Introduction
The previous chapters dealt with the interpretation of divergence, its types, strategies, and the rules involved in it. In this article, we have provided a cheat sheet that will cover all the divergence topics in short.
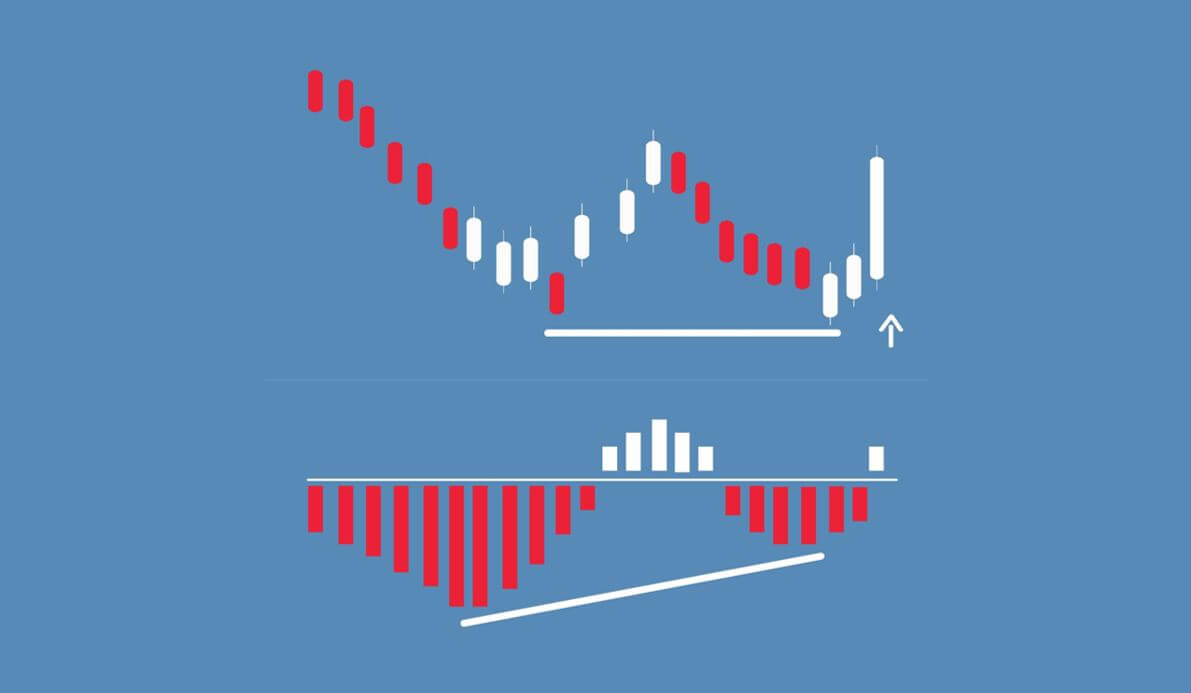
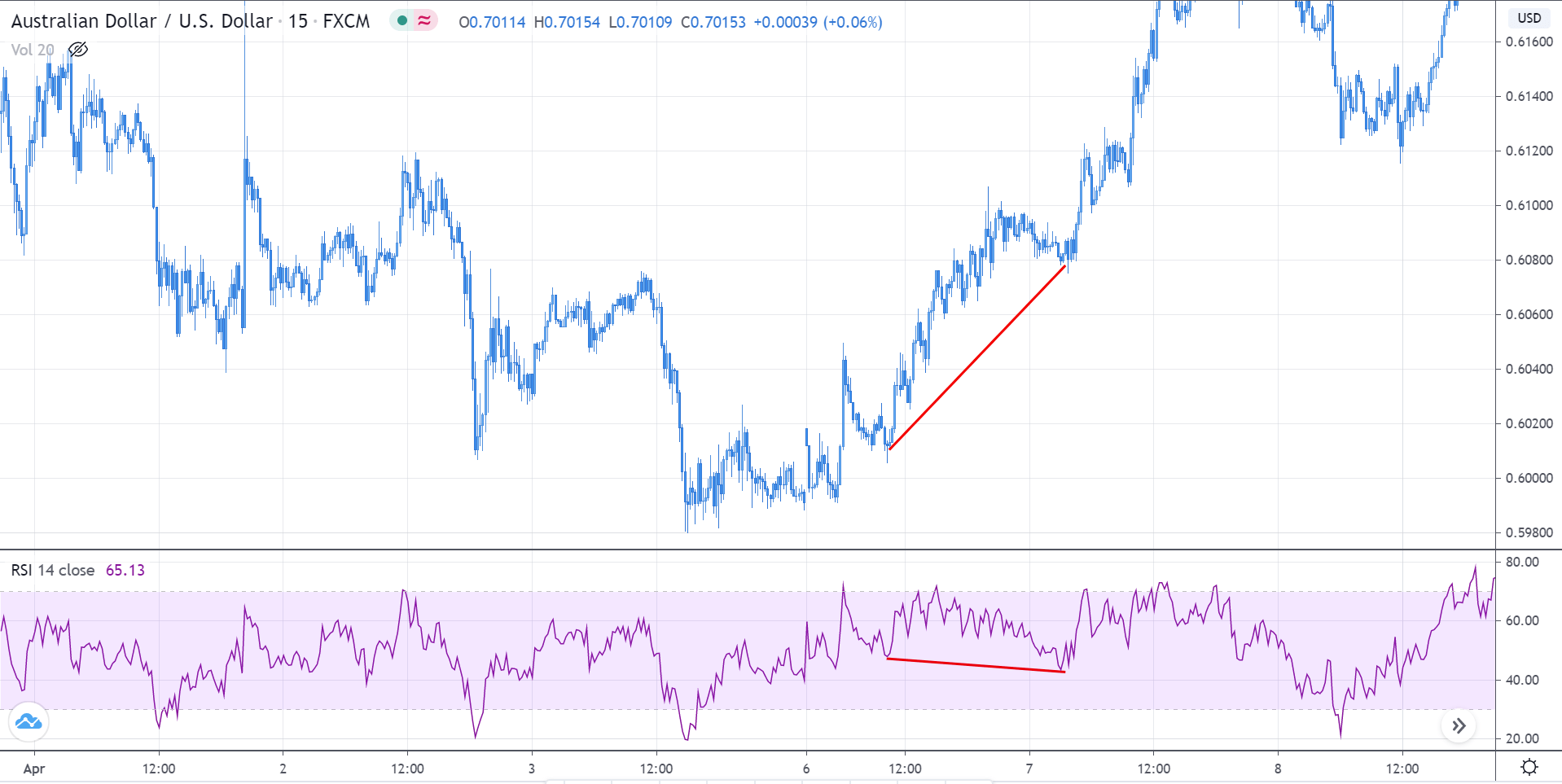
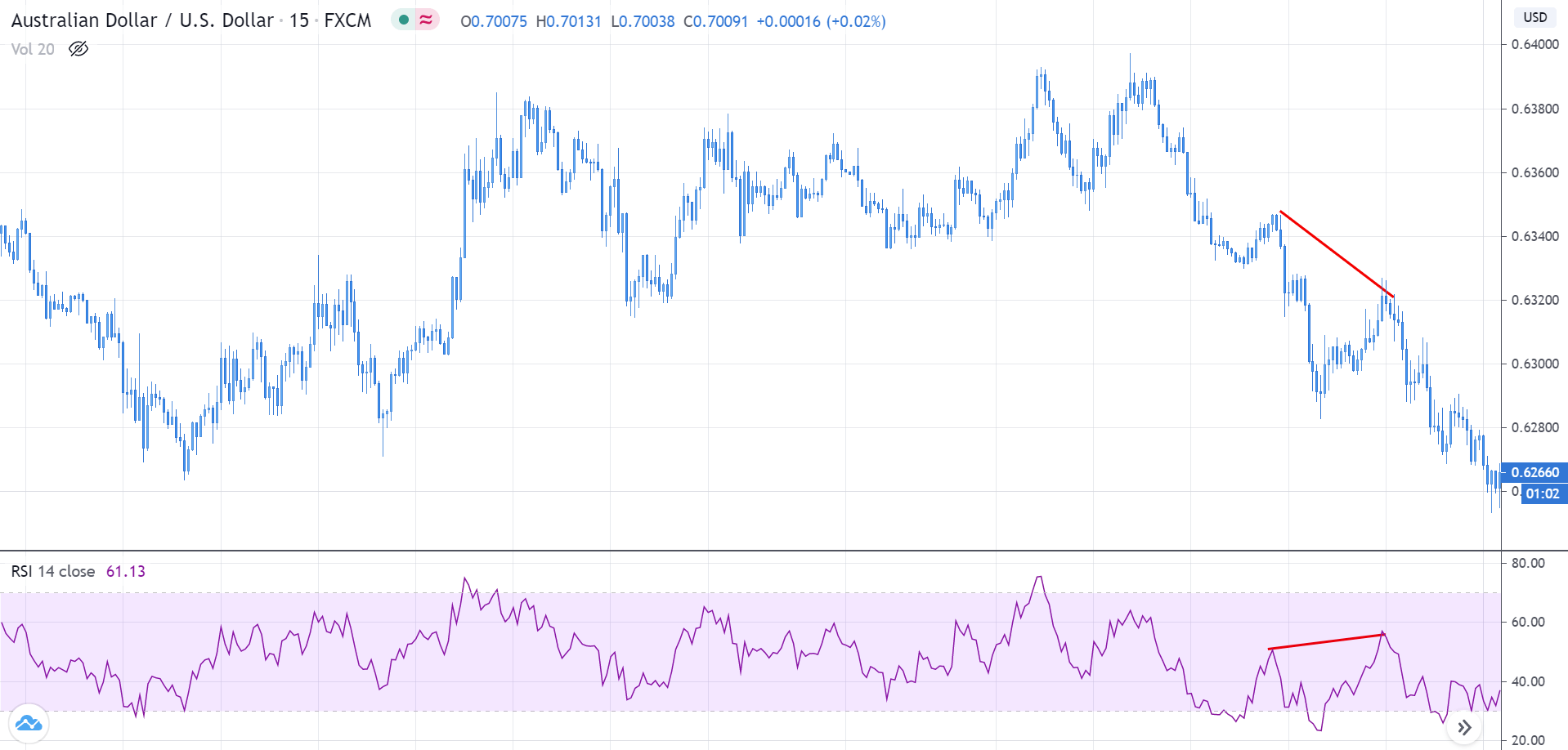
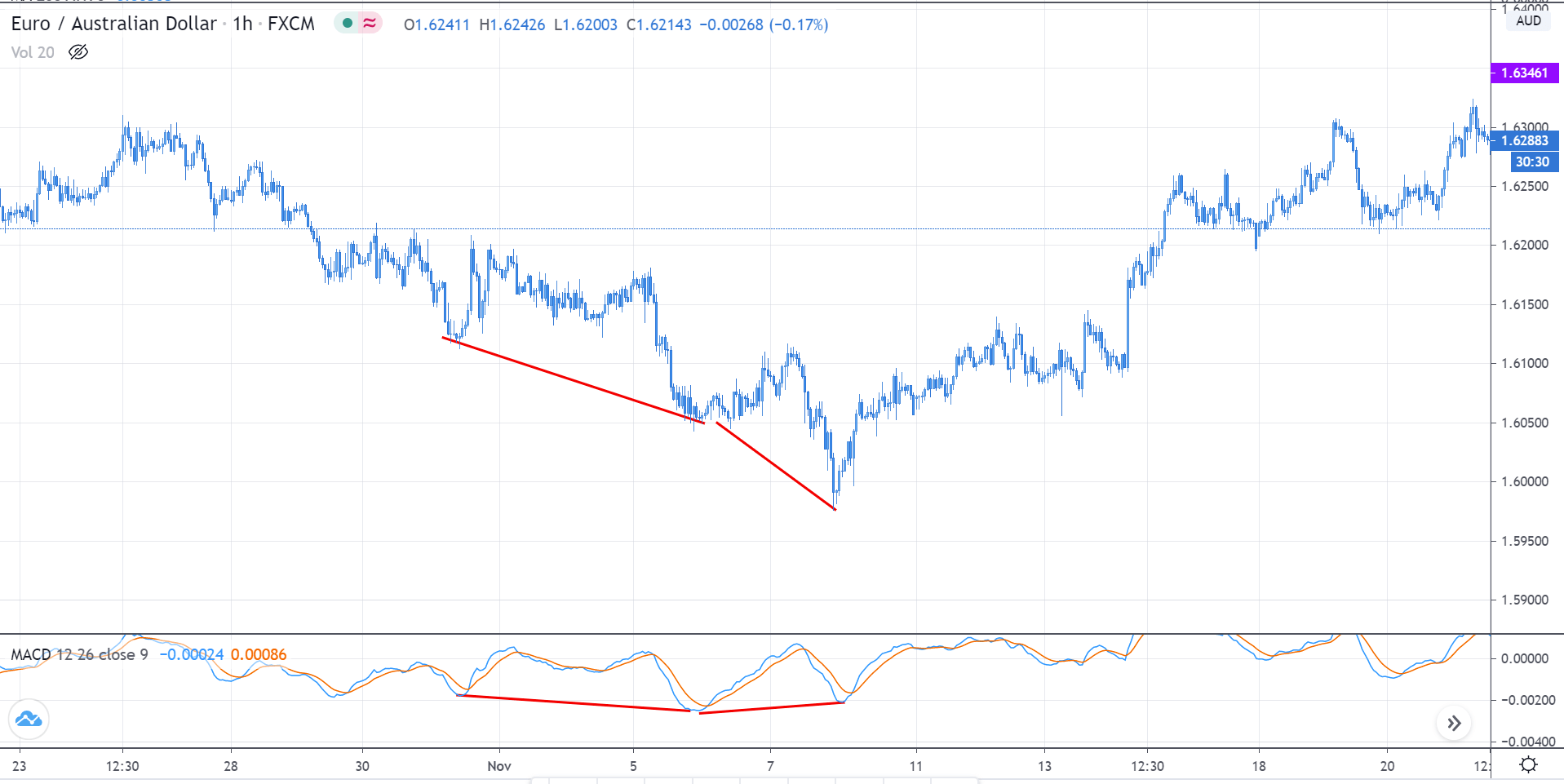
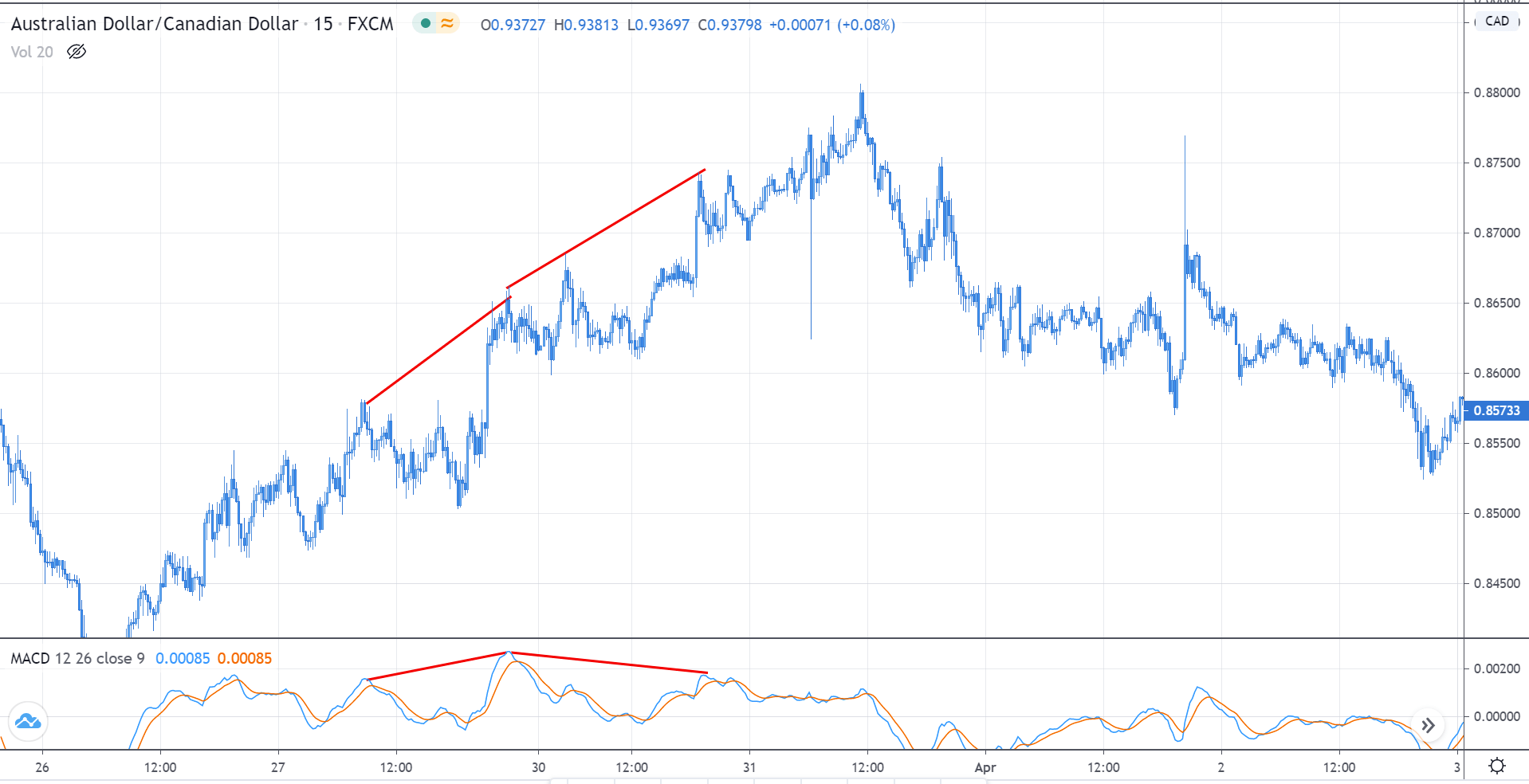
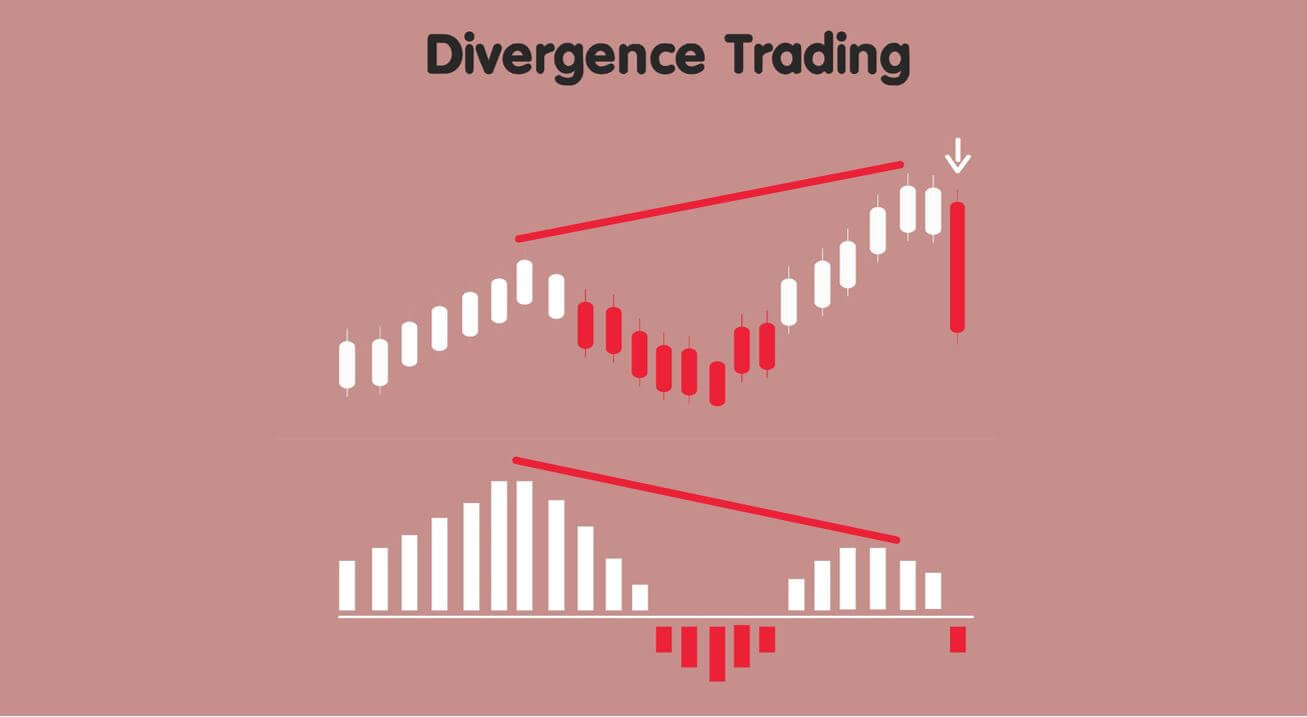
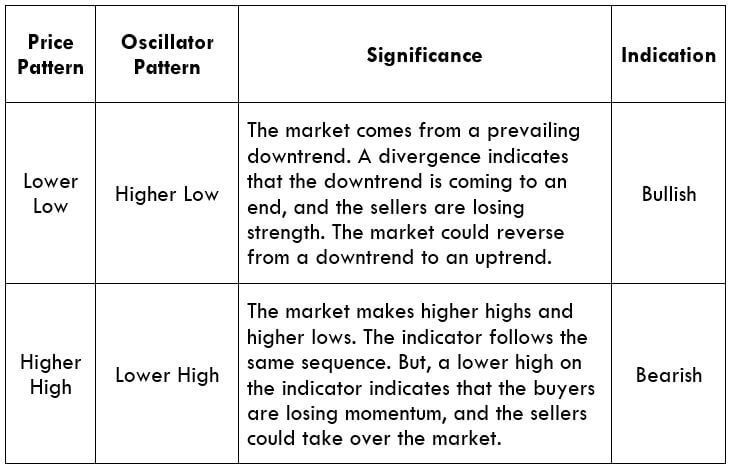
Divergence: This a concept in technical trading that determines if the market is going to reverse or continue the trend. It is identified when the price and the indicator move in opposite directions.
Based on the direction it will prevail in, there are two types of divergence:
- Regular Divergence
- Hidden Divergence
Each of them is divided into types – Bullish and Bearish, based on the direction they are biased. Here is a quick cheat sheet for trading Regular and Hidden Divergence.
Regular Divergence
Regular divergence is divergence, which indicates a reversal in the market. These occur during the end of a trend and are quite easy to spot.
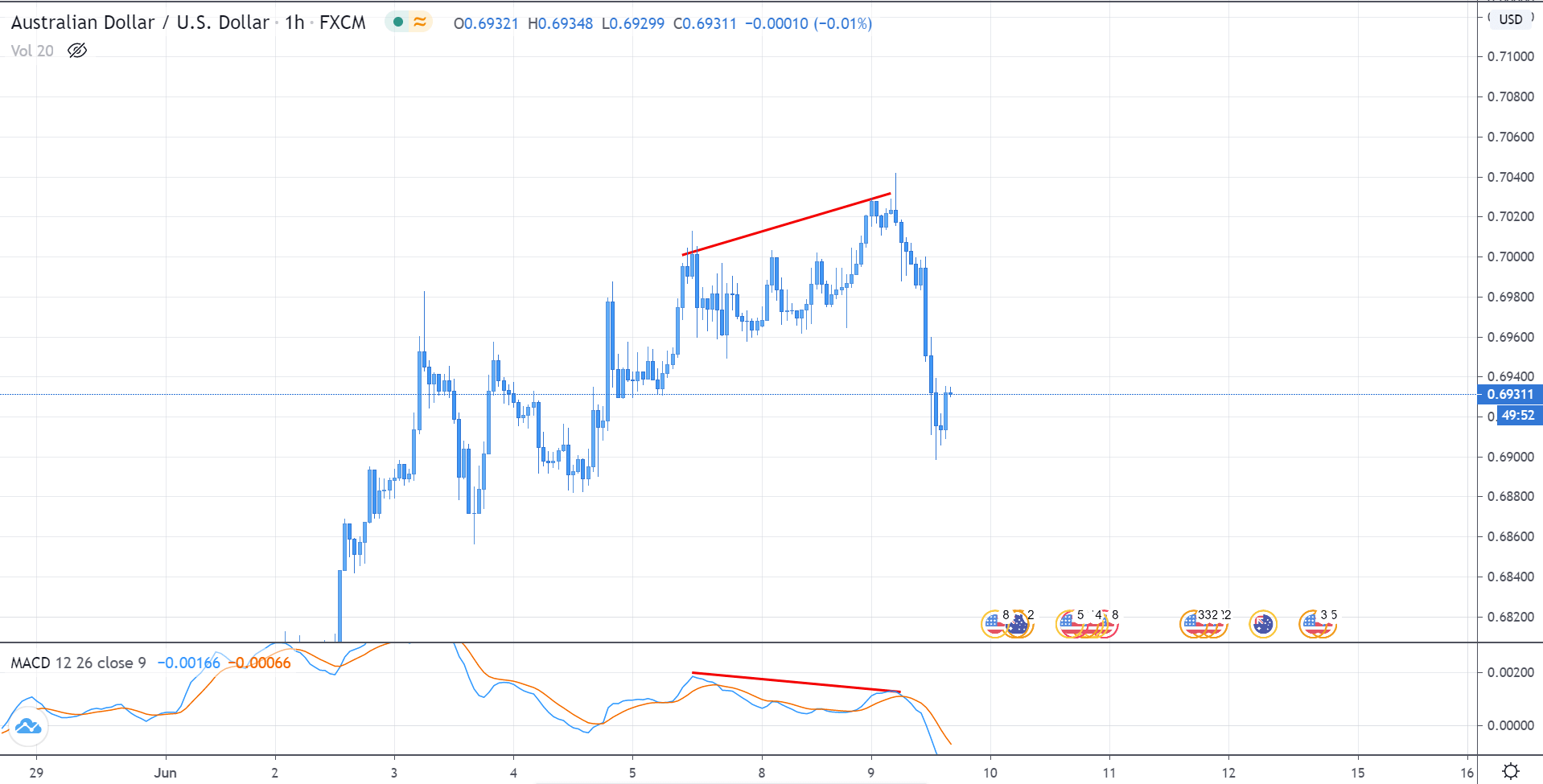
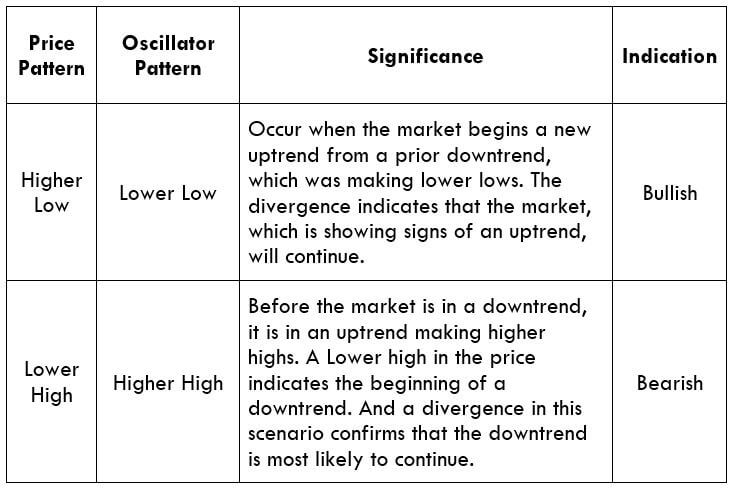
Hidden Divergence
Hidden divergence indicates a possible trend continuation. These usually occur at the beginning of a new trend and are comparatively tricky to spot.
Not all indicators can be used to spot divergence. Only momentum oscillators indicate a divergence in the market. Some of the most used momentum oscillators to determine divergence include Commodity Channel Index (CCI), Relative Strength Index (RSI), Stochastic, and William %R.
Divergence is a trading concept that works exceptionally well in some cases but fails to give the right indication sometimes. Thus, traders must follow every rule that is discussed in the previous article. We hope you found this course of Divergence trading informative and useful. Happy trading!