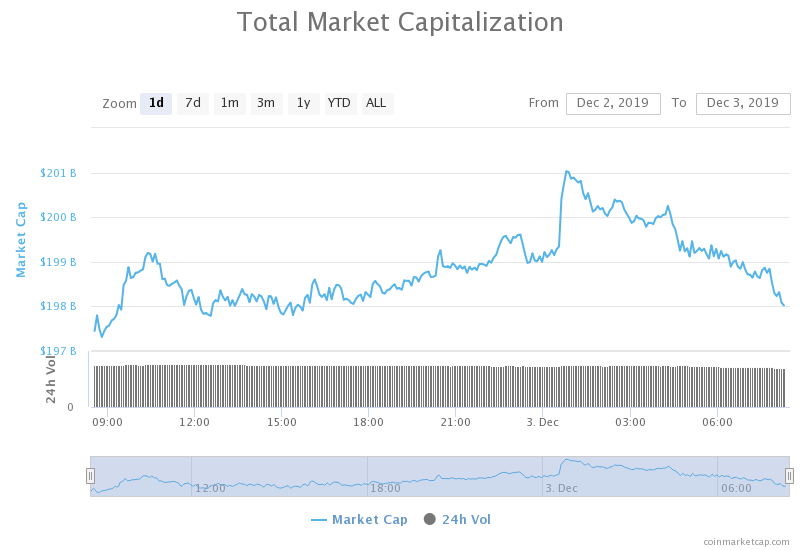
Public blockchain cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum utilizes cryptography technology to disguise users’ identity. To an extent, this protects users’ privacy, making the cryptos ideal for pseudonymous transactions.
However, the transparent nature of these cryptocurrencies’ ledger system compromises users’ complete anonymity. As such, it’s easy for malicious third parties to trace all your transactions and exploit this information to jeopardize your privacy. Now, this is where privacy coins come into play.
What Exactly are Privacy Coins?
Unlike public digital currencies, privacy coins offer robust anonymity that works by obfuscating your transaction history and amount, making it impossible for third parties to piece together your identity. To achieve it, privacy coins leverage various innovative technologies, giving them a competitive advantage, as far as users’ privacy is concerned.
While there are a good number of privacy coins in the market, we’ll be taking a comprehensive look into the best five coins, based on their technology, adoption, and market capitalization.
Monero – XMR
Started in 2014, Monero has grown to become one of the most popular privacy coins backed by a stable market cap. The coin gives its users complete control of their data and anonymity, allowing them to keep their transaction information away from privy eyes.
In addition to its default private key cryptography, the Monero employs CryptoNote proof-of-work protocol, to obscure all details related to a transaction, including the source of funds. To further enhance users’ privacy, the protocol is complemented by unique technologies such as Ring Signatures, Ring Confidential Transactions (RingCT), and Stealth Address.
As the name suggests, Ring Signature technology works by bringing a group of signers to sign a single transaction. This forms a ring where only the sender can generate and send a one-time-key, while the actual recipient will be the only one who can detect and spend the funds linked to the key. With the technology in place, it becomes difficult for any transaction to be traced back to any user, which in turn secures users’ privacy.
To guarantee that the coins have not been fraudulently fabricated in the transaction, RingCT creates a cryptographic proof which verifies that the sum of the input and output amounts is equal. The technology does this without disclosing the actual transaction numbers, thereby masking the amount the two parties transacted.
Stealth Address, on the other hand, is designed to make all transactions untraceable. Basically, a one-time-key is created for each transaction, giving the sender and recipient the freedom to disconnect themselves from a transaction. What’s even better is that the key isn’t linked to the recipient’s wallet address, making it harder for an outside observer to trace the amount sent.
Dash – DASH
Dash coin is an open-source peer-peer cryptocurrency that was launched after Bitcoin forked in 2014. In fact, the coin borrows heavily from its parent, BTC, in terms of privacy protection. It utilizes a concept known as PrivateSend, which is an improved version of Bitcoin’s CoinJoin, designed to anonymize transactions.
Essentially, the concept works by allowing multiple parties, usually three users, to pre-mix their coins into a single transaction, and then send these coins to new addresses, randomly. The transactions are further taken through a series of such operations, which makes the amount, the sender and destination unknown to third-parties.
The instant-send feature of the coin facilitates faster transactions, by channeling inputs and outputs along the second tier of the Dash blockchain.
Although not related to privacy protection, Dash coin also features a management mechanism that oversees future funding and network development through a self-governing community know as Decentralised Governance by Blockchain (DGBB).
ZCash – ZEC
Being an iteration of Zerocash, ZCash implements it’s predecessor’s protocol that is based on zero-knowledge cryptography known as ZK-SNARKs. As intricate as it may sound, the technology’s functionality is pretty straightforward.
Basically, ZK-SNARKs encrypts all transactional details that are stored on the network, which include information about the sender, the recipient, and the amount transacted. In the process, the technology also verifies that the data being exchanged is authentic, without necessarily broadcasting the said information, besides the fact that it is true.
Keep in mind that using this privacy feature is optional, and thus users can opt to have their transaction recorded publicly. But it’s believed that users who choose the transparent option end up compromising the security of the entire network.
PIVX – PIVX
Private Instant Verified Transaction (PIVX), which also goes by the same tickle symbol as its acronym, is an open privacy coin with a growing popularity. It was launched as a Dash coin fork but runs on the Proof-of-Stake algorithm rather than Proof-of-Work used by Dash coin. This means that PIVX doesn’t rely on miners to verify transactions and, as such, rewards the coin holders, who are also responsible for validating transactions.
However, to be among the users who are rewarded with coins as well as approve transactions, you must have a stake of at least 10,000 tokens. After achieving the threshold token, you are allowed to own a master node, which gives you the power to on how the development budget will be used and even submit developmental suggestions.
PIVX also has a near-instant transaction verification feature and can be trusted in safeguarding users’ privacy.
Verge – XVG
Much of Verge’s popularity can be attributed to the endorsement it received from John McAfee, a reputable businessman in the cyber-space. Although it is quite unstable, the coin has succeeded in providing a fast and decentralized way of making transactions, while maintaining users’ privacy.
By default, Verge integrates the Tor network into its wallet, encrypting your IP address, such that your online transactions can be linked to you.
Its most privacy protection arsenal is the Wraith protocol that allows users to switch between public and private ledger systems.
As with Bitcoin, the public ledger system displays your account balance, wallet address, and that of the recipient, in addition to the actual amount you are sending. Choosing the private ledger option keeps these details under wraps, protecting you from third parties who may be trying to trace your transactions.
Other noteworthy features include 5 Proof-of-work algorithms, which have a limited target block time, improving protection against attacks.
Takeaway
With the increasing cybersecurity threats, protecting your online privacy becomes a priority, especially when transacting cryptocurrencies. Sure, there is no problem in displaying your transactions history for all to see, since you don’t have anything to hide in the first place. But the idea that third-parties can use your transactions to trace activities should prompt you to keep your cyber-footprints untraceable.
As such, you may consider investing in some of the digital currencies mentioned above in an effort to protect your personal privacy.