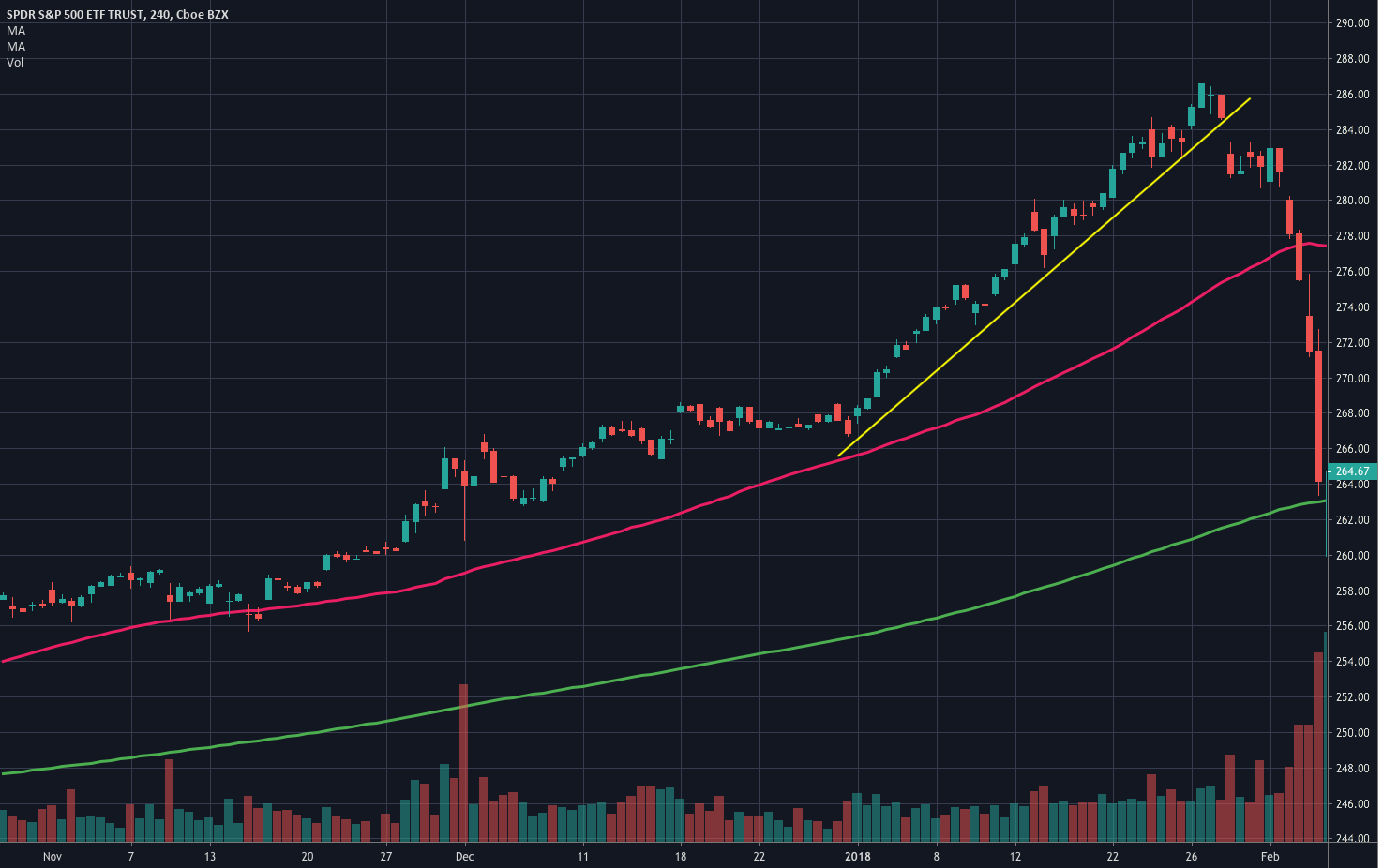
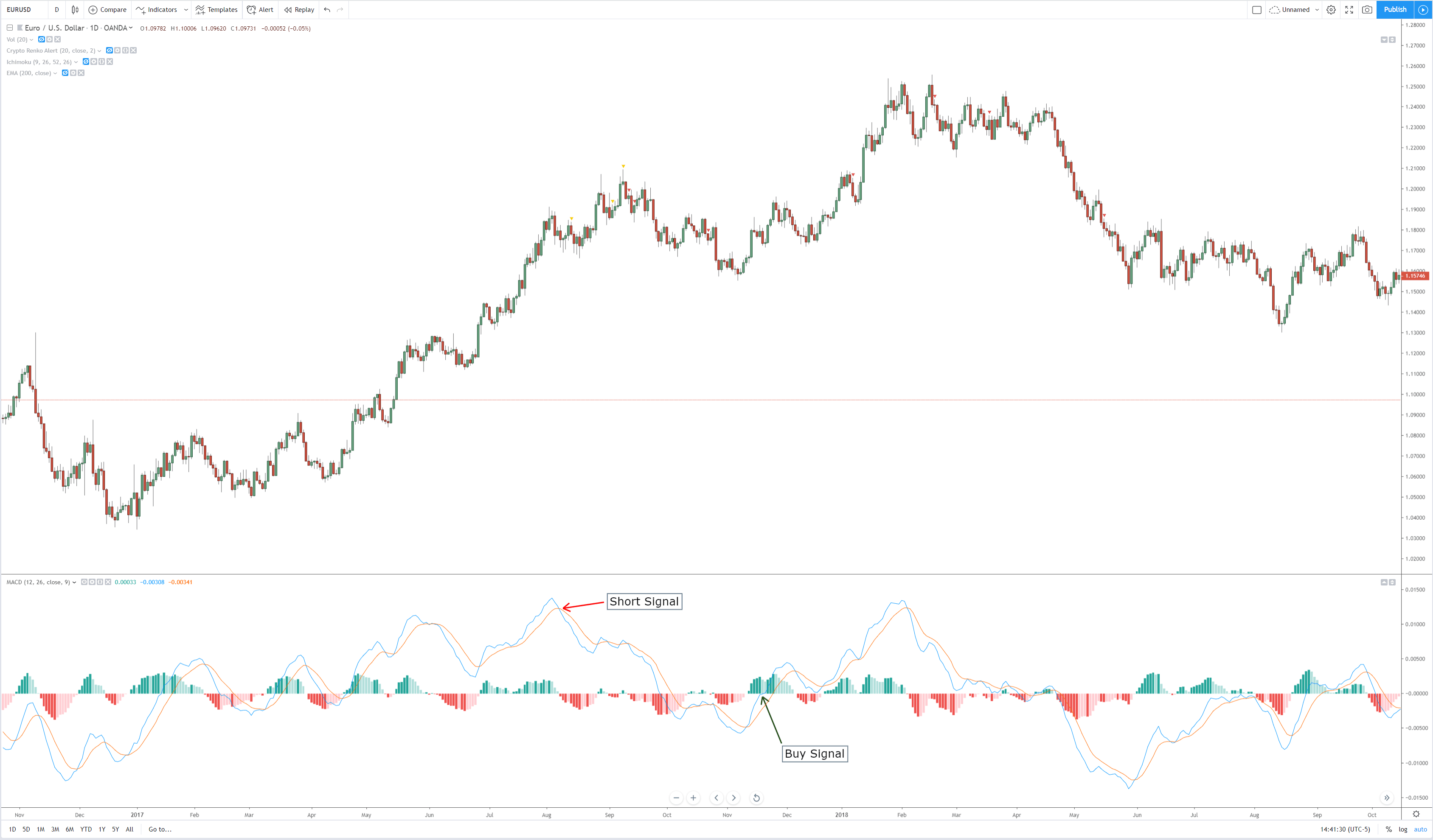
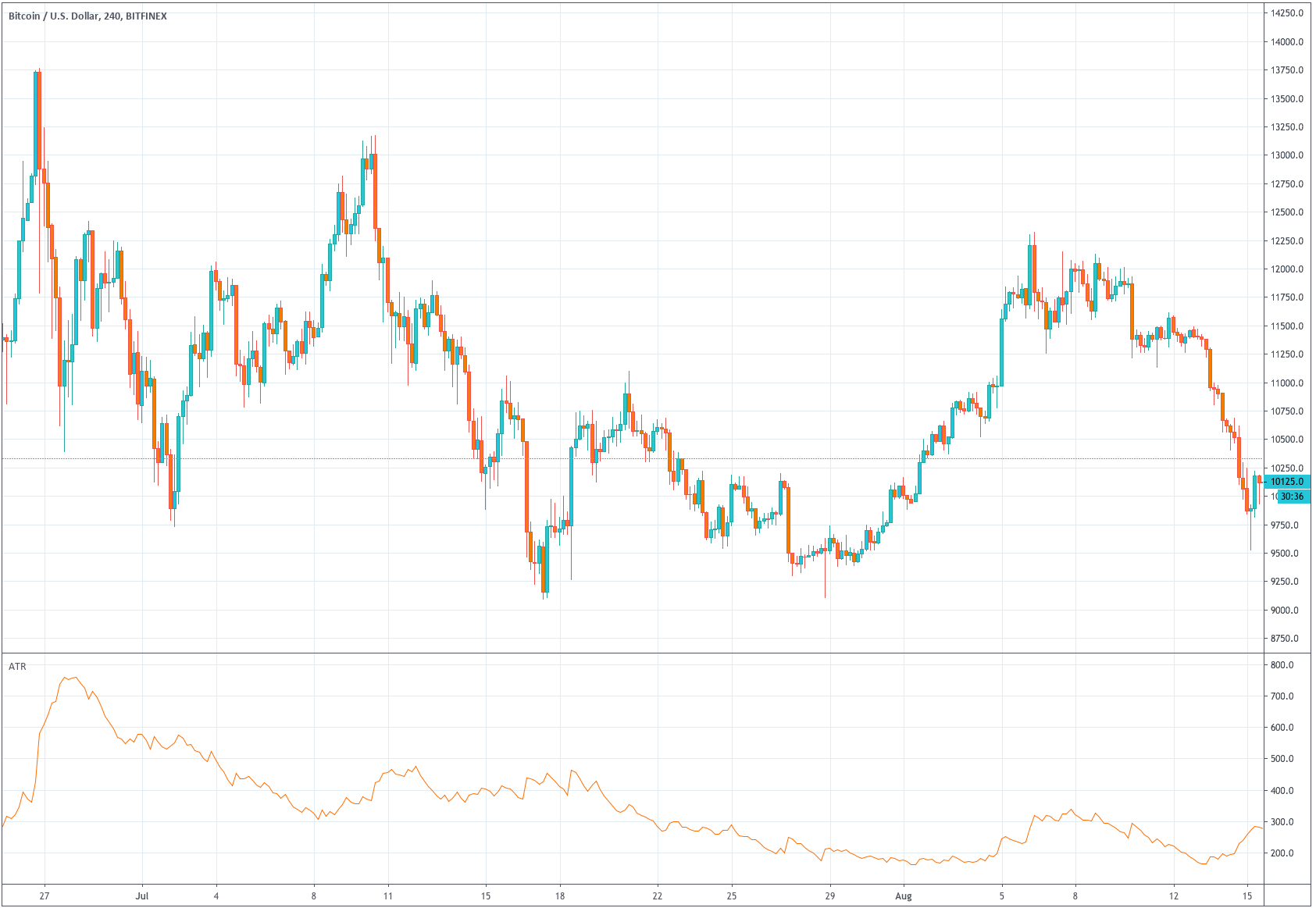
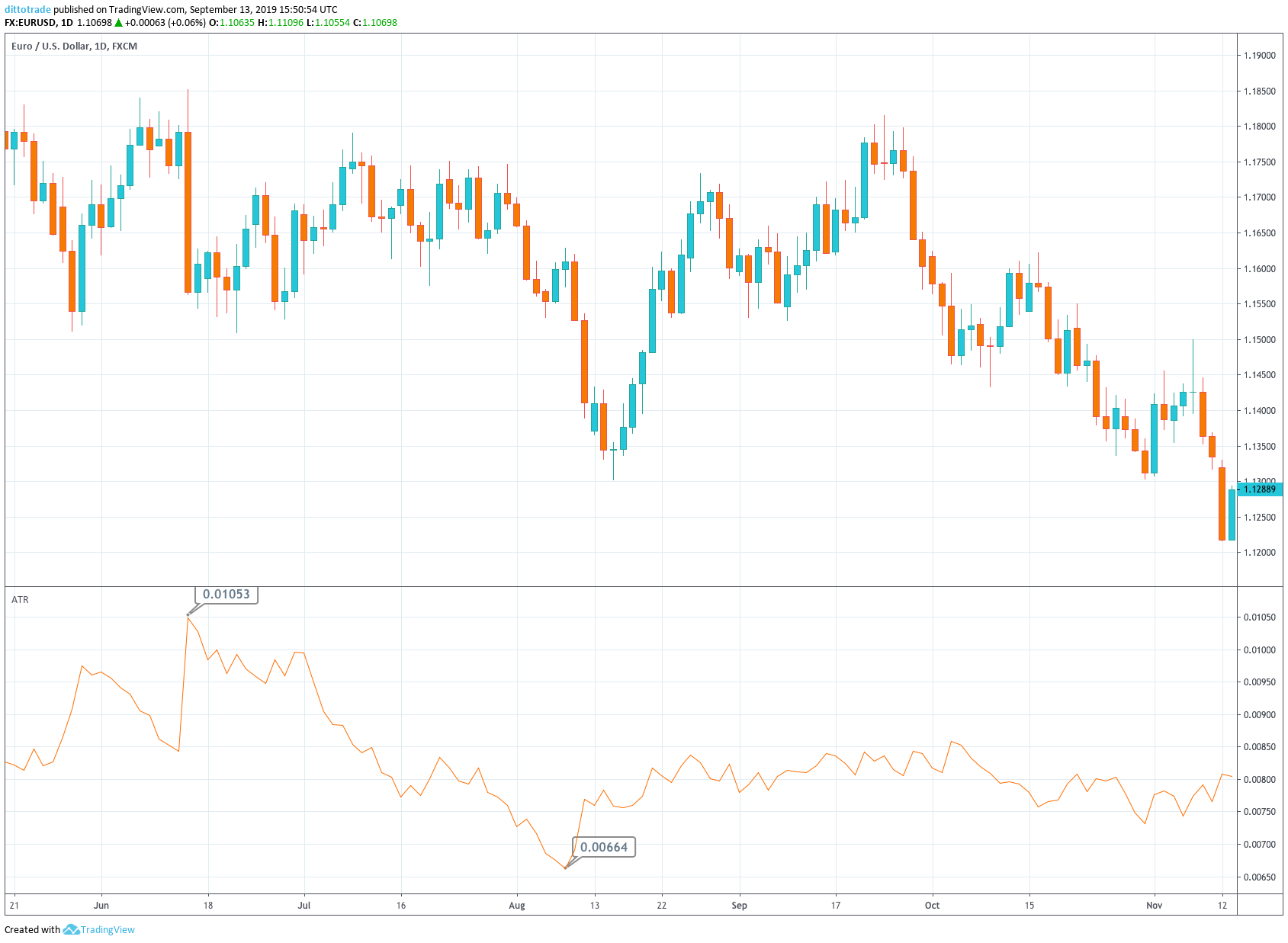
To evaluate, the quality of a strategy is an old quest, and its answer has to do with gambling theory, although it can apply to any process in which the probability of profits is less than 100%. Of course, the first measure to know if our system is winning is when the current portfolio balance is higher than in its initial state. But that does not give very much information.
A better way might be to record winners and losers, and have a count of both so that we could apply some stats. It would be interesting to know the percentage of winners we get and how much is won on average. That also applies to losers.
We could try to find out if our results are independent of each other or they are dependent.
Finally, we could devise a way to obtain its Mathematical expectancy, which would show how profitable the strategy is.
Outcomes and probability statements
No trader is able to know in advance the result of the next trade. However, we could estimate the probability of it to be positive.
A probability statement is a figure between zero and one specifying the odds of the event to happen. In simple terms,
Probability = odds+ / ( odds+ + odds – )
On a fair coin toss game: odds of heads (against, to one) = 1:1
probability Fair coin toss = 1/(1+1)
= 0.5
Probability of getting a Six on a dice:
odds = 5:1 – five against to one
Probability of a Six = 1/( 1+5) = 0.16666
We can also convert the probability into odds (against, to one) of occurring:
Odds = (1/ Probability) -1
As an example, let’s take the coin-toss game:
Odds of a head = 1/0.5 -1 = 2-1 =1:1
That is very handy. Suppose you have a system on which the probability of a winner is 66 percent. What are the odds of a loser?
System winners= 0.66 so -> System losers = 0.34
loser odds = 1/0.34 – 1 = 2 -> about 2:1.
That means, on average, there is one loser for every two winners, which means one loser every three trades.
Independent vs. Dependent processes
There are two categories of random processes: Independent and dependent.
A process is independent when the outcome of the previous events do not condition the odds of the coming one. For example, a coin toss or a dice throwing are independent processes. The result of the next event does not depend on previous outcomes.
A dependent process is one where the next outcome’s probability is affected by prior events. For example, Blackjack is a dependent process, because when cards are played, the rest of the deck his modified, so it modifies the odds of the next card being taken out.
This seems a tedious matter, but it has a lot of implications for trading. Bear with me.
What if we acknowledge our trades are independent from each other?
If we consider that our trades are independent, then we should be aware that the previous results do not affect the next trade, since there is no influence between each trade.
What if we know our system shows dependency?
If we know that our system’s results are dependent, we could make decisions on the position size directed to improve its profitability.
As an example, let’s suppose there is a very high probability that our system gets a winner after a loser, and also a loser after a winner. Then we could increase our trade size every time we get a loser, and, also, reduce or just paper-trade after a win.
Proving there is dependency on a strategy or system is very difficult to achieve. The best course of action is to assume there is none.
Assuming there is no dependency, then it is not right to modify the trade size after a loser such as martingale systems do since there is no way to know when the losing streak will end. Also, there is no use in trading different sizes after a winning or losing trade. We must split the decision-making process from trade-size decisions.
Mathematical expectancy
The mathematical expectancy is also known as the player’s edge. For events that have a unique outcome
ME = (1+A)*P-1
where P is the probability of winning, and A is the amount won.
If there are several amounts and probabilities then
ME = Sum ( Pi * Ai)
The last formula is suitable to be applied to analytical software or spreadsheet, but for an approximation of what a system can deliver, the first basic formula will be ok. Simply set
A = average profit and
P = percent winners.
As an example, let’s compute the mathematical expectancy of a system that produces 40% winners and wins 2x its risk.
ME = (1+2)*0.4 -1
ME = 3*0.4 -1
ME = 0.2
That means the system can produce 20 cents for every dollar risked on average on every trade.
Setting Profit Goals and Risk
Using this information, we can set profit goals. For instance, if we know the strategy delivers a mean of 3 trades every day – 60 monthly trades- The trader can expect, on average, to earn (60 * 0.2)R, or 12* R, being R his average risk.
If the trader set a goal of earning $6,000 monthly he can compute R easily
12*R = $6,000
R= $6000/12 = $500.
That means if the trader wants a monthly average of $6,000, he should risk $500 on every trade.
Final Words
On this article, we have seen the power of simple math statements, used to help us define the basic properties of our trading system, and then use these properties to assess the potential profitability of the strategy and, finally, create a simple plan with monthly dollar goals and its associated trade risk.