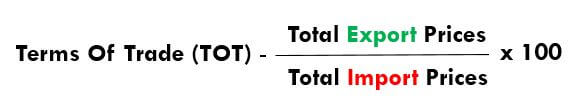
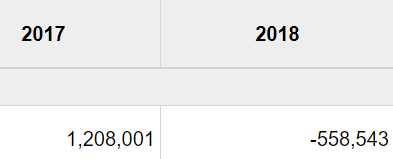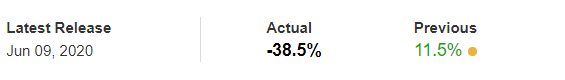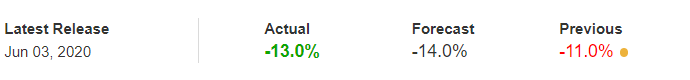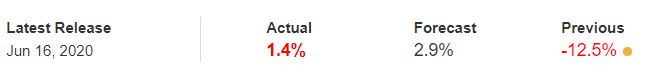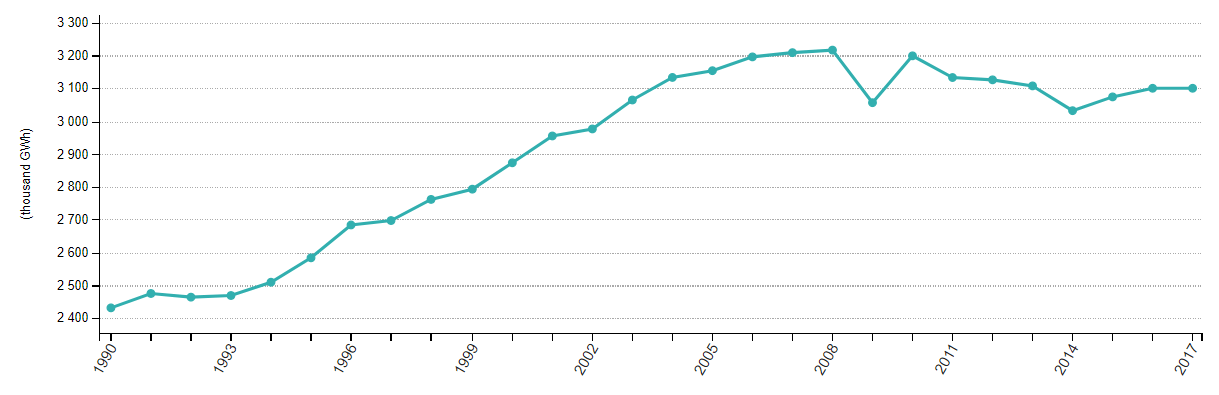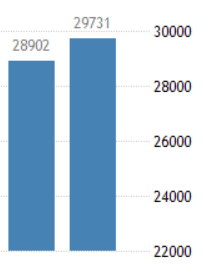Have you ever asked yourself what key factor has the power to substantially and irrevocably impact the trade of currencies? Many have tried to reach this answer and, at the same time, many have failed, dragging the weight of financial losses and blown accounts along. What makes a trader successful in the end? Are we to focus on the factors obstructing traders’ passages to growth or the ones facilitating the prospects of earning a profit? We now have access to countless sources offering volumes of educational material, but we still hurdle the same barriers that prevent us from becoming better traders. We have long learned about indicators, charts, and strategies, among other fundamental concepts introduced at the very beginning of our forex trading careers.
Unfortunately, most traders fail to grasp the one idea that has sparked so much controversy within the forex community by now that the focus on the results is often blurred and compromised by the traders’ specific sets of beliefs regarding what is right. The spot forex market enjoys a continuing influx of traders from a number of different markets, boldly attempting to tap into their previously acquired experience and knowledge and apply them onto the world of trading currencies. Combined with the less experienced traders’ rite of passage and poor choice of information sources, the overall failure rate is rather ominous. However, it appears that most losses increasingly deal with the topic of sentiment, which entails a wider set of believers and facts every trader must absolutely strive to understand. Due to the above-mentioned state of the market, it is high time that the debate over sentiment and its impact on traders’ success was dealt with once and for all.
Unlike any other market, the spot forex market is severely monitored and controlled by the big banks, such as Deutsche Bank, JP Morgan Chase, and HSBC, whose power to affect the market can turn a seemingly ideal plan into a bloodbath unless you understand how to approach this issue. While the big banks have the power to detect market activity, they cannot see your specific order. However, should you take the most popular market position, there is a high probability of undergoing some very painful financial losses. While we may not know the extent of tools the big banks’ use to maintain control and insight, every trader can also gather a vast pool of information on market activity by using the IG Client Sentiment Indicator (https://www.dailyfx.com/sentiment) or FXCM SSI (https://twitter.com/fxcm_marketdata?lang=en), which are charts showing where the focus of attention is. Moreover, owing to these two sources, we can tell whether traders are going long or short along with where the price went in the end. Interestingly enough, apart from sharing the same information regarding where the price is going, both banks and traders have a common goal – profit.
So, if you were to ask yourself what action they would take if they noticed great concentration in a specific area of the chart, what do you believe your answer would be? If you imagine that all traders decided to move net long on EUR, what would the big banks do: a) keep EUR long for an extended period of time, bestowing all traders with a nice financial reward; b) immediately take the currency’s price short, forcing the majority to exit their long trades at a loss; or, c) maintain EUR as it is, lure the traders going long even further only to “unexpectedly” take the currency short? Most traders get trapped because the banks will almost always choose the second or the third option and will do that repeatedly and consistently. The moment where most traders get confused is believing that they can outsmart the system, still not recognizing what needs to be done when the banks change the price from long to short here, so they keep dragging themselves deeper and deeper in the mud.
Now that we can see how reliance on sentiment plays out in the field, we need to address the right approach to surpassing this obstacle. First of all, whenever there is a high concentration of activity in one part of the chart, this should be a clear signal for every trader to start feeling alarmed. At this point, we need to forget the human tendency to conform and practice the contrarian approach. What this implies is that each trader should strive to recognize to which direction the majority is heading and refrain from following the mass. The basis of this attitude is neither disobedience nor rebellion, but the understanding that we have two distinctly different methods of trading in this $3—6 trillion market – the right and the wrong way. If all those traders spiraling out of control placed patience, money management, and trading psychology before relying on the wrong sources, the big banks’ impact would certainly not be as negative a factor as it is in these cases. If the big banks ever disappeared, there is a great chance that the nature of this market would entirely change, possibly even becoming similar to the stock market. It is important that traders stop feeling angry about their losses and start taking advantage of the existence of the big banks.
This further entails that concentrating on notions such as order books, expiration dates, etc. is entirely redundant for trading currencies. We may never exactly know how the big banks manage the spot forex market, but what we can do is acknowledge the phenomenon which occurs repetitively and decide what to do about it. It is high time traders stopped wondering why or how things happen and started to ponder what they can do individually to measure control in their own trading. We can accept the inevitability of outside influences, but, at the same time, we should use the information we can gather, notice similarities, and feel comfortable making difficult choices.
When we think about the core of the forex market, we cannot assume the existence of qualitative sameness, where trading currencies, stocks, or commodities are considered to be indistinguishable. In contrast to what some sources may say, terms such as supply and demand, herd mentality, buy low/sell high, and more have no impact on the quality of trading currencies and are, thus, potentially dangerous because of the increased probability of missing the point. The spot forex market essentially revolves around the need to think about the reasons why a particular price moves in a specific direction. Traders’ main task is not to apply a set list of tactics incorporated from other markets, but make sure that they stay off the banks’ radar as successfully as possible. By becoming part of the minority, you will increase wins and decrease losses – which the majority of traders running after reversals, for example, may never experience.
The majority of traders also use common and outdated tools (e.g. Japanese Candlesticks) which offer information visible to everyone, pushing large numbers of traders to react to the same signals and thus immediately drawing the attention of the big banks. What is more, even the choice of currencies can have an effect on the future of a trade. For example, USD is always in demand, making the pairs involving this currency always on the banks’ radar to a greater degree than in other cases, which is why caution is advised especially for beginners. Traders can early on also feel threatened by the news involving regulatory bodies taking action to limit traders’ freedom. Do not get frightened because you see some exorbitant amounts they charge in the media, because once broken down per trader, these amounts approximately turn out to be a day’s work. Overall, do not get distracted by methods which are inapplicable in trading currencies or news for that matter because what you never want to do is be the line moving in a completely opposite direction from where the money is going in the chart.
To become more knowledgeable about the impact of sentiment on trading in the spot market, you should consider exploring the IG Client Sentiment Index for education purposes. The tool has proved to be less useful when the price is consolidating, but the opportunity to see the overall movement will serve as an invaluable lesson. Detecting whether traders are going long or short and where the price is actually going will almost always show you that the currency will more often than not go in the opposite direction, serving as an obvious confirmation of why going with the majority is never a good idea. Unlike with the USD-based pairs where such phenomenon frequently occurs, other currencies may vary in the degree of susceptibility to the big banks’ involvement simply because the number of individuals trading these other currencies is lower.
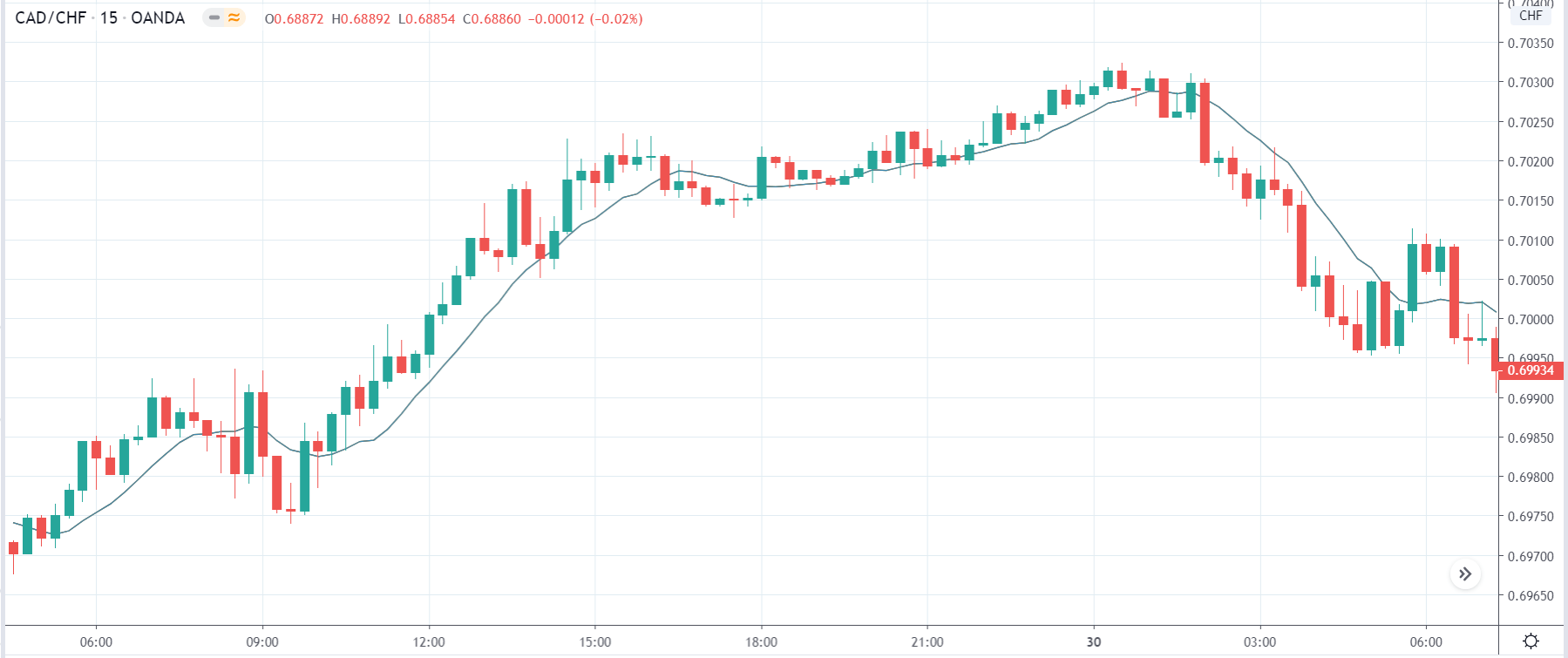
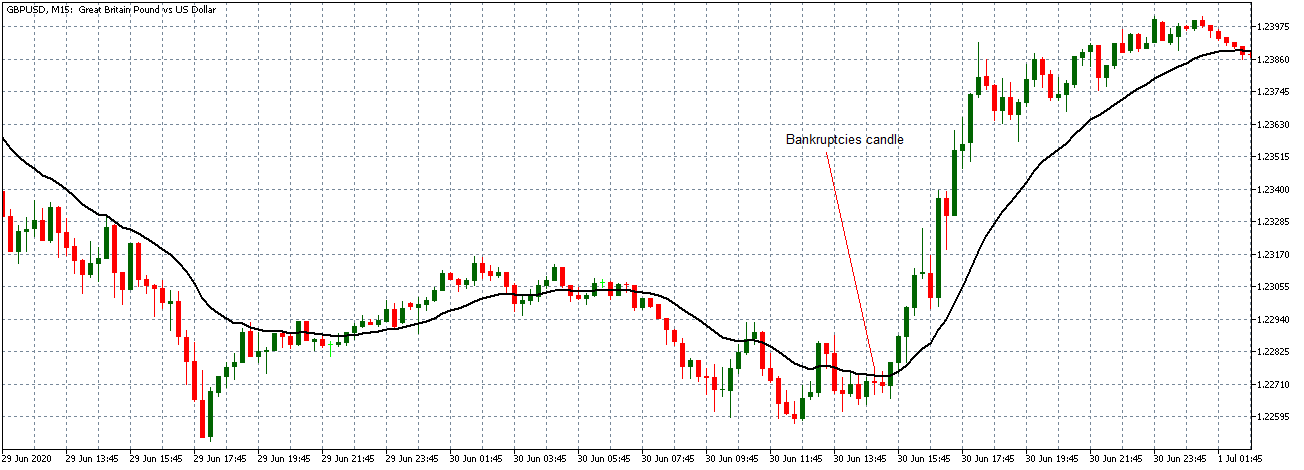
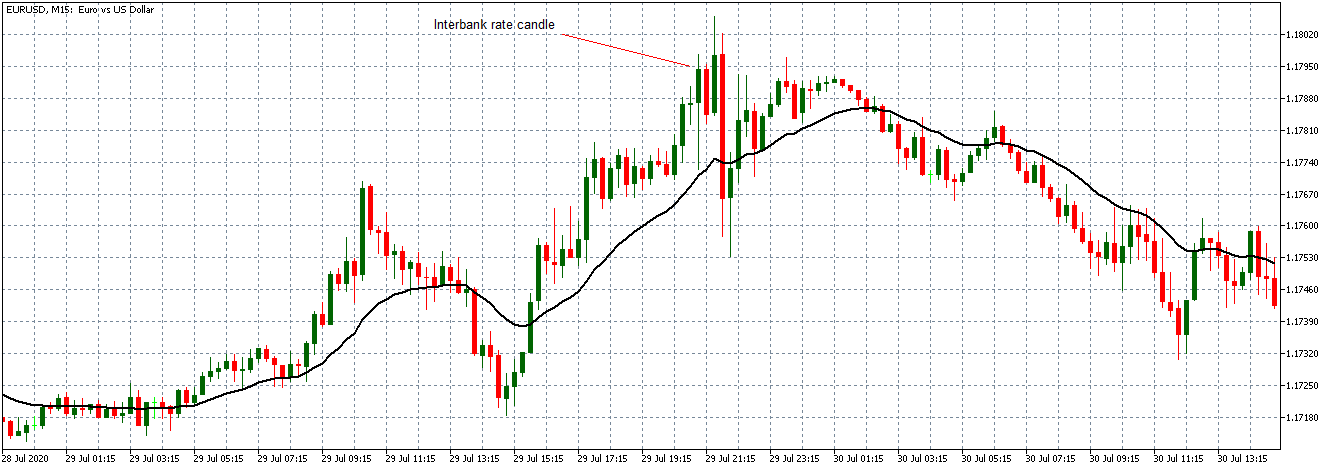
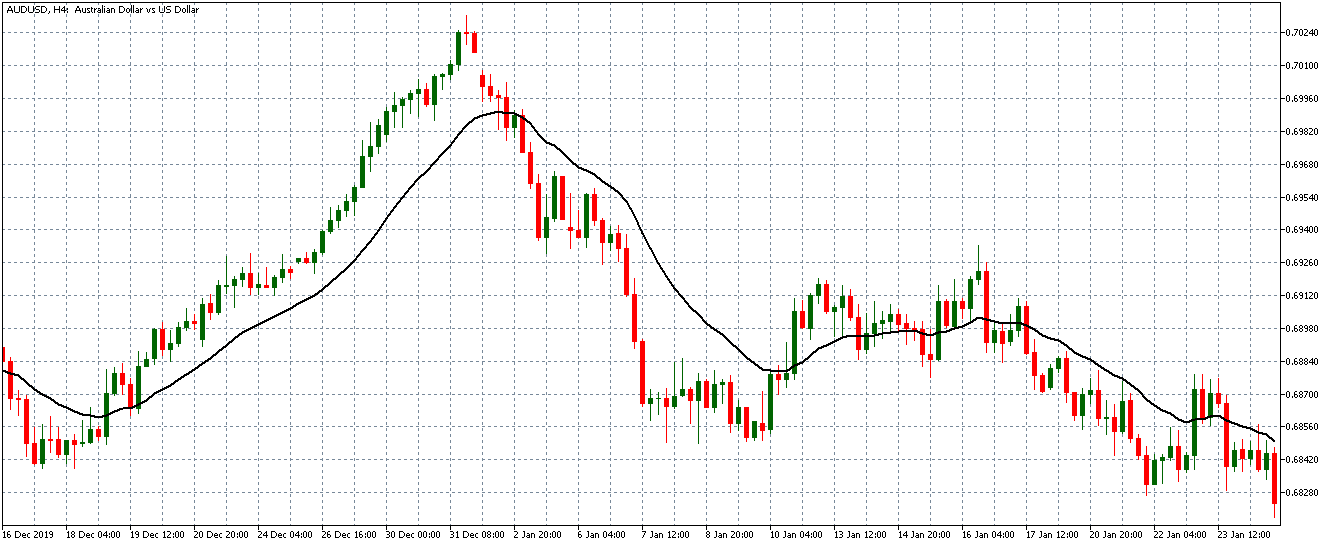
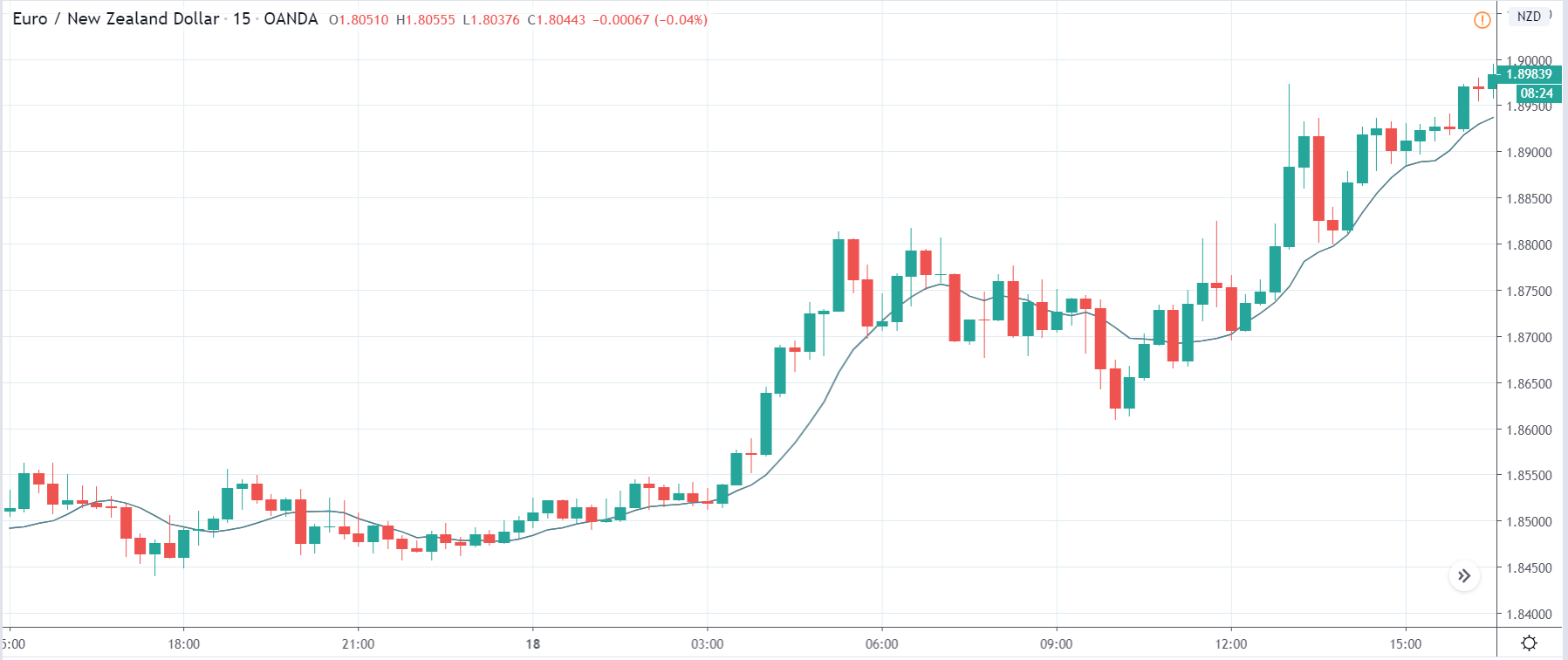
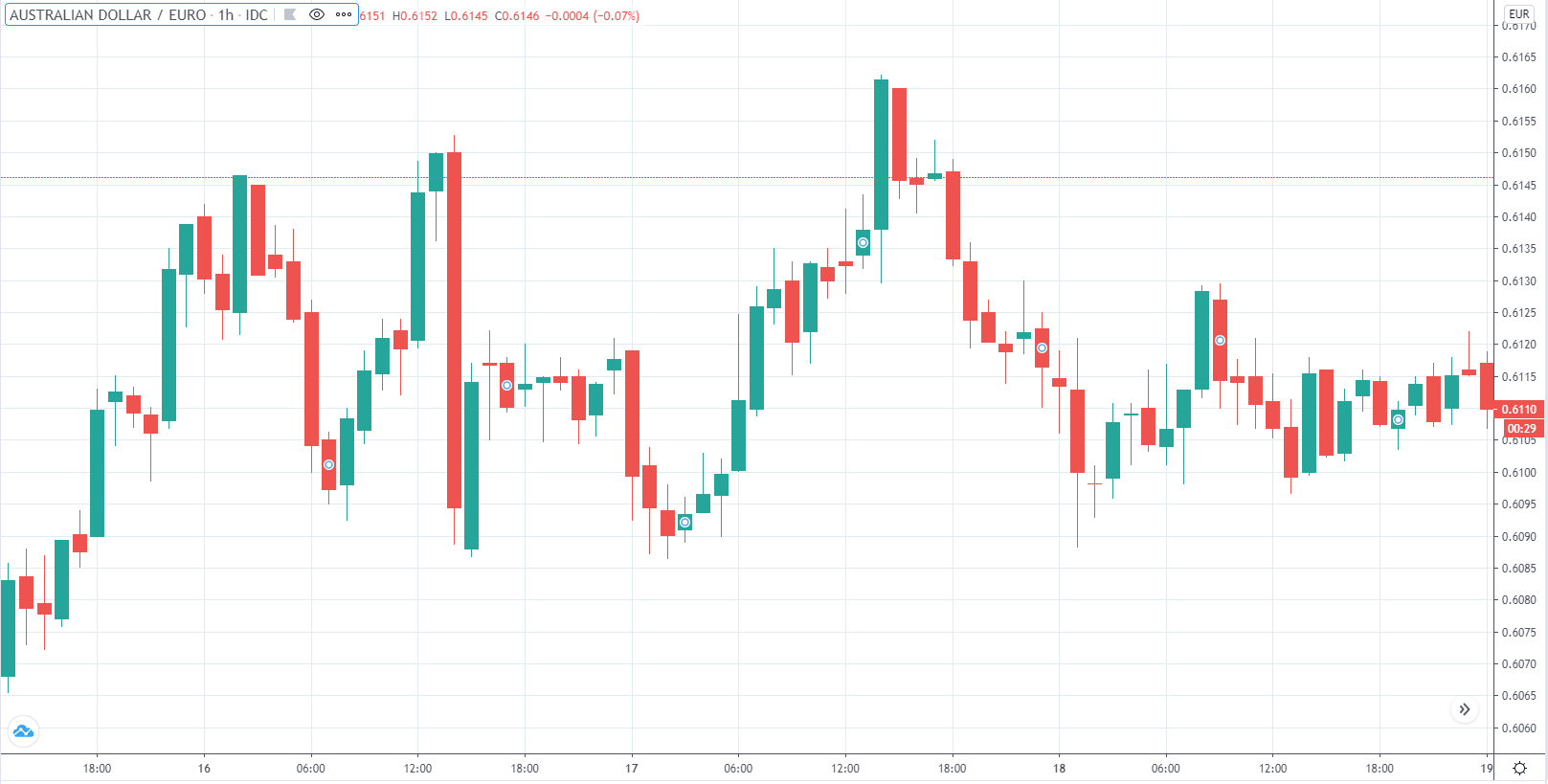
The first image below, for example, successfully captures how the individuals trading on the EUR/USD currency pair behave, transparently documenting this common occurrence. As you can see at the beginning of the chart, each time traders are impatiently moving from net short to net long, the price will almost always start moving towards the opposite direction. The chart further shows how traders at one point changed their minds for a short while, causing the price to react. Then they decided to go long, after which the price started going short and the two lines once again crossed paths going into entirely opposite directions. The same coordinated behavior is present everywhere in the chart, which should serve as an indication of the need to take a different approach.
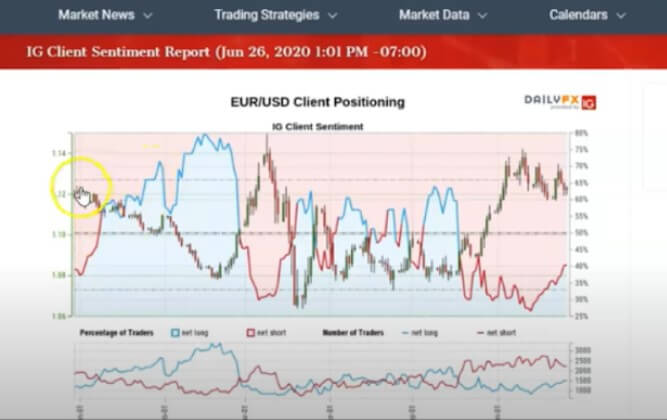
Sentiment, as we already explained above, is not equally applicable to all currencies. If you are interested in a currency pair which does not involve USD, such as EUR/GBP, you would then need to look for the combination of information you can gather from both the EUR/USD and GBP/USD currency pairs, focusing on where most traders are in these charts. Likewise, client sentiment may be applicable to some markets, such as the spot forex market, but there are certain exceptions. For example, precious metals rarely exhibit any correlation in this regard. If you are trading spot gold against USD, for instance, you should know that the banks certainly have control over the currency, but they have practically no dominance over gold. In this case, it is the price of gold that has a say and determines what will happen to that pair. Therefore, banks cannot truly manipulate the prices the way they would normally do in each and every case.
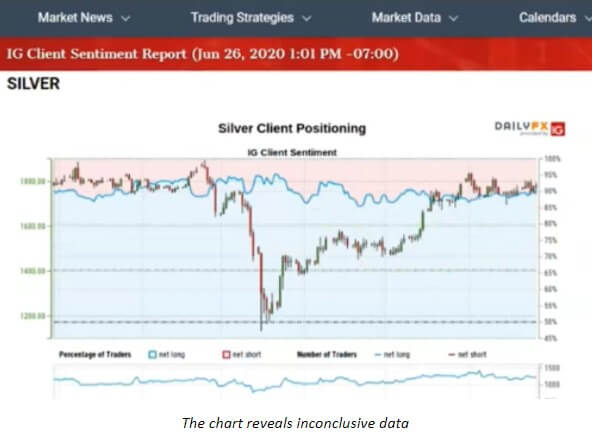
The involvement of banks becomes even more questionable when we observe some other trades, such as the one involving silver, as shown below. In terms of the stock market, we can find no evidence of sentiment influencing individuals stocks; however, certain indices prove not to be impervious to this phenomenon. While the IG Client Sentiment is practically the most heavily traded index we know, you may still use some smaller versions such as the CAC or the XETRA DAX. Despite the fact that the information will probably not be the same quality as with the most popular sentiment index, you will still be able to find some useful data. Most importantly, even with these less versatile indices, you can generally obtain the information on where the majority of people are unless you are looking into precious metals or crypto markets where you will find no correlation, further raising the question of why such data is even provided on these platforms. Unfortunately, such terrible fundamental mistakes keep happening, but it appears that the vast number of these traders choose not to open their eyes, thus giving the big banks the opportunity to cream off the profit so easily.
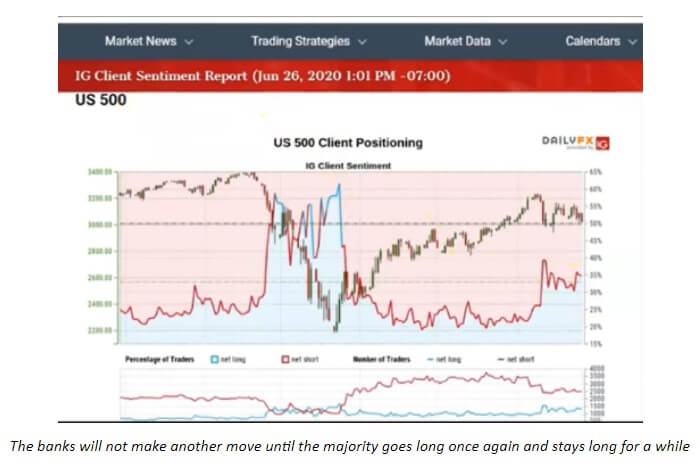
Traders must become aware of another essential difference regarding their approach to sentiment. As it appears, many traders keep falling for the same trap, believing that the only important matter in getting off the big banks’ radar is knowing the direction where everyone is heading to and opting to go the opposite way. What is more, they typically wait for the lines to cross or colors to change to make their move, using the IG Client Sentiment as a trend confirmation indicator. Unfortunately, no matter which pair you may choose to trade, using the IG Client Sentiment as a trend confirmation indicator will probably not give you the result you are looking for. Even if you put effort into finding ways how to use this tool more effectively, testing out every possible option, you should know that the knowledge about where the majority of traders are at a certain point in the chart is not the type of information you should be focusing on.
What is truly relevant is the insight into where these individuals are going, and where the mass is headed is where you will see the most appalling scenarios. You could most definitely benefit even more from some other indicators, which could be of more assistance to your trades. However, be mindful of the fact that even if you get a signal to go where the majority is at a particular moment, you should not feel worried. If the majority of traders are going long and your signal is telling you to go long as well, do not give in to the fear, but rest assured knowing that the concentration of traders in one place is not truly what you should be concerned about, but the direction they are taking. If you are wearing yourself down, distrusting the indicators you chose to serve you in your trading, you will very likely miss out on some extremely good opportunities. The best solution to this challenge is building your own algorithm and learning to trust that system.
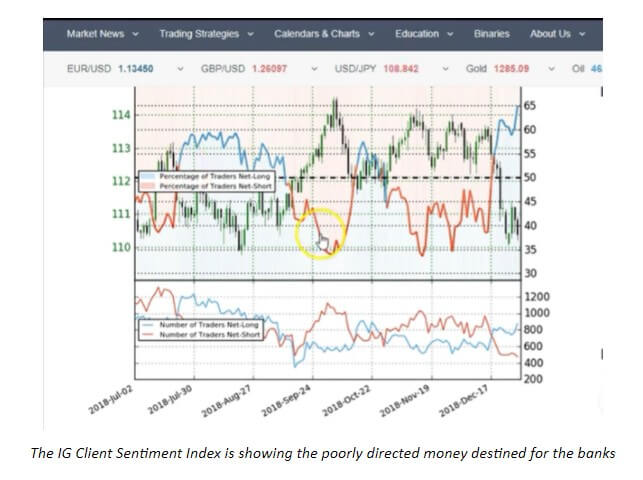
A lot of sources discuss what constitutes the very essence of trading in the spot forex market. Especially for beginners, the access to sources attaching the same value to sentiment as to technical analysis and fundamental analysis can be utterly detrimental. This, however, does not undermine the impact of sentiment nor does it strive to prove how sentiment is unimportant, being the key driver in this market with the ability to move prices towards specific directions. The biggest problem traders have in dealing with sentiments is the fact there is little we can do about it. Chasing sentiments is simply equal to trying to predict the whims of people hungry for success. We cannot control people’s emotions or use them to foresee where millions of traders are going to go because it is an attempt to control the uncontrollable.
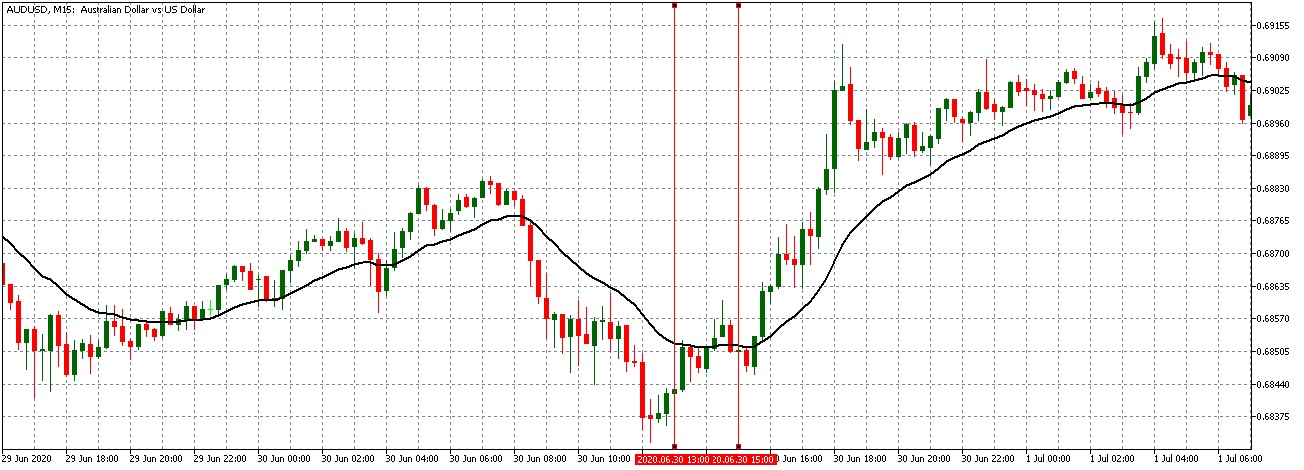
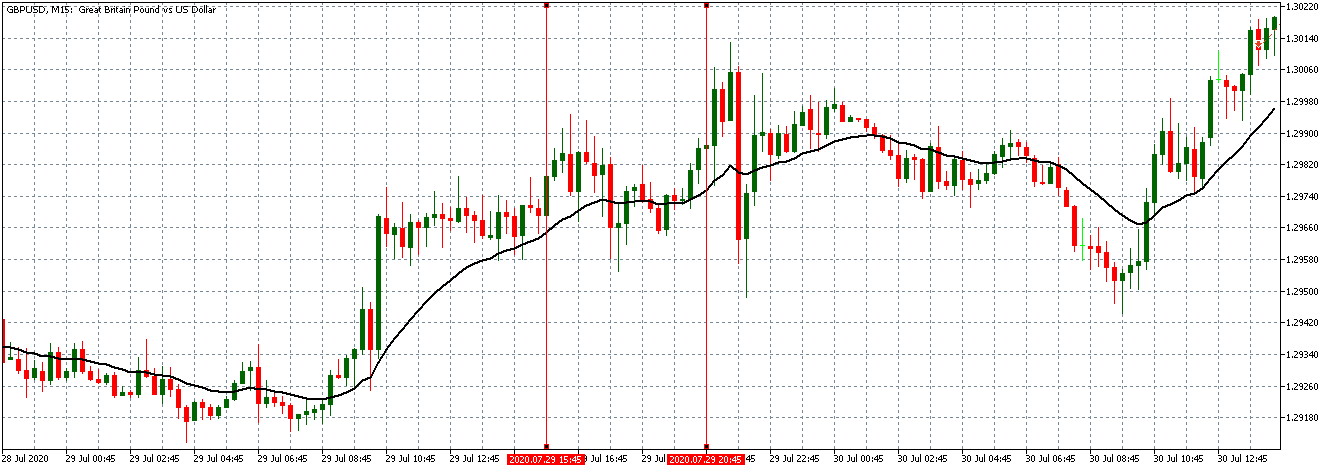
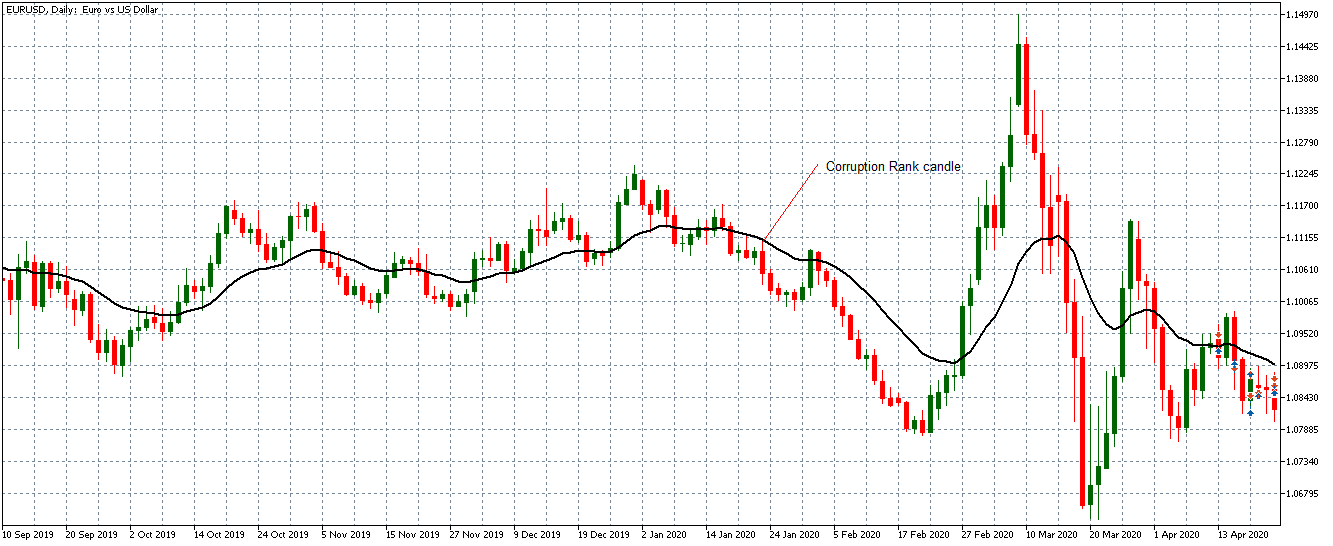
Since the greatest portion of traders keeps chasing the sentiment, your task is to do exactly the opposite. By eliminating sentiment from the equation, you will save yourself from facing scenarios such as the one in the image below. Not all places in this chart indicate the exact phenomenon we discussed today, but from the middle towards the right end, we see several places where most traders made one big move only to see the money go in the opposite direction. Nonetheless, the belief that just because millions of traders are going long at a specific time, we should go short is also an example of a short-sighted approach. We may not have control over people’s sentiments, but we can most definitely strive to learn about indicators, testing different tools, and working towards setting up our own algorithm.
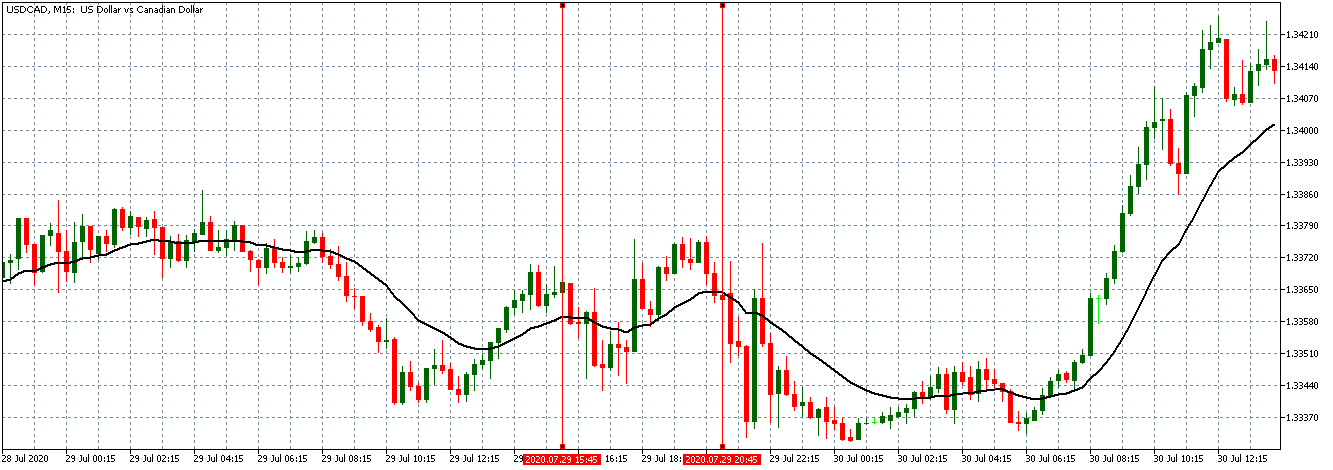
Such knowledge could have helped traders who got caught up in the situation shown in the chart below because just by refocusing on the two lines where the white pointer is, they could have caught the big move and salvaged their trade. In addition to building up knowledge on trading and indicators, traders must bear in mind that indicators are result-oriented tools which are not truly meant to predict the future. Considering the fact that news inevitably gets in the way at some point (e.g. what the past year’s flash crash did to indicators), traders need to adopt skills that can raise them above the level of sentiments and provide some stability in this seemingly unpredictable market.
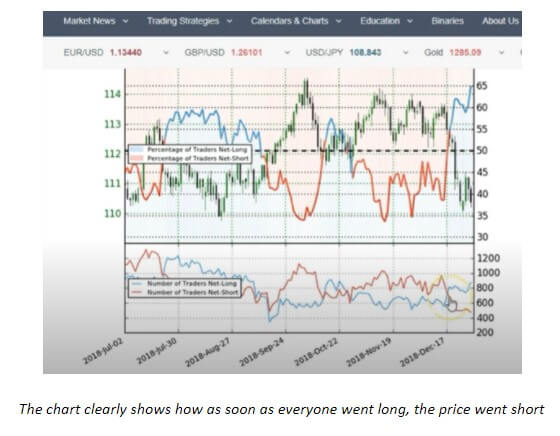
If you still believe that you can yield the power of sentiments, although generally not advisable, there is one method in which you can attempt to do it. Before using IG Client Sentiment, traders relied on the SSI indicator developed by FXCM, an ex-U.S. company that, unlike now, used to have more presence on MT4. Despite the fact that it does not make its applications available for U.S. customers, FXCM does have extremely useful products showing sentiment that you include in your chart. They also have their own proprietary trading software done in a different code, which you might still be able to use if you can transpose indicators from one language to another. If this is not the case, you may still find an easier solution by following FXCM Market Data on Twitter, which will offer a window into the actual SSI Indicator even if you do not have access to it.
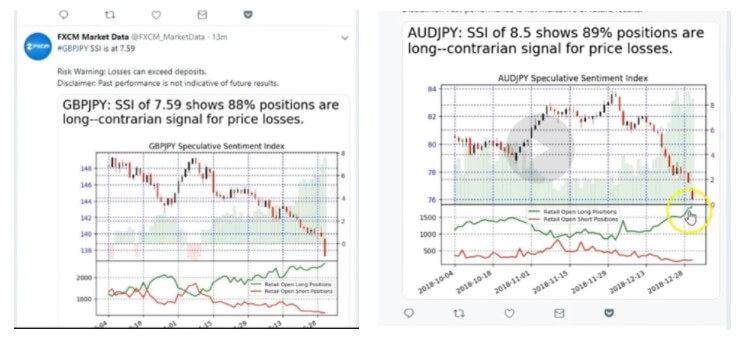
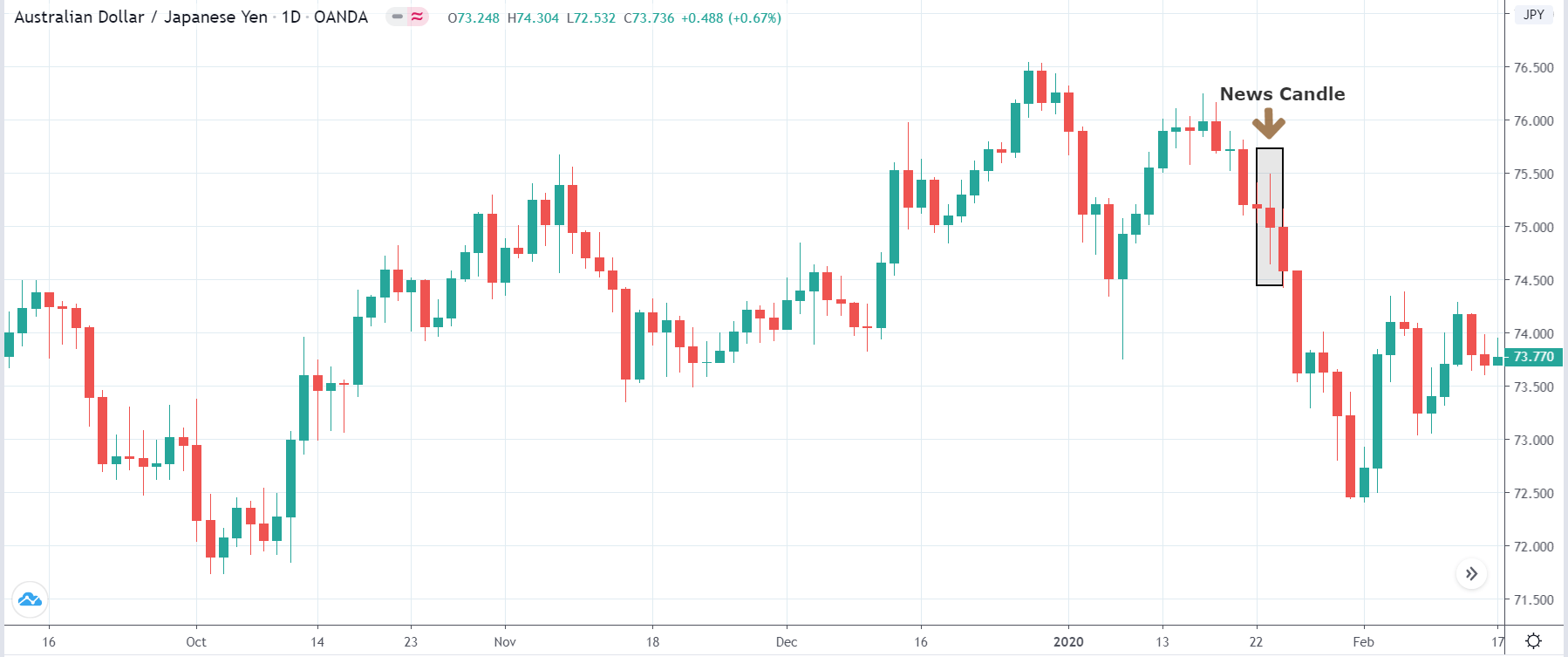
Some of the benefits it provides include the GBP/JPY pair which we cannot find on IG Client Sentiment. This particular twitter feed is excellent at showing you charts that are relevant at that point in time. For example, the cropped image on the left below shows a chart revealing some unexpected activity, which tells us that there is a slight chance that the sentiment is about to reverse. Quite similarly, the AUD/JPY chart next to it with the yellow pointer indicates the crucial moment where any trader trying to catch a reversal would severely endanger their trading accounts and financial stability. Therefore, we must be particularly careful with this tool, whose greatest contribution to the forex community is the ability to use it as a reflection tool. Attempting to use it for prediction purposes, hoping to discover where the price might go, would require the understanding that a set-up algorithm would tell you much better where to go and what to do.
Overall, predicting the whims and the sentiments of millions of traders around the world has never been a good idea, and you must be extremely cautious when dealing with this topic so as not to end up where the majority does. Should you ever notice any extremes with regard to sentiments on the pair you are trading at the time, you are advised to stop and exit the trade. A great example of a situation where closing up was necessary was the 2019 flash crash, when the ratio between short and long traders on the USD/CAD currency pair was 4:1 (i.e. 80% short) because of which we could safely conclude that the price could not have gone much higher. Some experts who traded on this currency pair at the time state that they relied on their experience, leaving the trade just before their indicator was about to exit the trade itself. Nonetheless, until you are certain that you have enough knowledge, the right mindset, and necessary experience, do not let yourself get carried away, potentially endangering not just one trade but your entire forex trading career.
We could not stress enough how volatile relying on sentiments is, but if you really must proceed on such a trade in that manner, make sure that you use all the available resources. Twitter, for example, is a tremendous source of information, and taking notes is an excellent way to both memorize quickly and keep important data in one place. You can explore updates about IG Client Sentiment Index on DailyFXTeam, learn about additional SSI currency pairs on FXCM_MarketData, or discover some invaluable educational materials and market comments on This_IS_VP4X. If you are intent on growing as a forex trader, aim to include technical indicators, money management, and trade psychology into trading, which will essentially help you put a system together that will bring you money in the long run. What most traders, whom you could see in the charts added in this article, did was miss out on invaluable opportunities because they never put any effort into building a proper system.
Once you develop trading skills and reach the professional level, you may not need to use your own money to trade any longer because you will surely be noticed by different companies that will want to invest in you. Before that happens, you should start acknowledging the role of the big banks in this market and, if needed, let go of all strategies used previously in some other markets. Even though the phenomenon we analyzed today does not frequently happen in the precious metals or crypto markets, making use of techniques and indicators specific for the spot forex market will alleviate the external impact and safeguard you from any market instability. Moreover, understand that with forex, there are no shortcuts and that you have set yourself up for a long road of learning and growing.
Luckily, today’s article equipped you with the knowledge some individuals who have been trading for more than five years still do not know. You should now be able to avoid areas in charts that are open to manipulation and preserve your finances, which will be further fortified by not trading reversals or using the same common tools as every other trader does. Finally remember that your only chance to succeed is by getting out of the pool of traders who focus on the sentiments, as it is key in differentiating between emotion-driven and indicator-driven individuals. Building a currency trading career based on emotions, bereft of any technical skills, is not a long-term strategy, and if you are passionate about trading in the spot forex market, eliminating sentiments and devising an algorithm will get you right from where you are to being a professional trader.






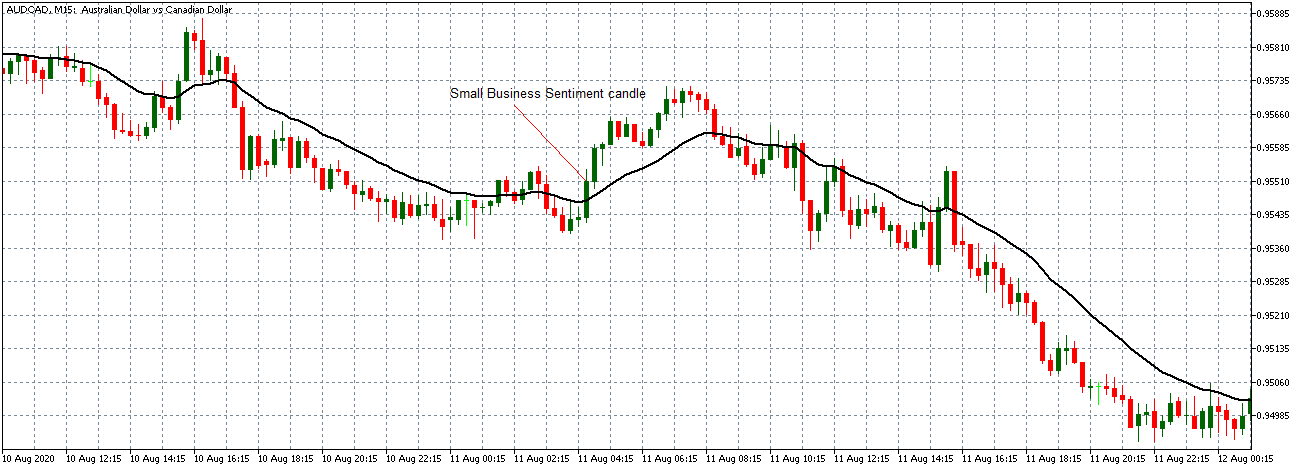

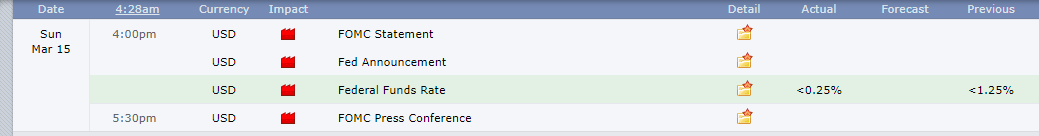
















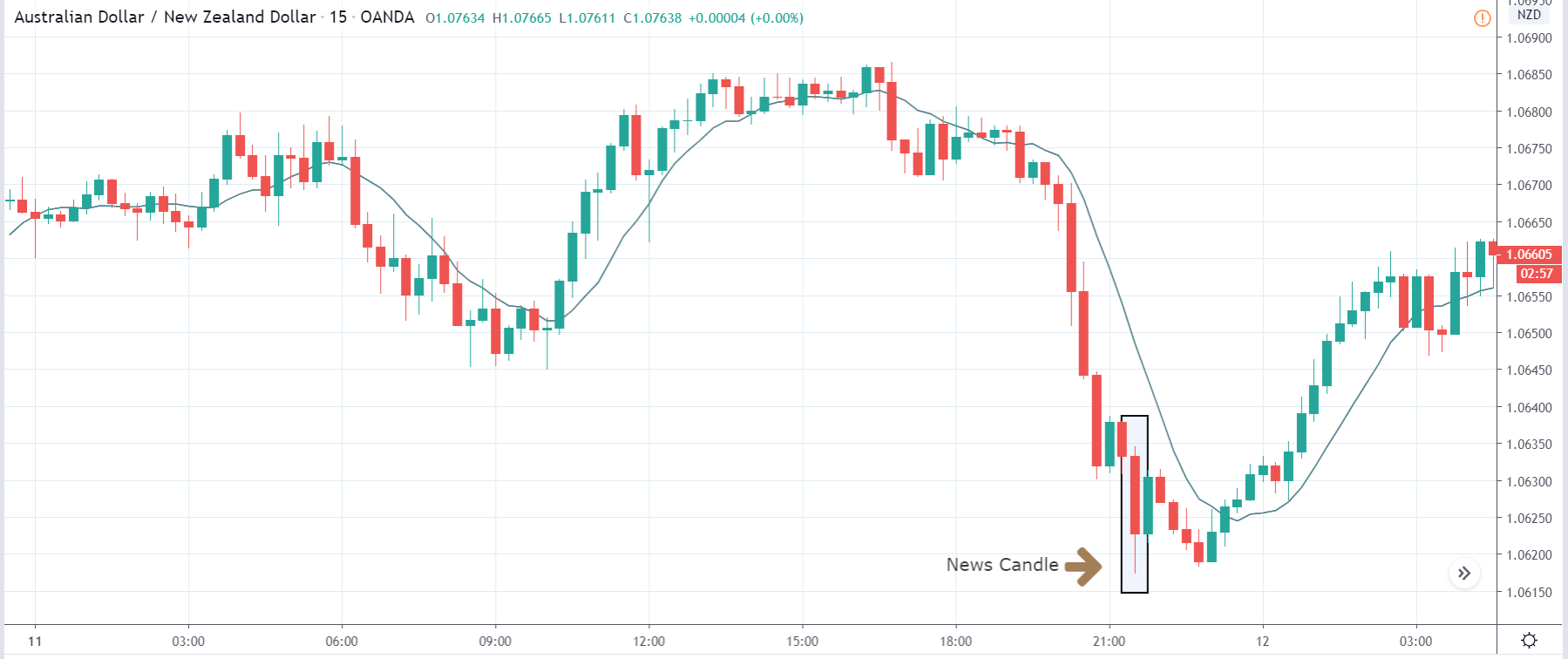
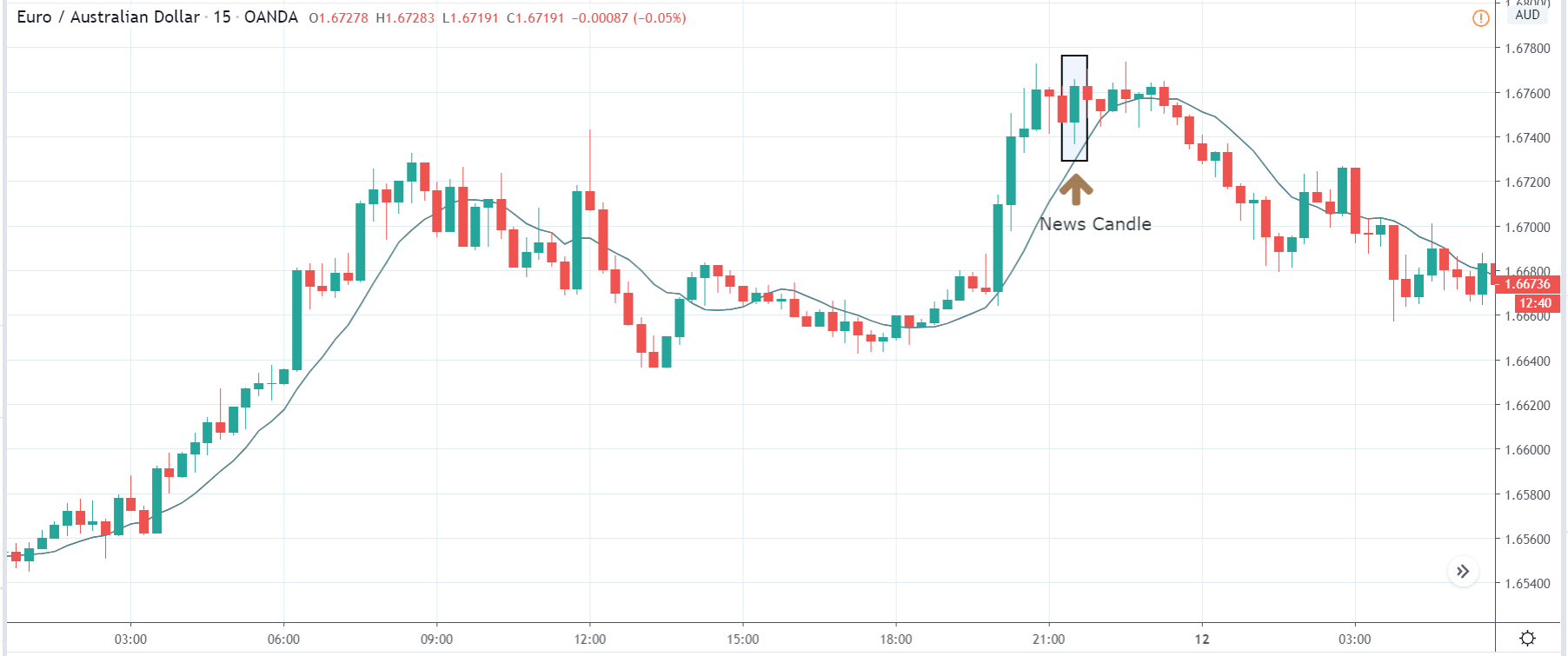




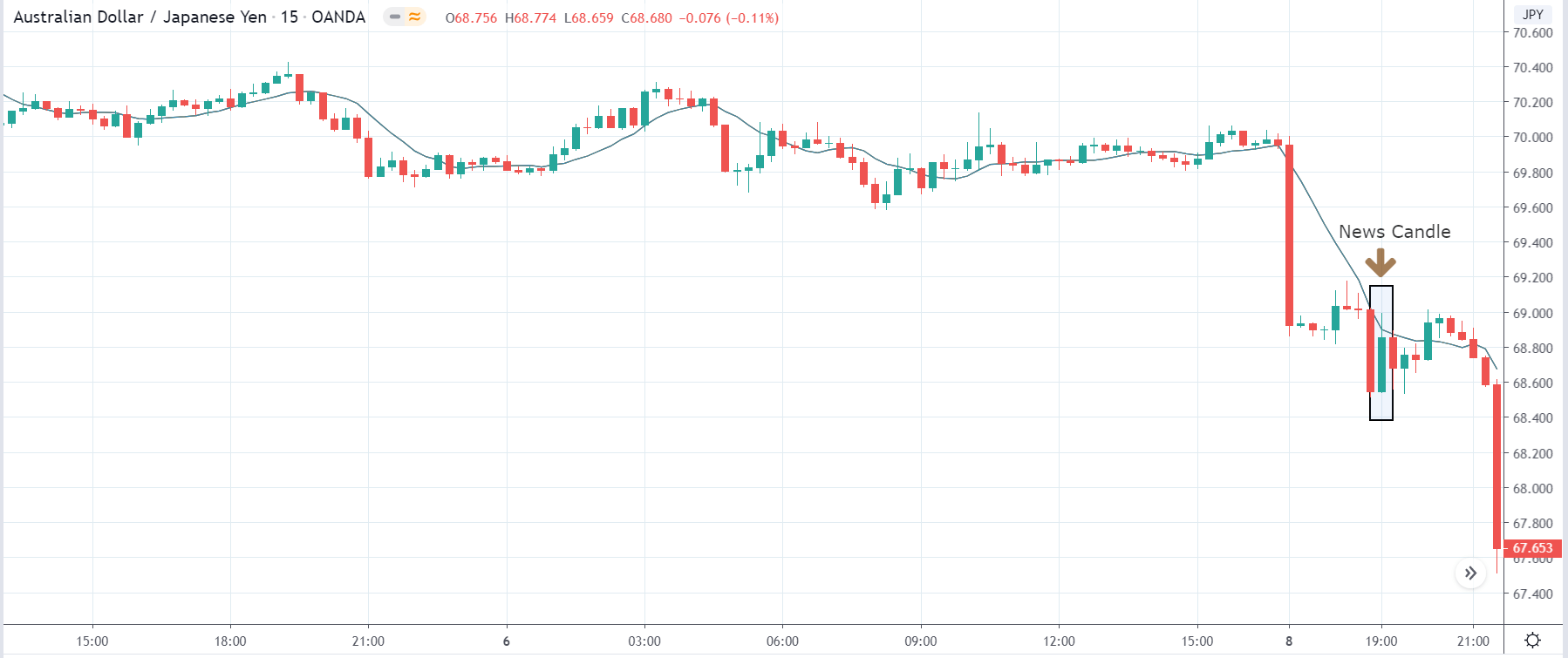
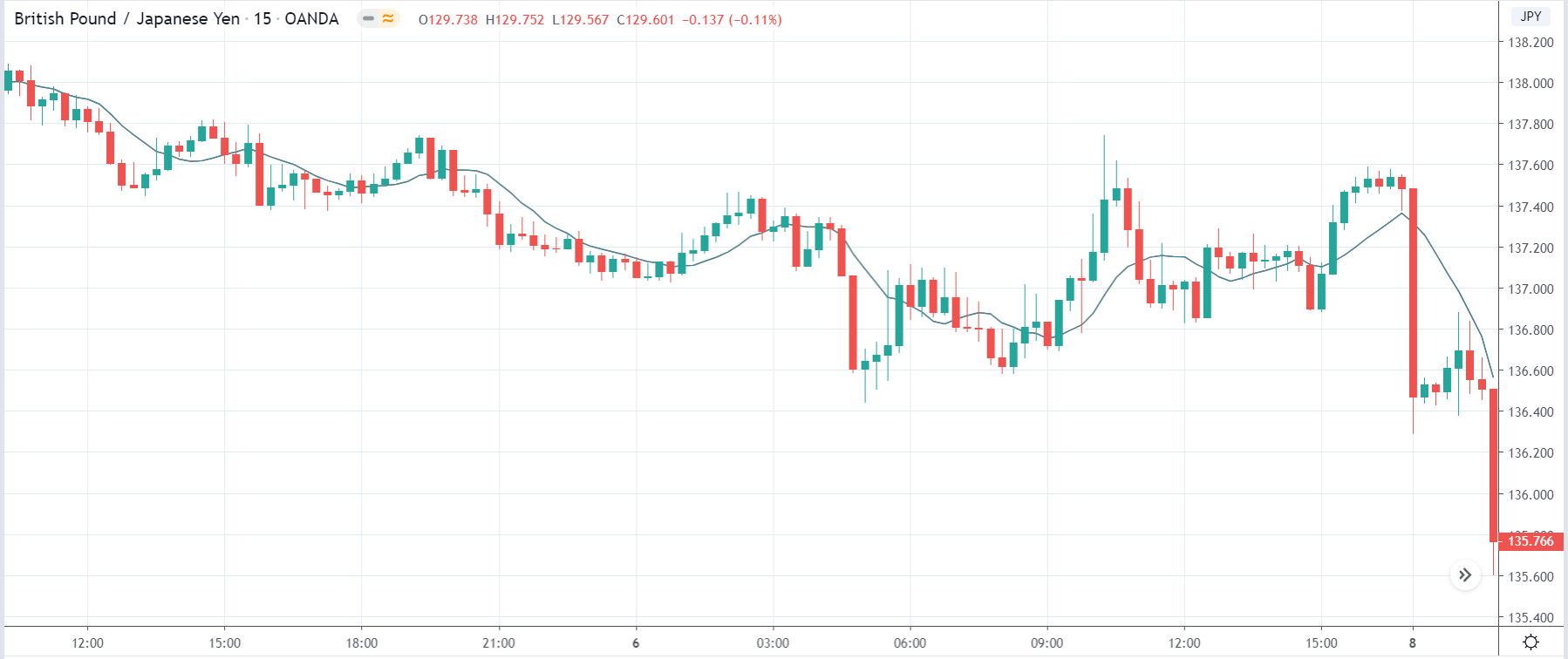
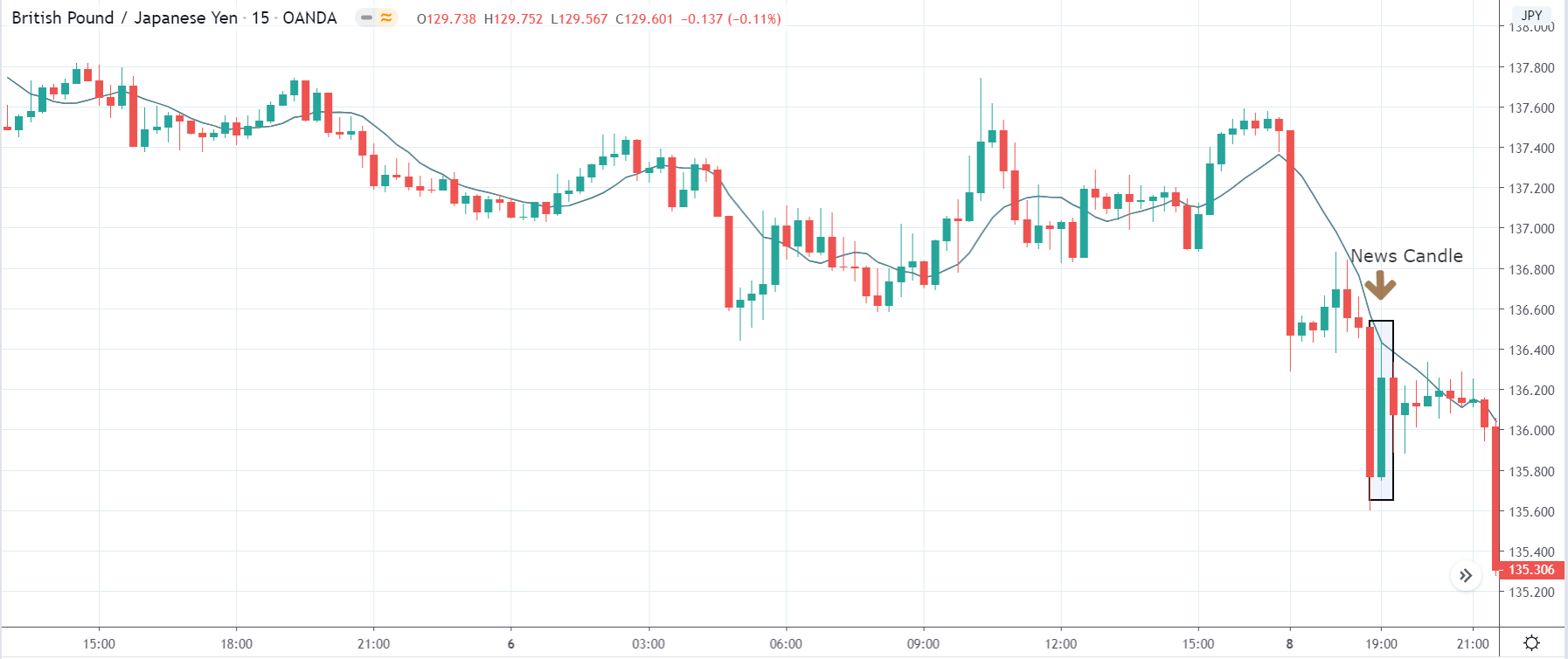
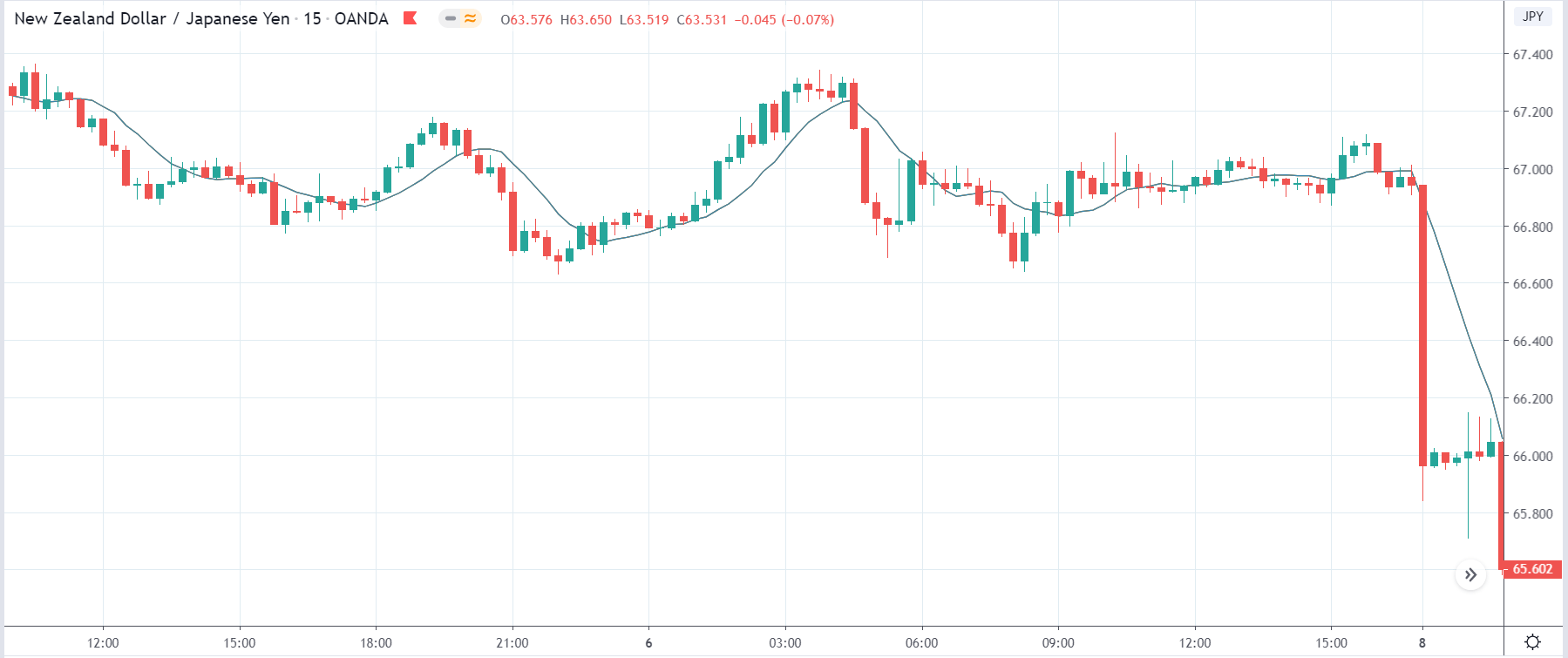
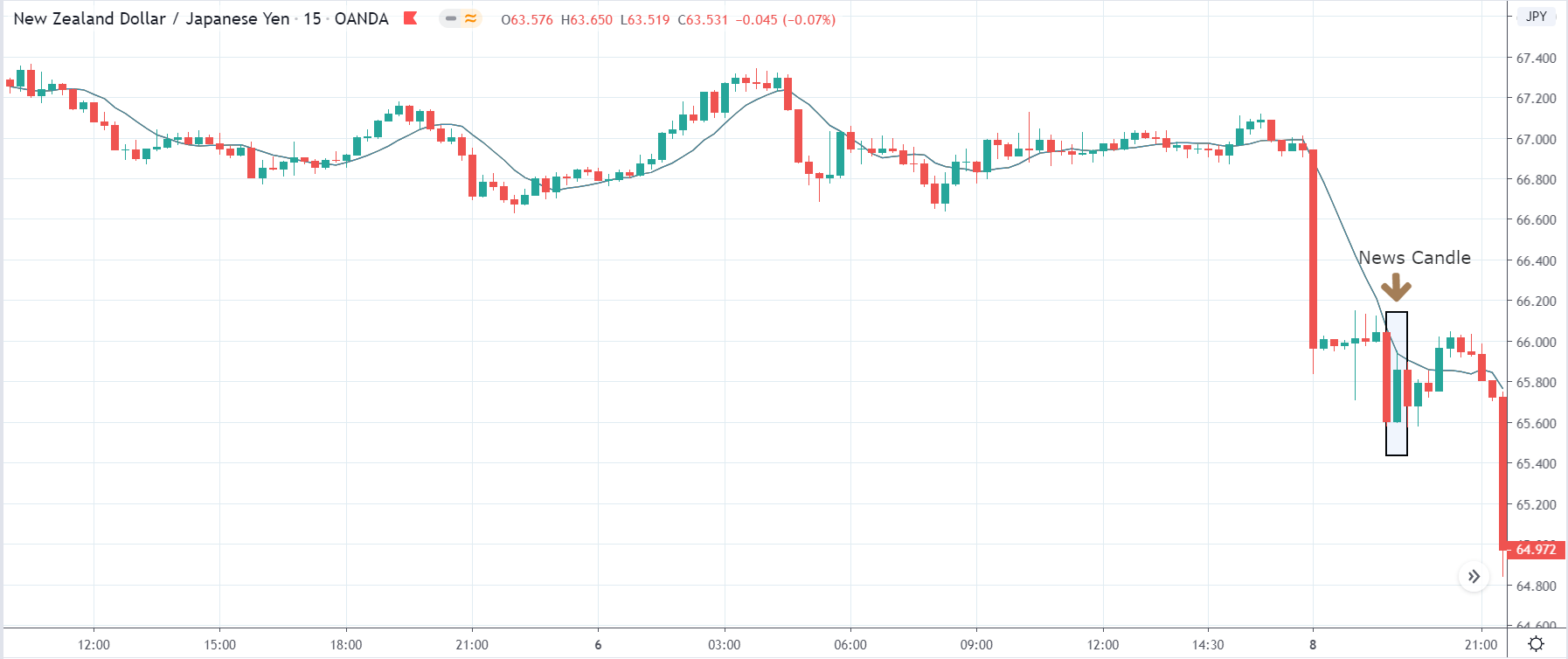



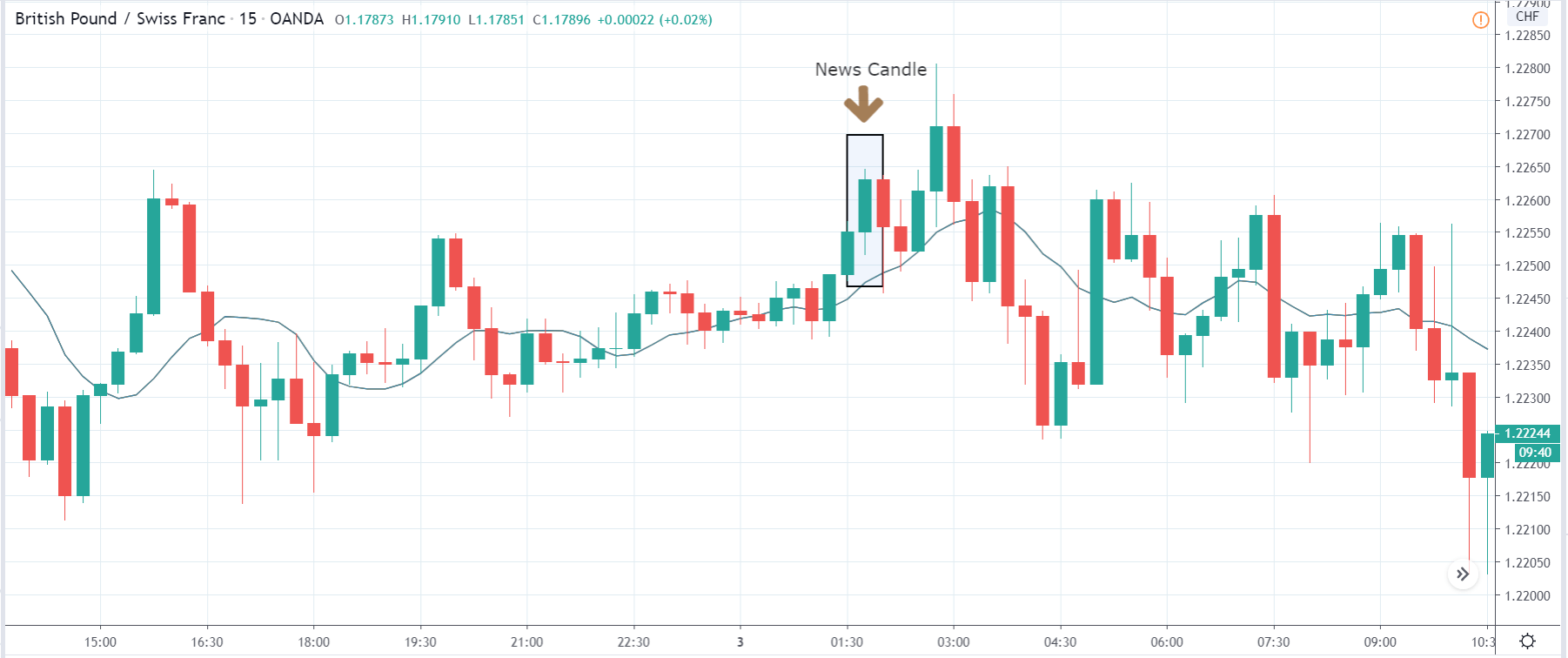
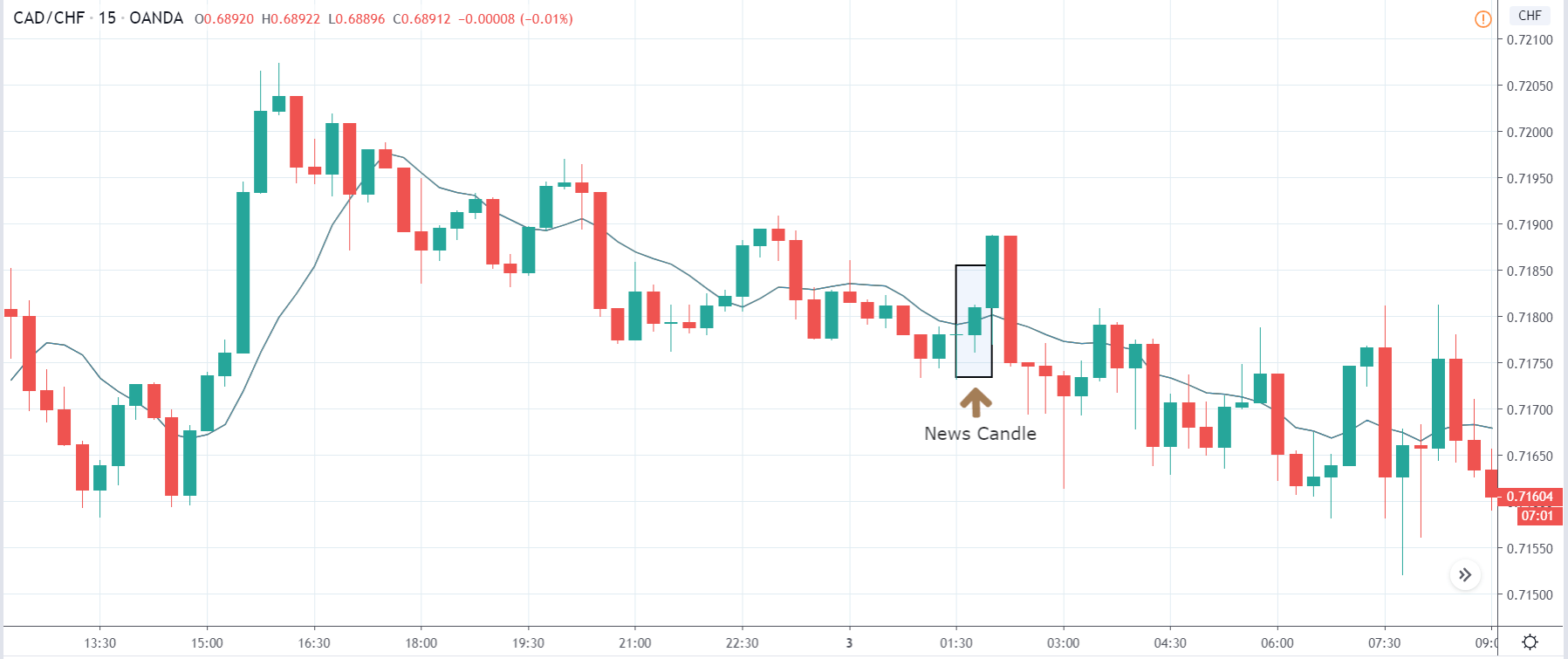

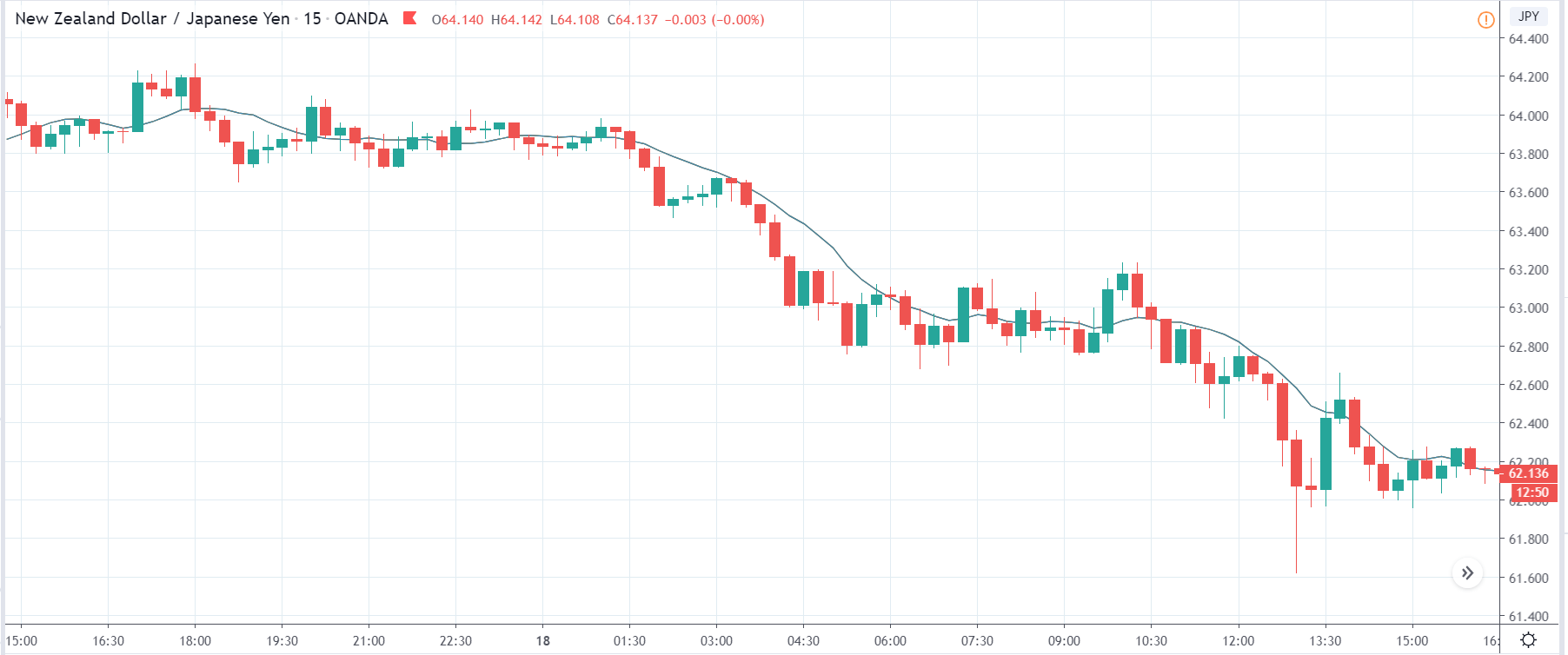
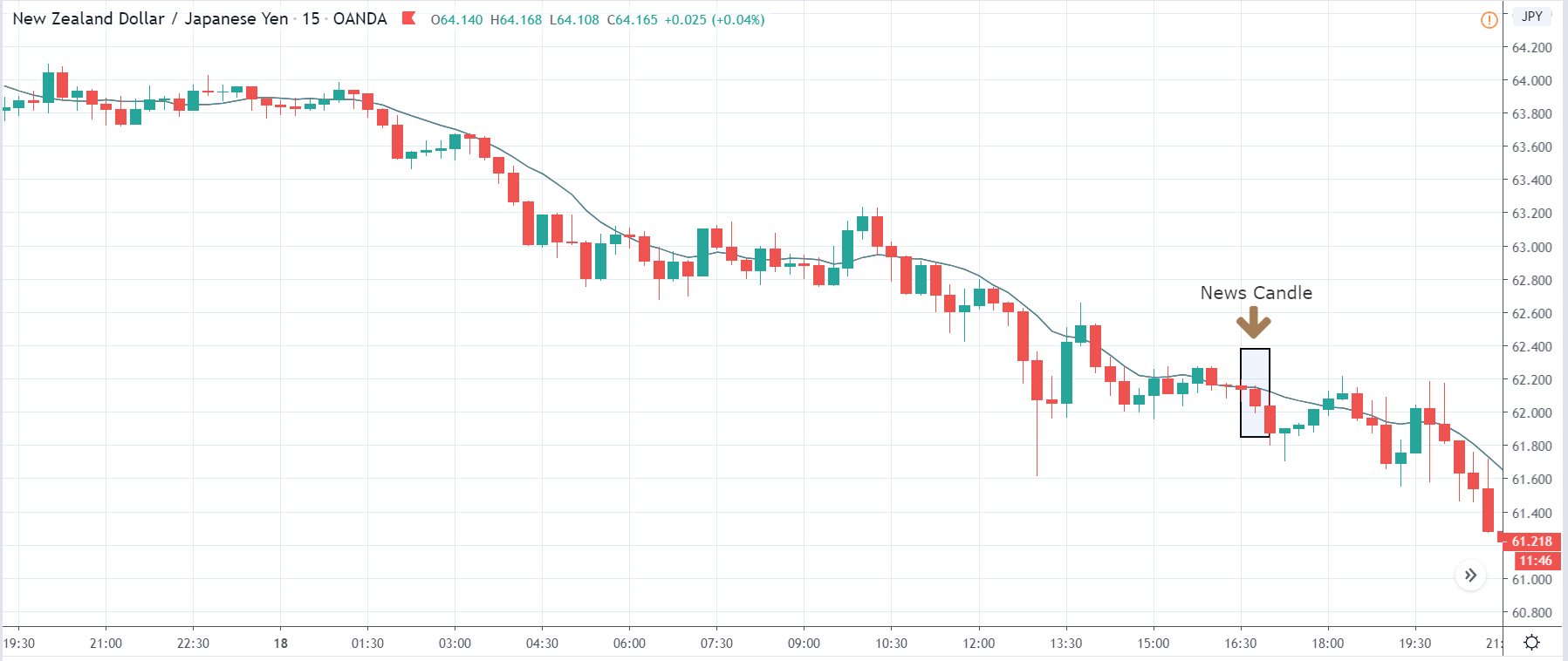



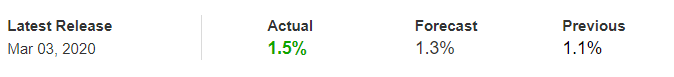
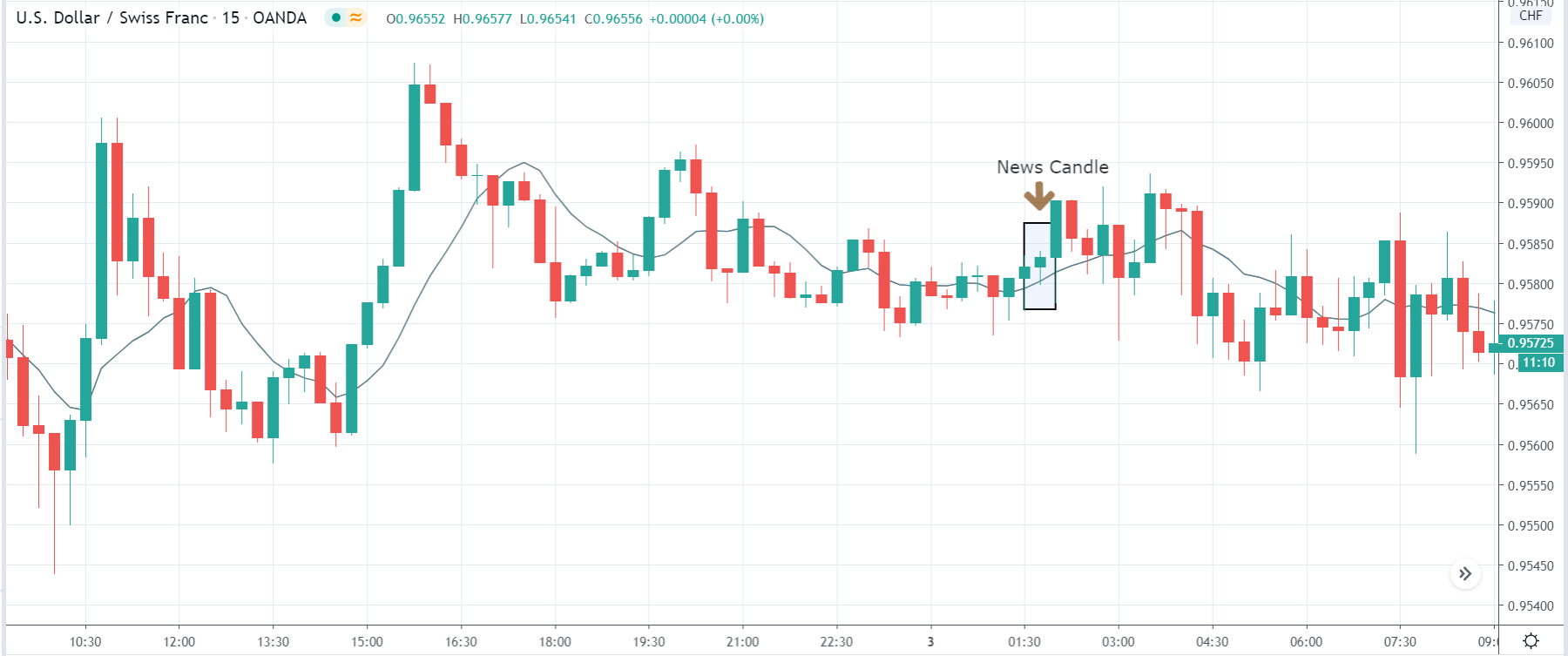


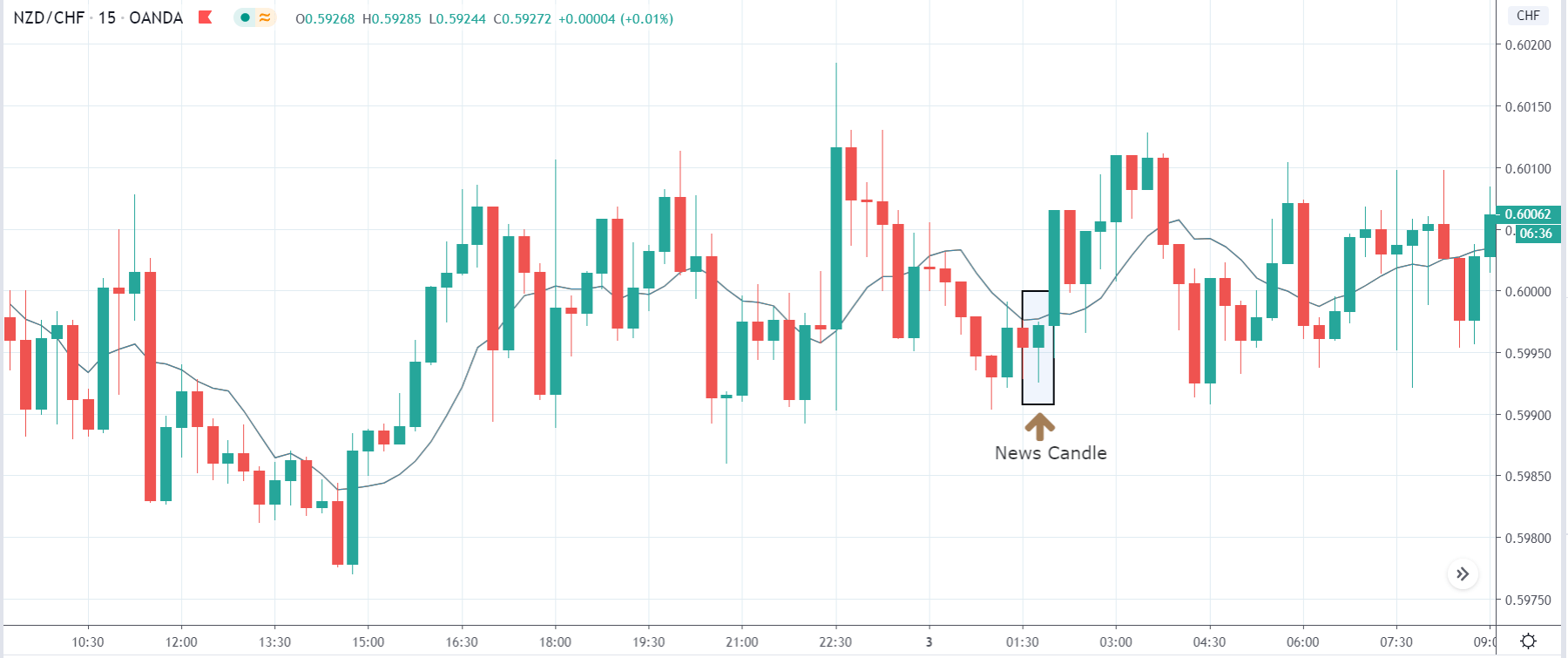


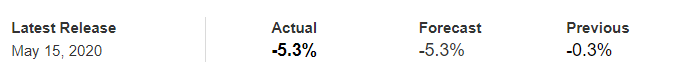









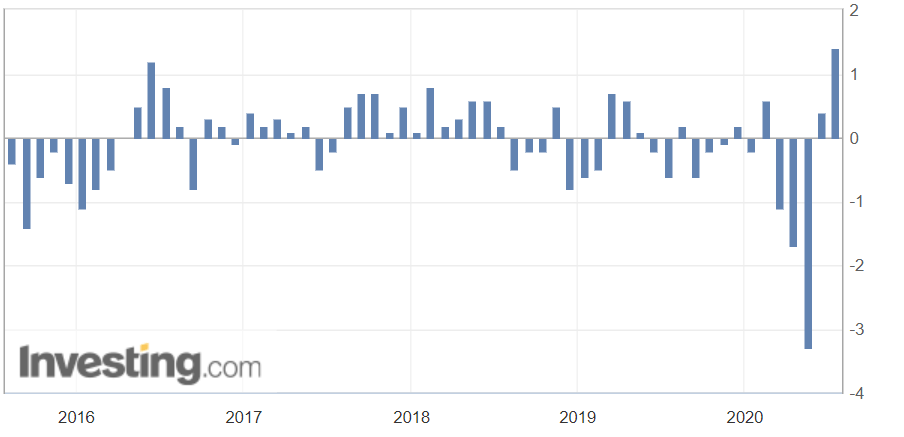




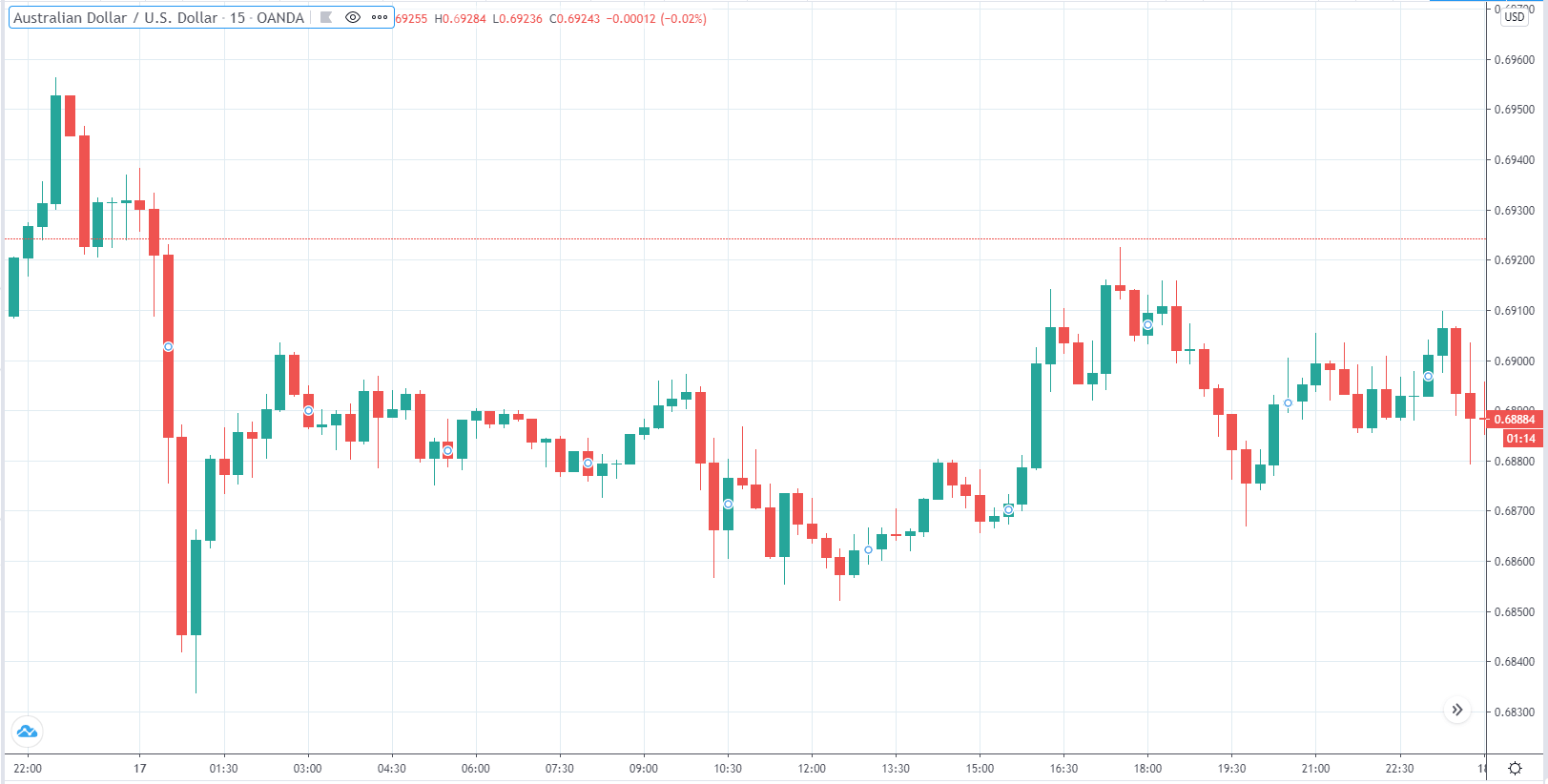
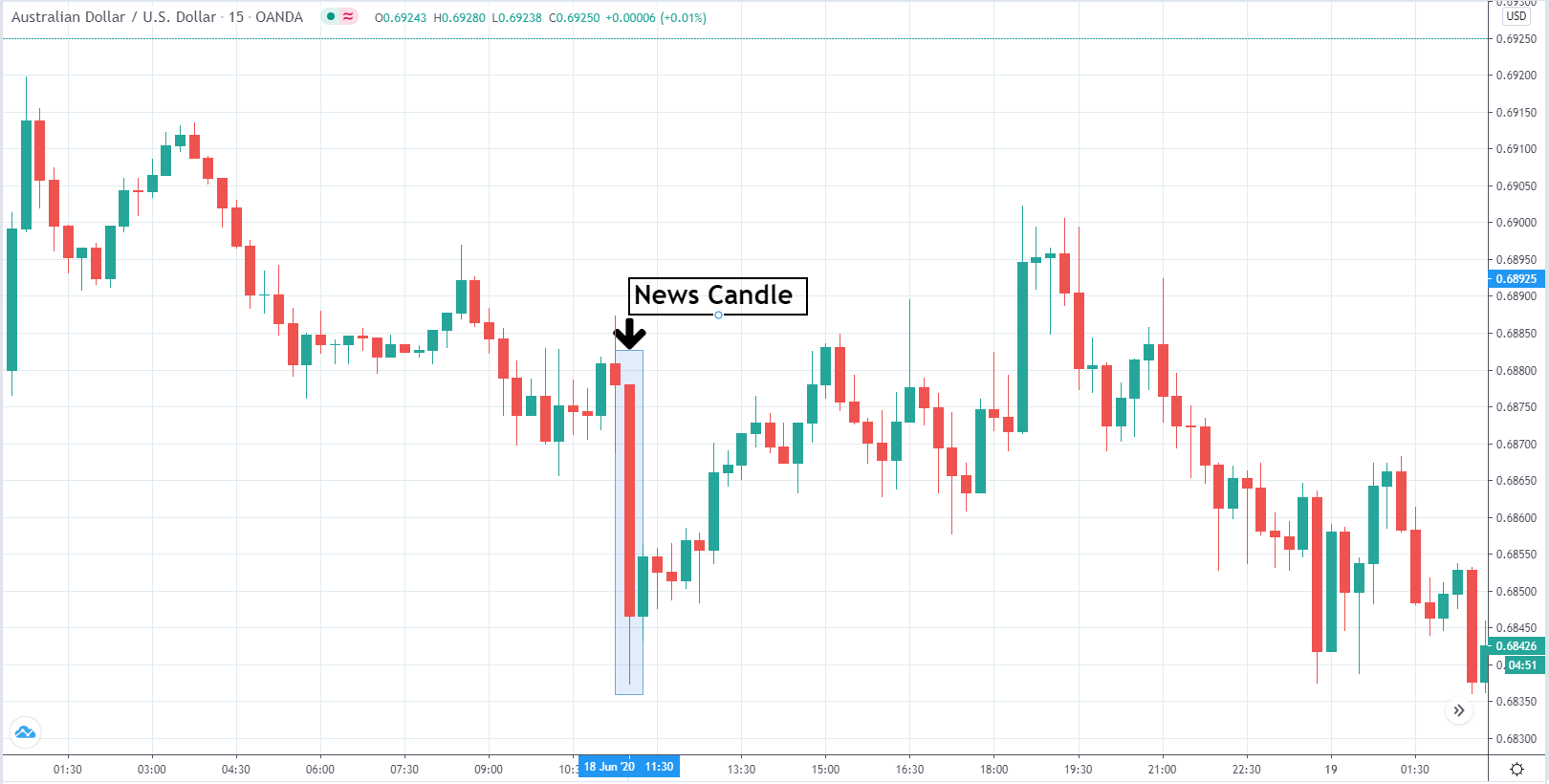

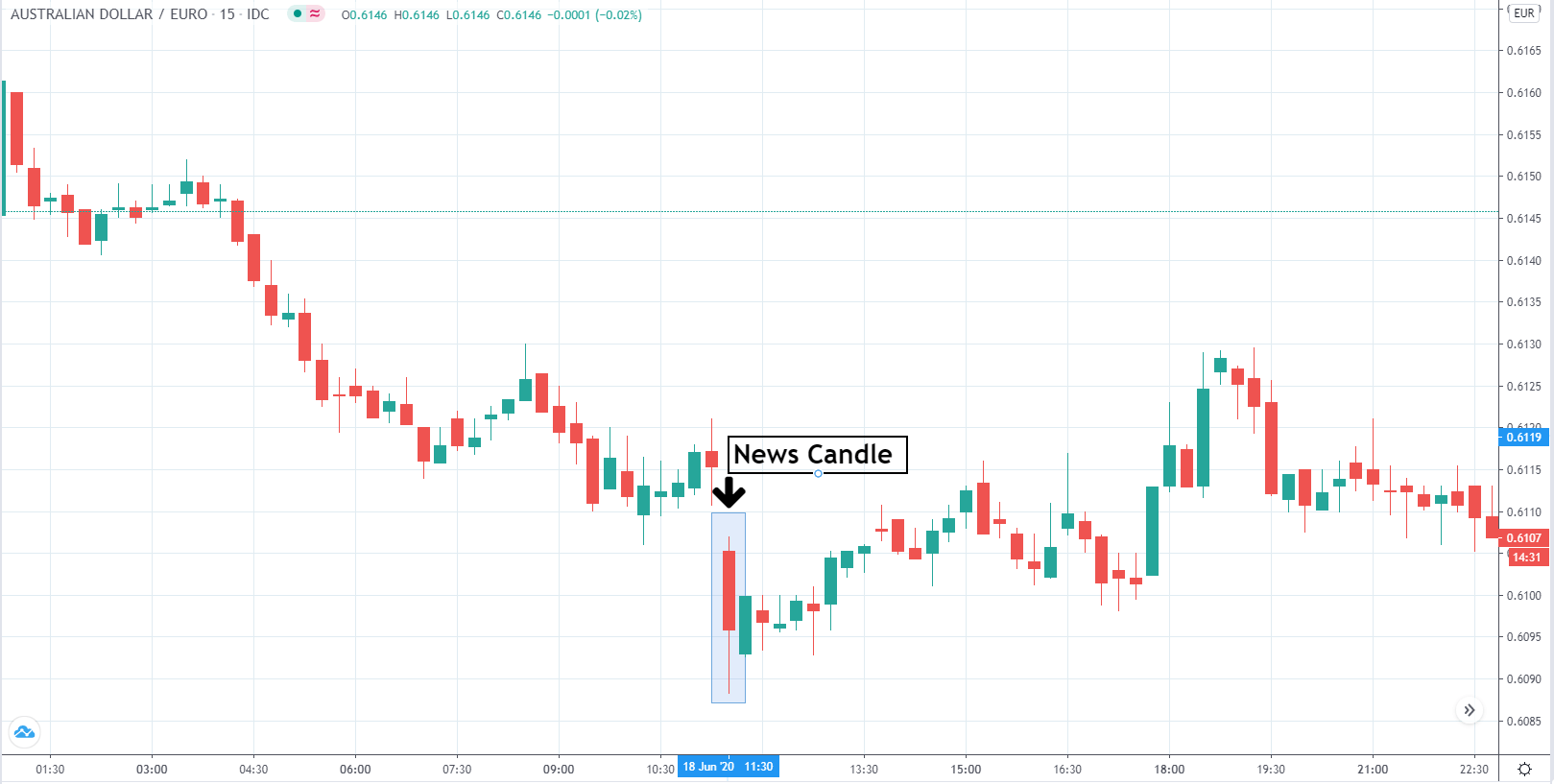
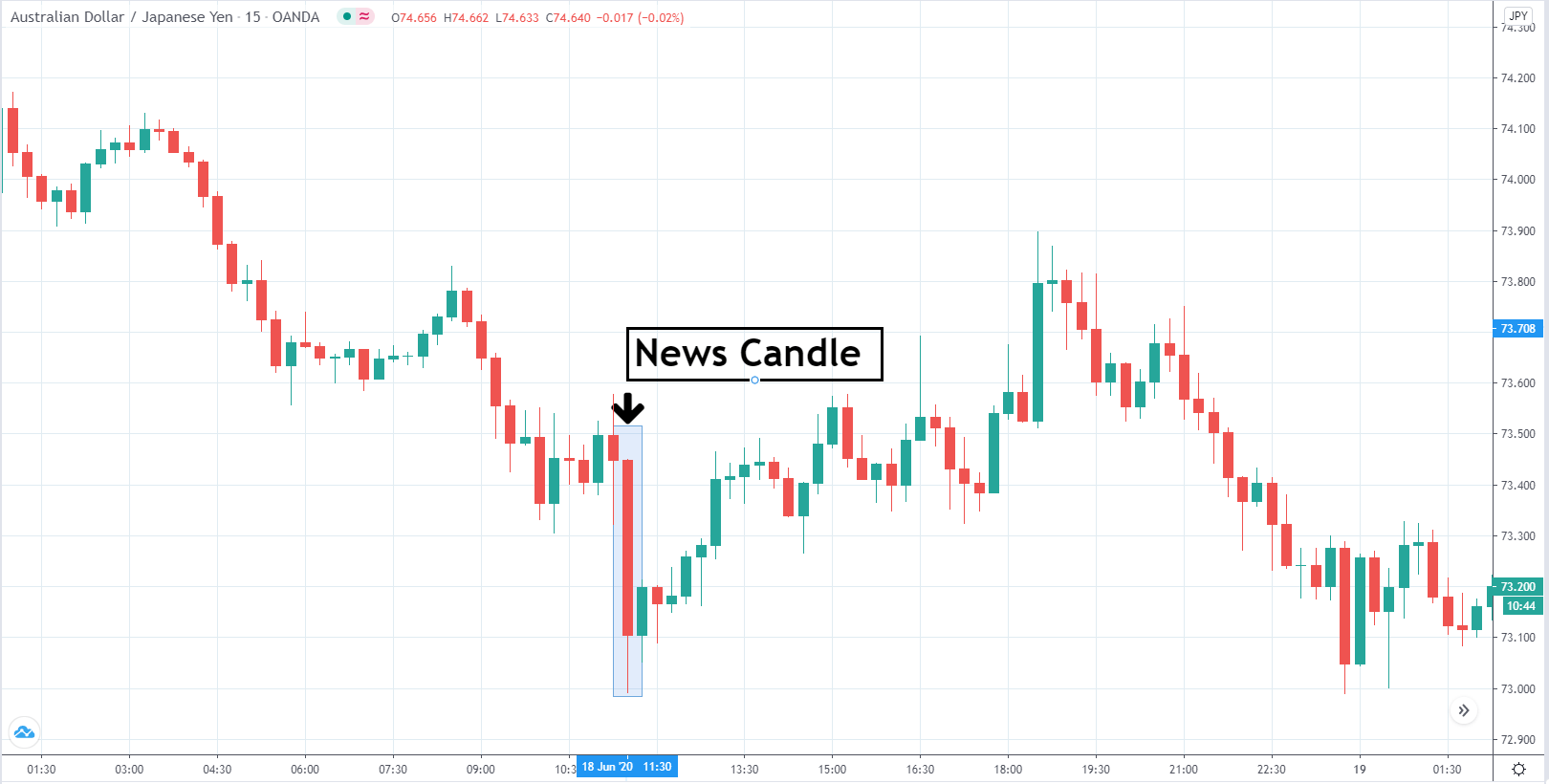





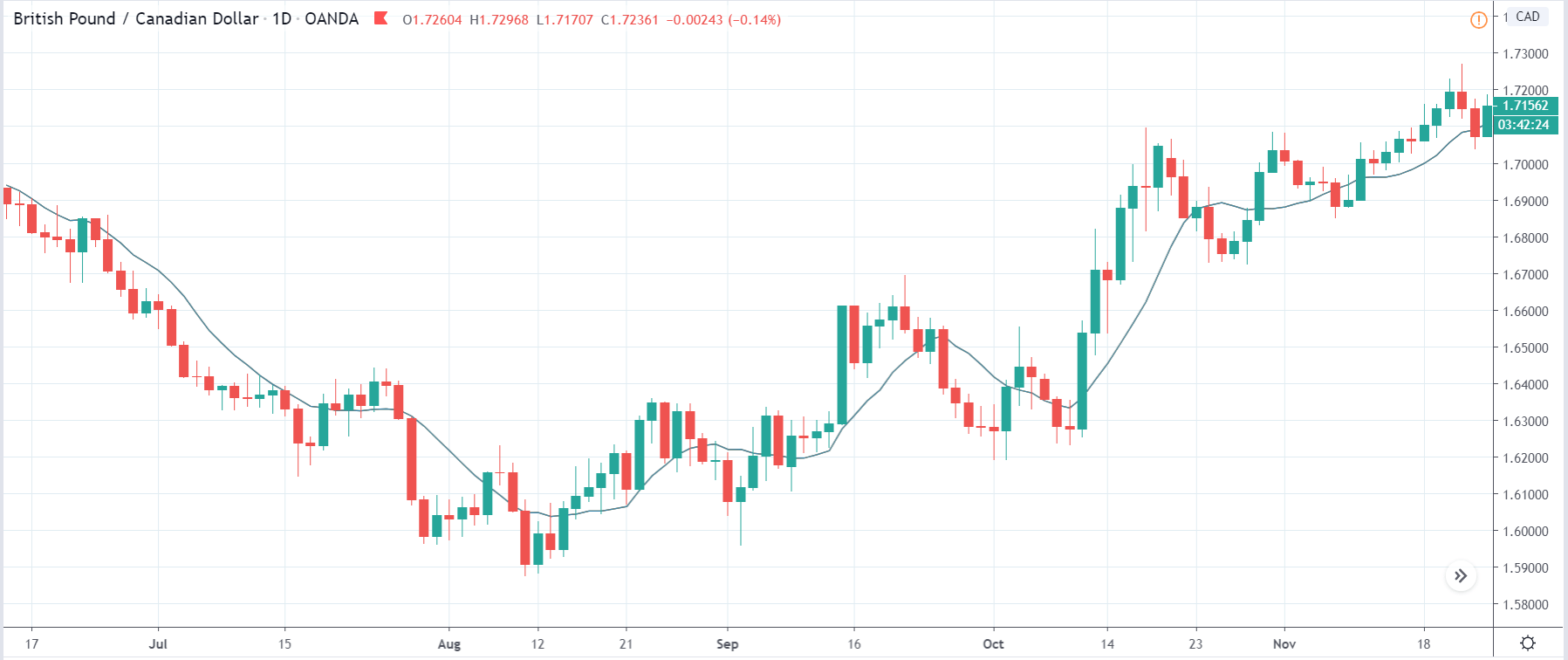
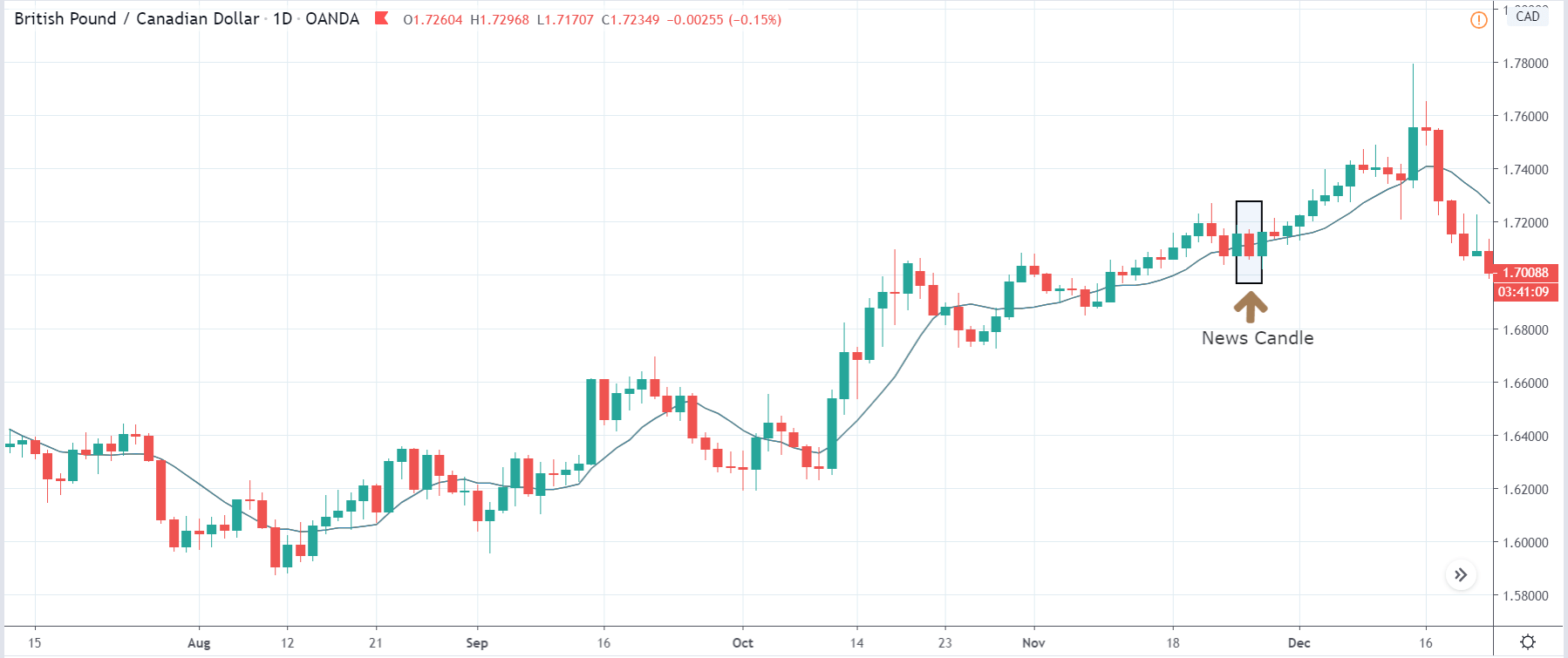
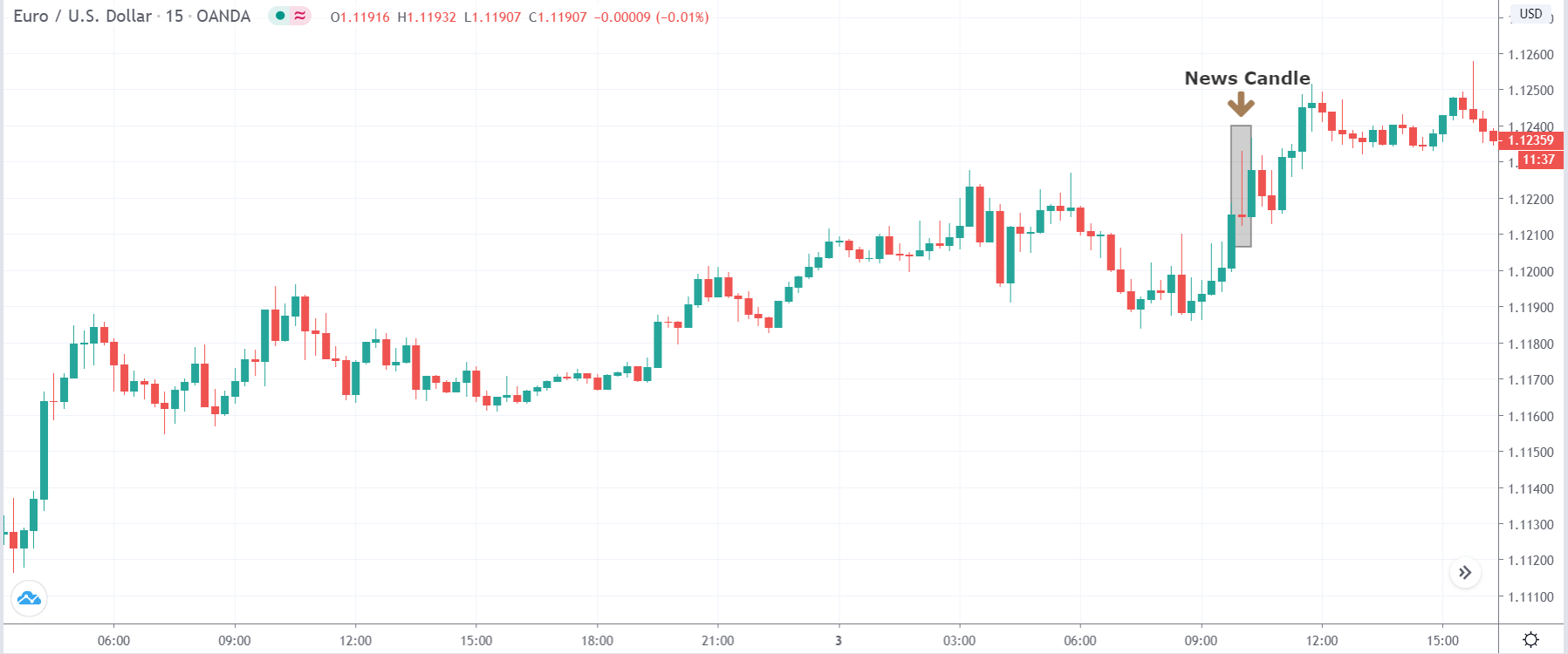
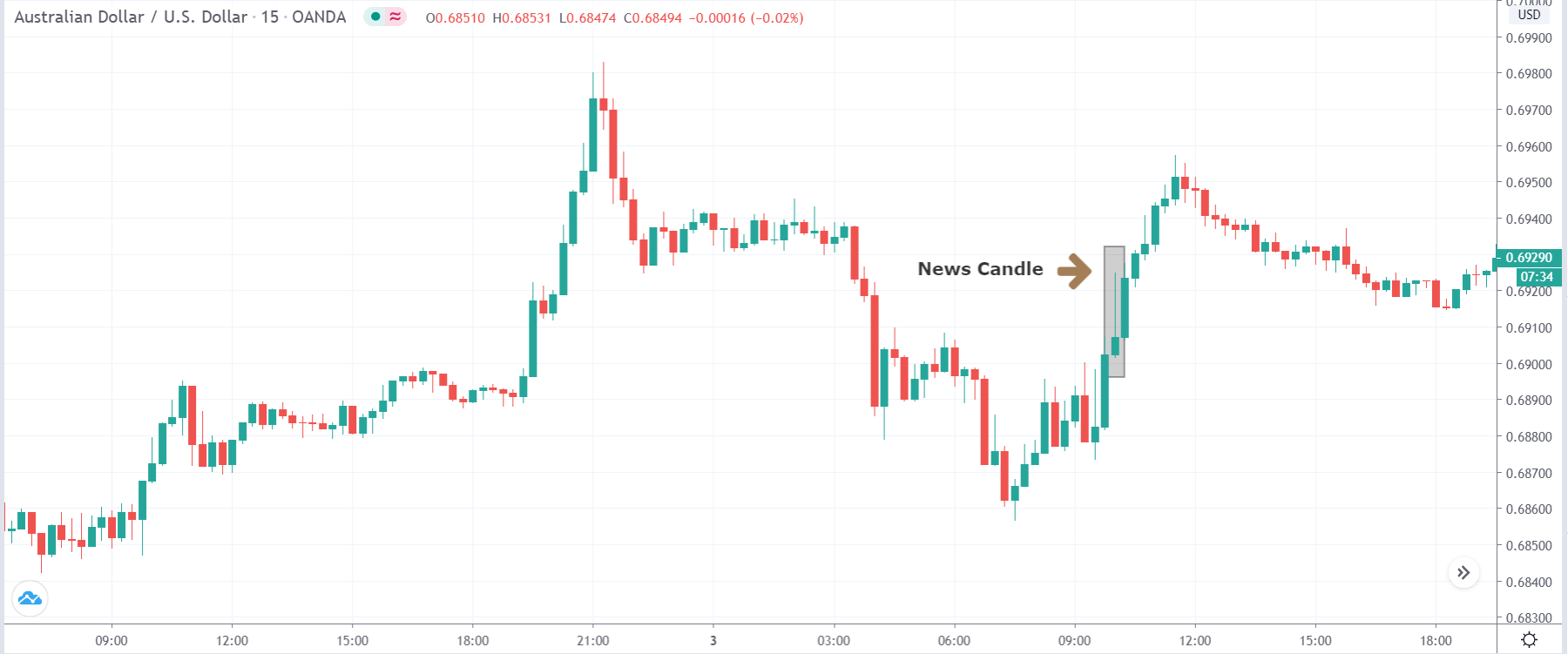
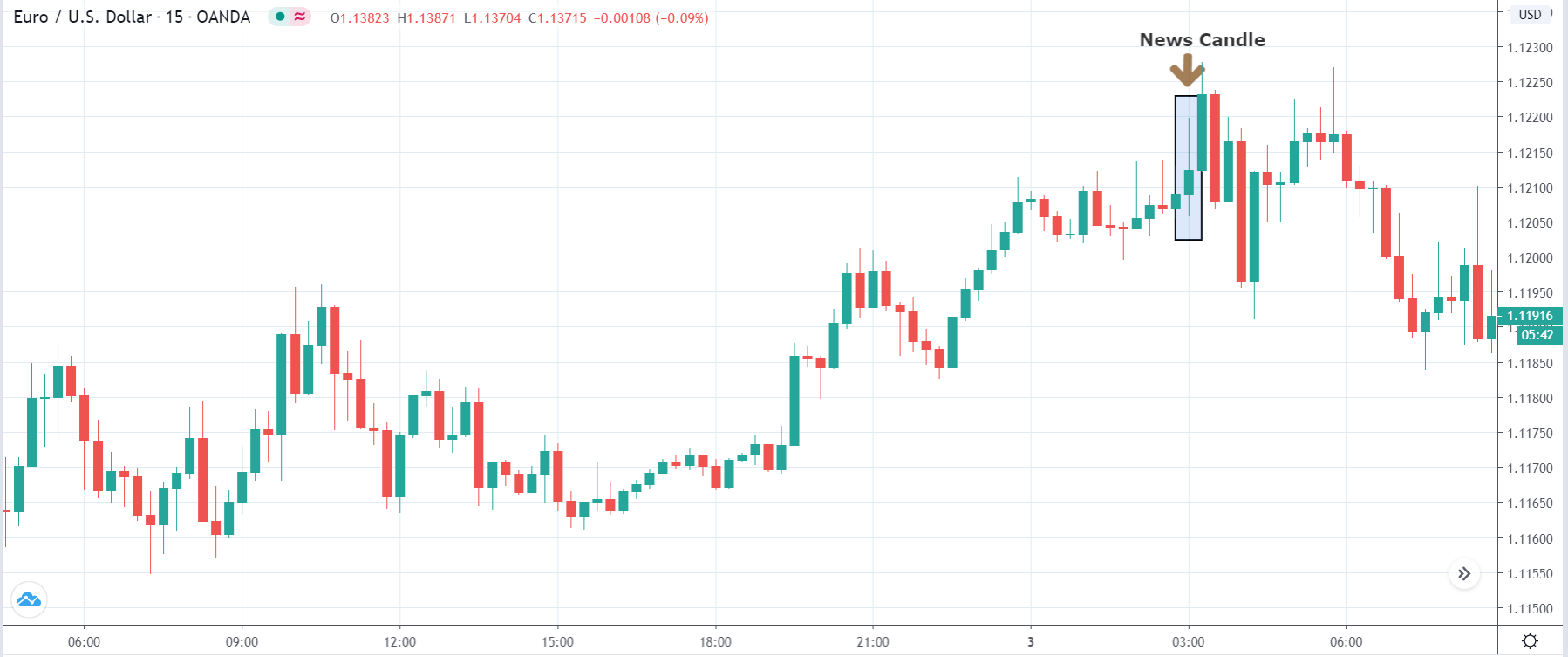
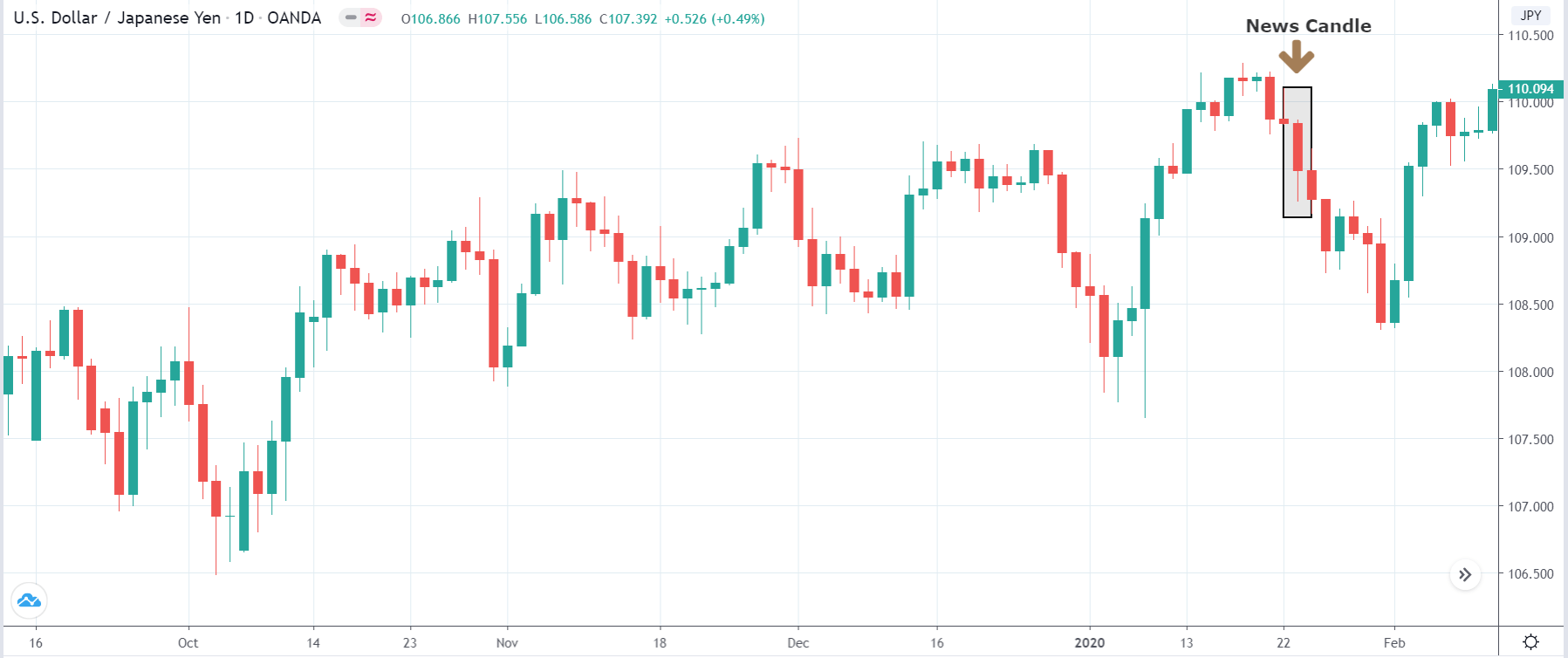
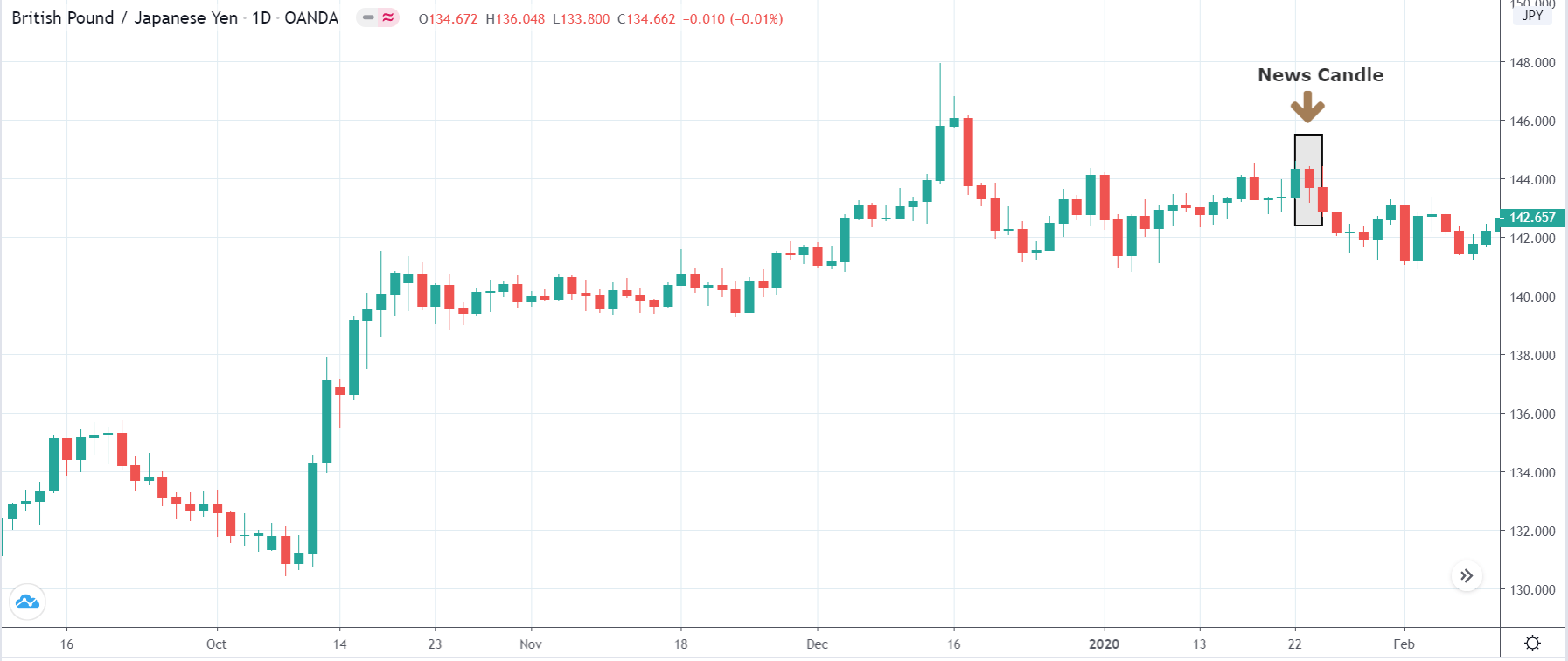
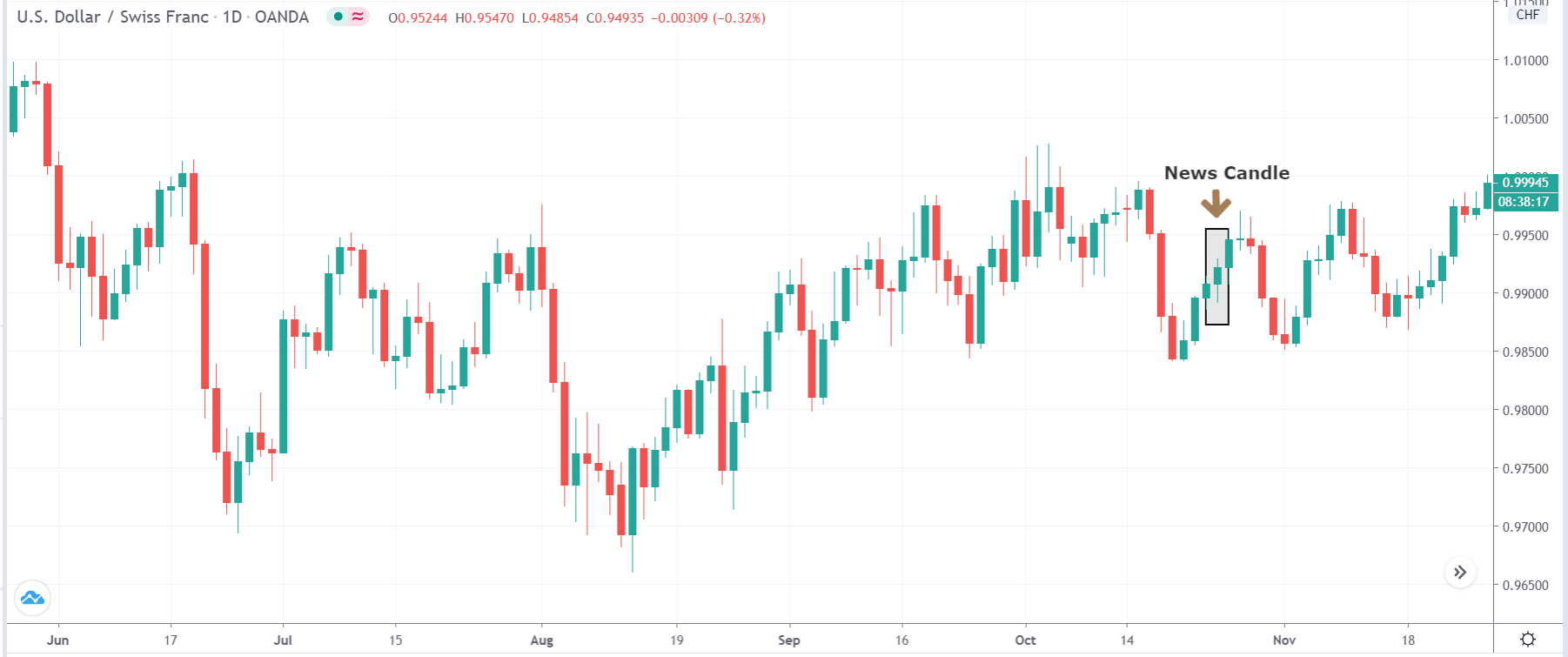
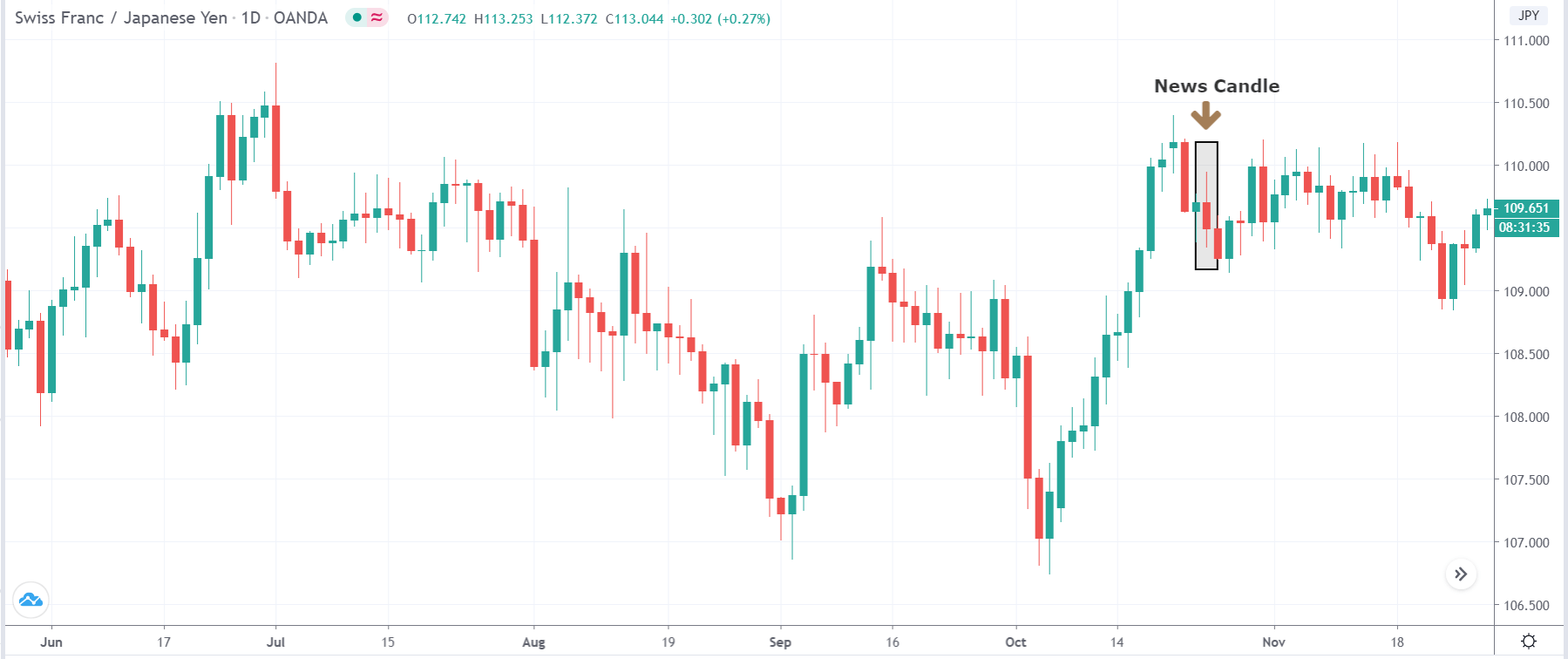
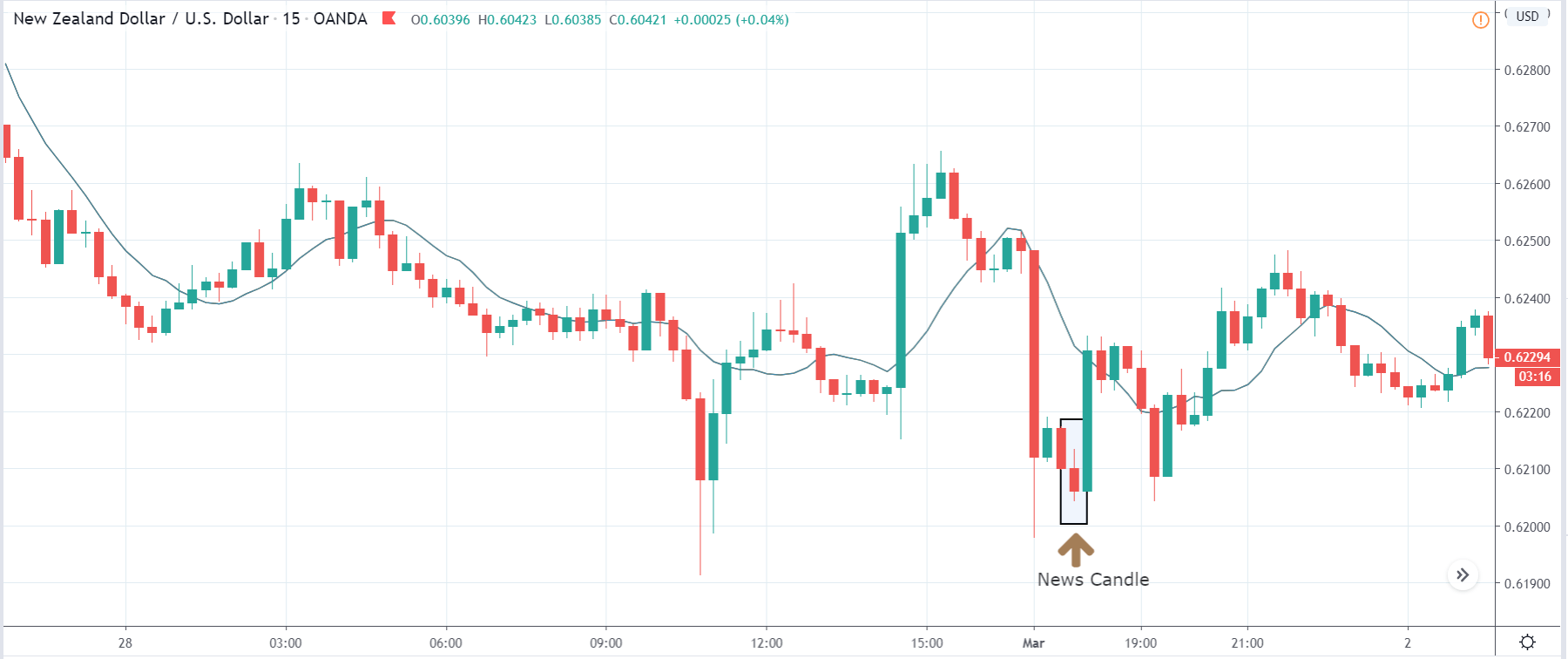
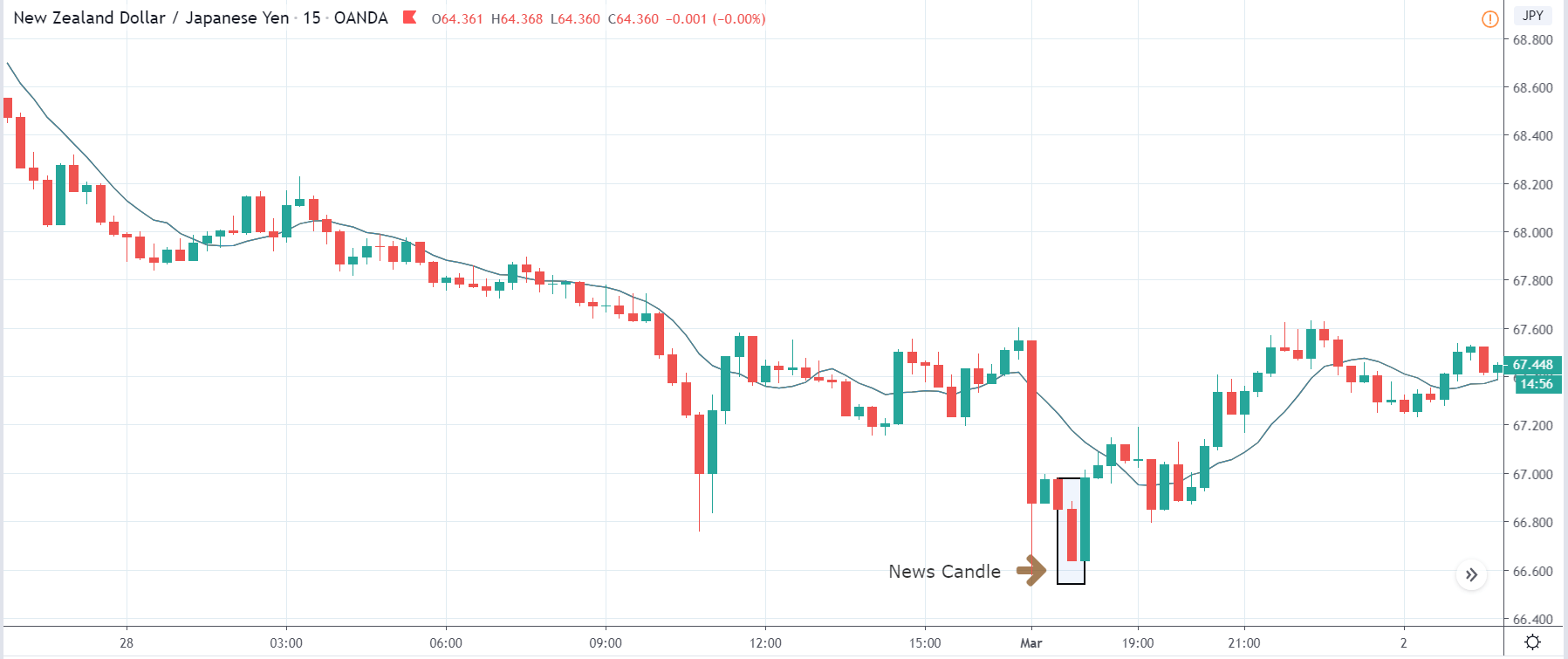
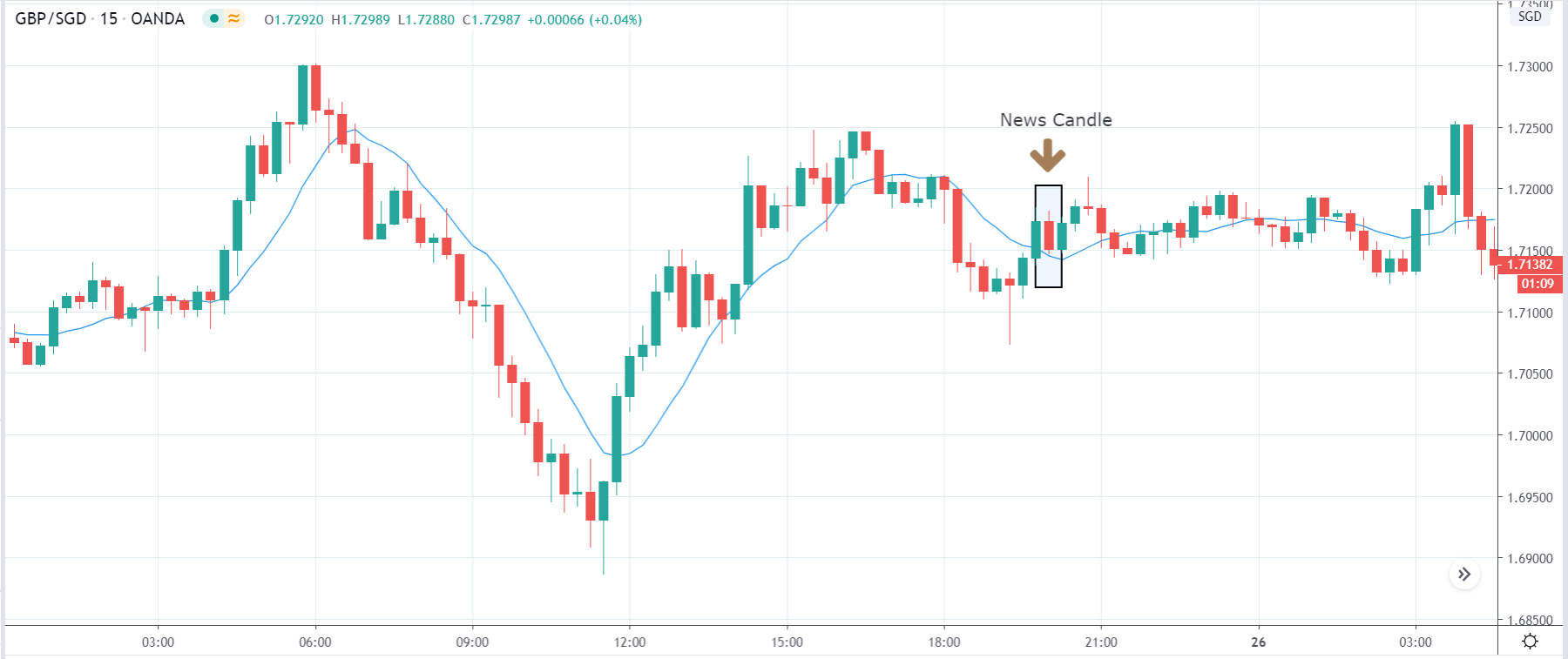
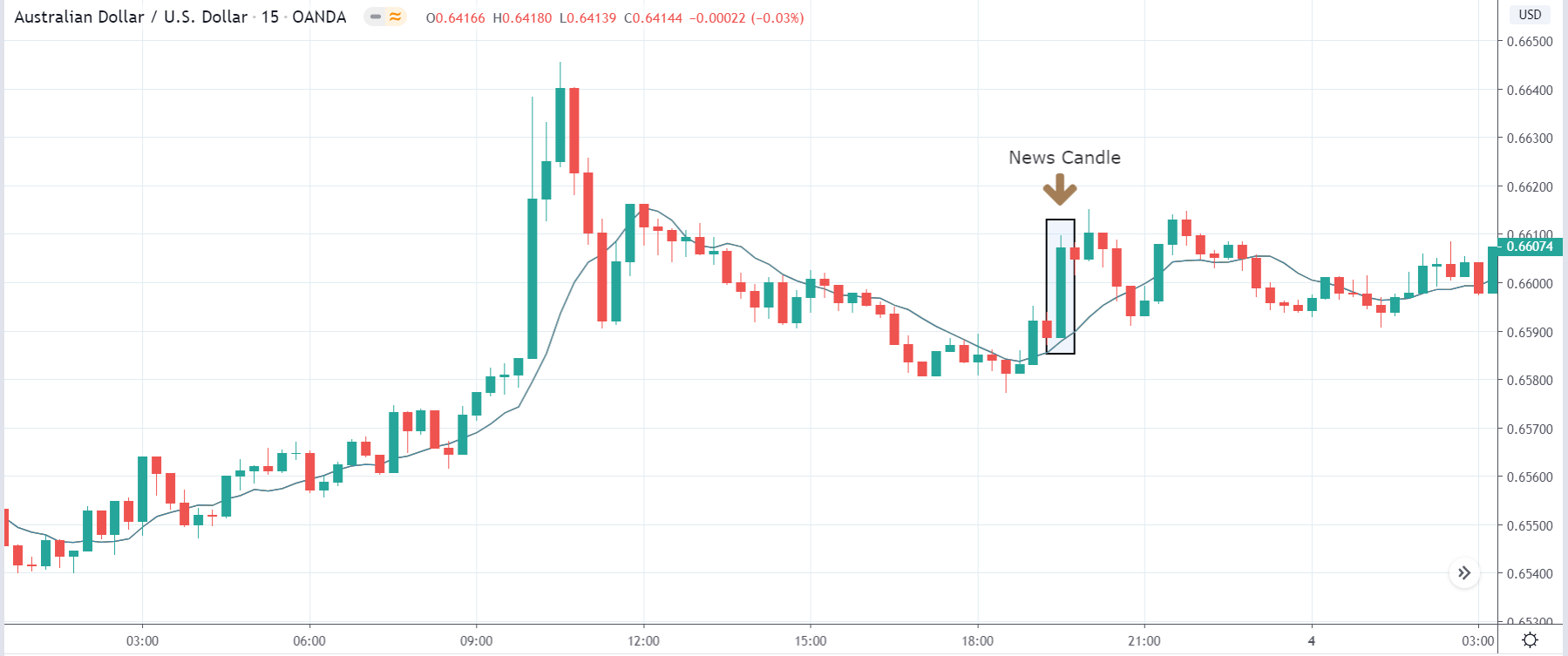
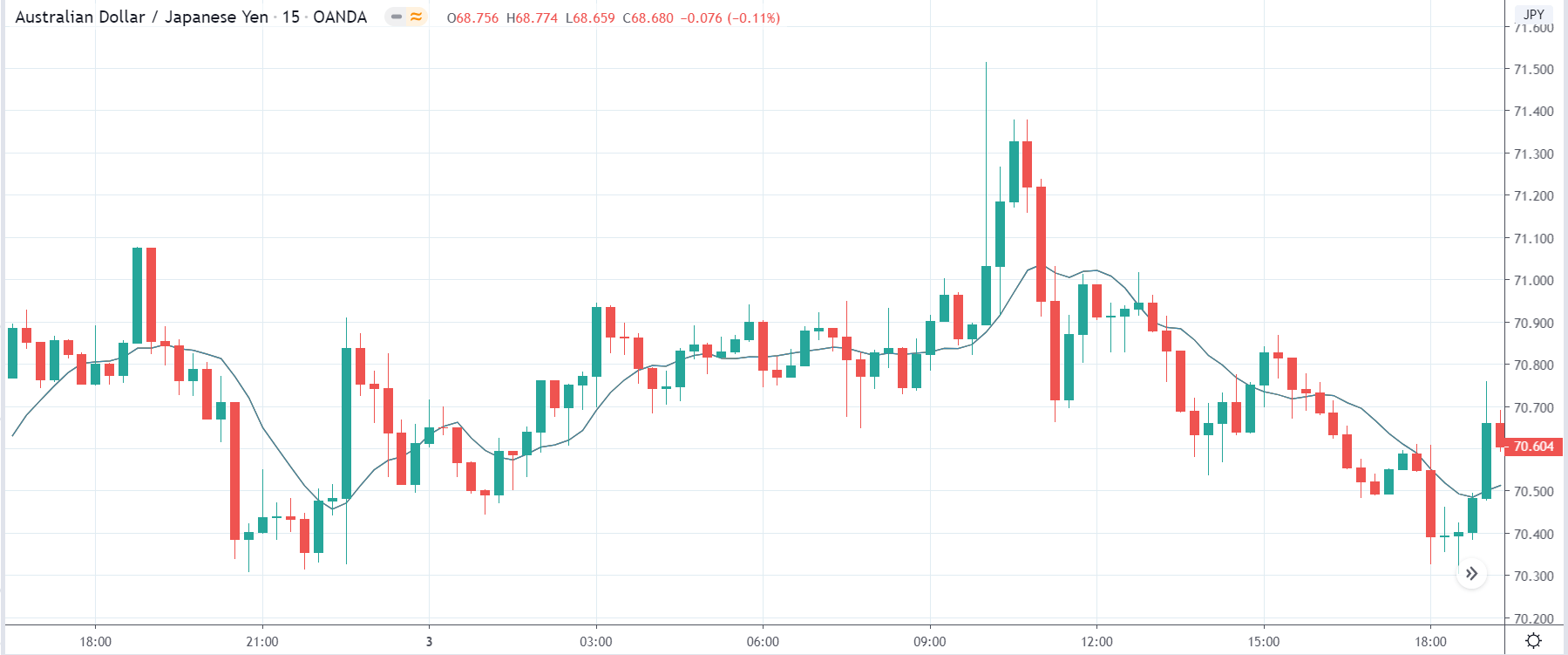
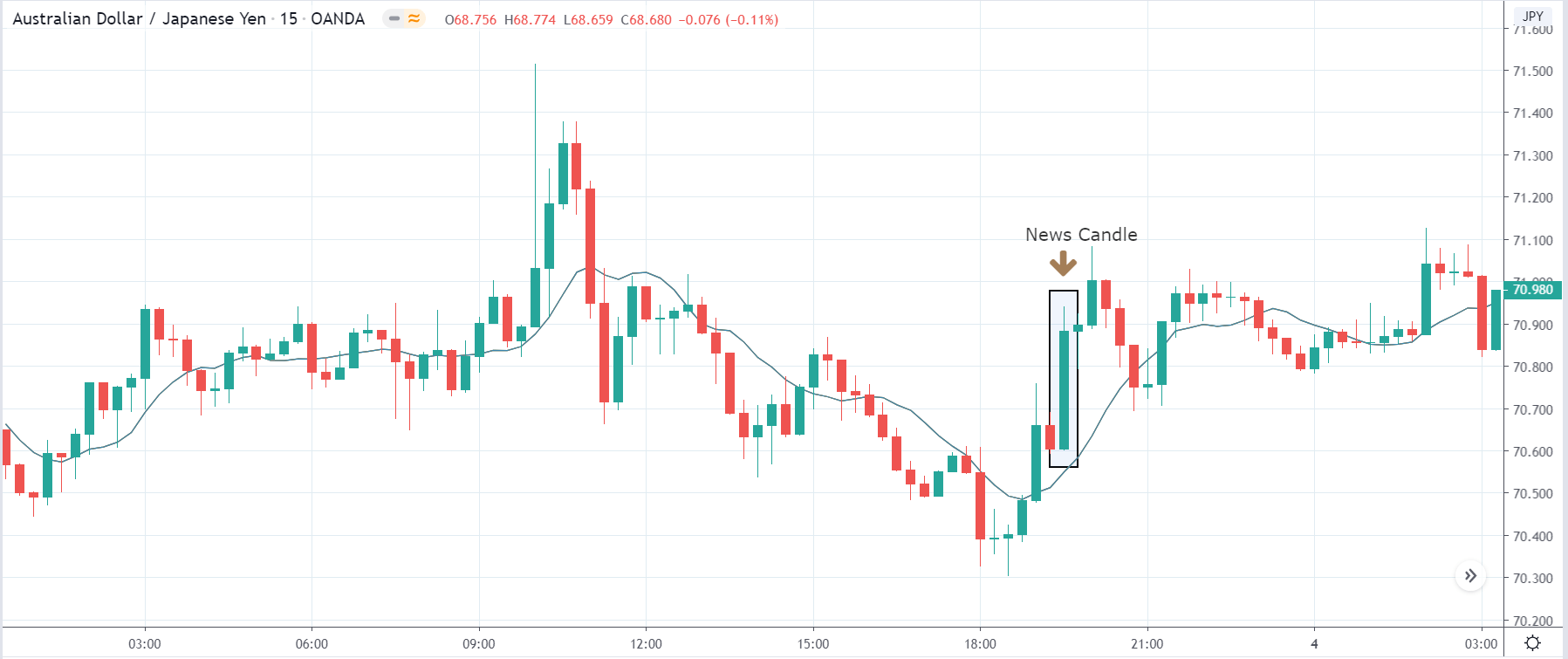
 -Avoid. Avoidance is one of the best measures in your strategy. Avoid the news.
-Avoid. Avoidance is one of the best measures in your strategy. Avoid the news.
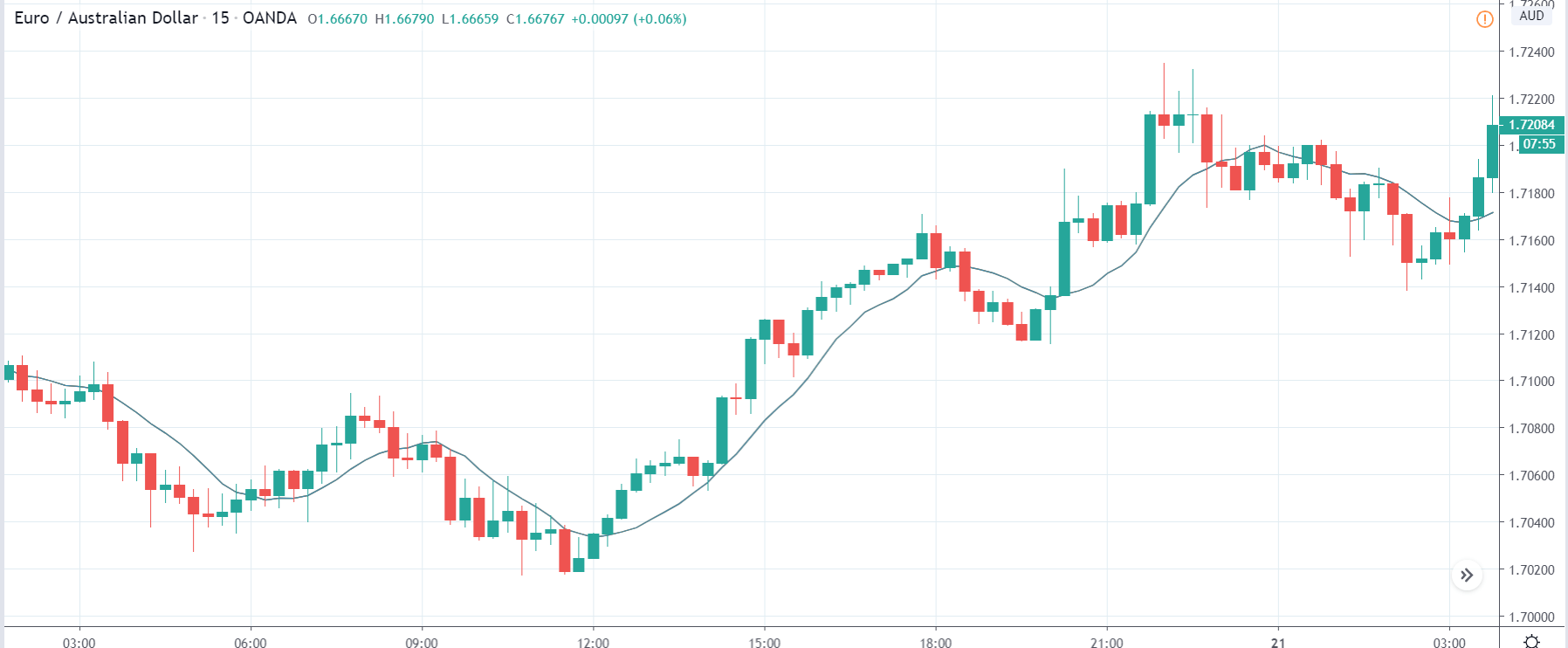
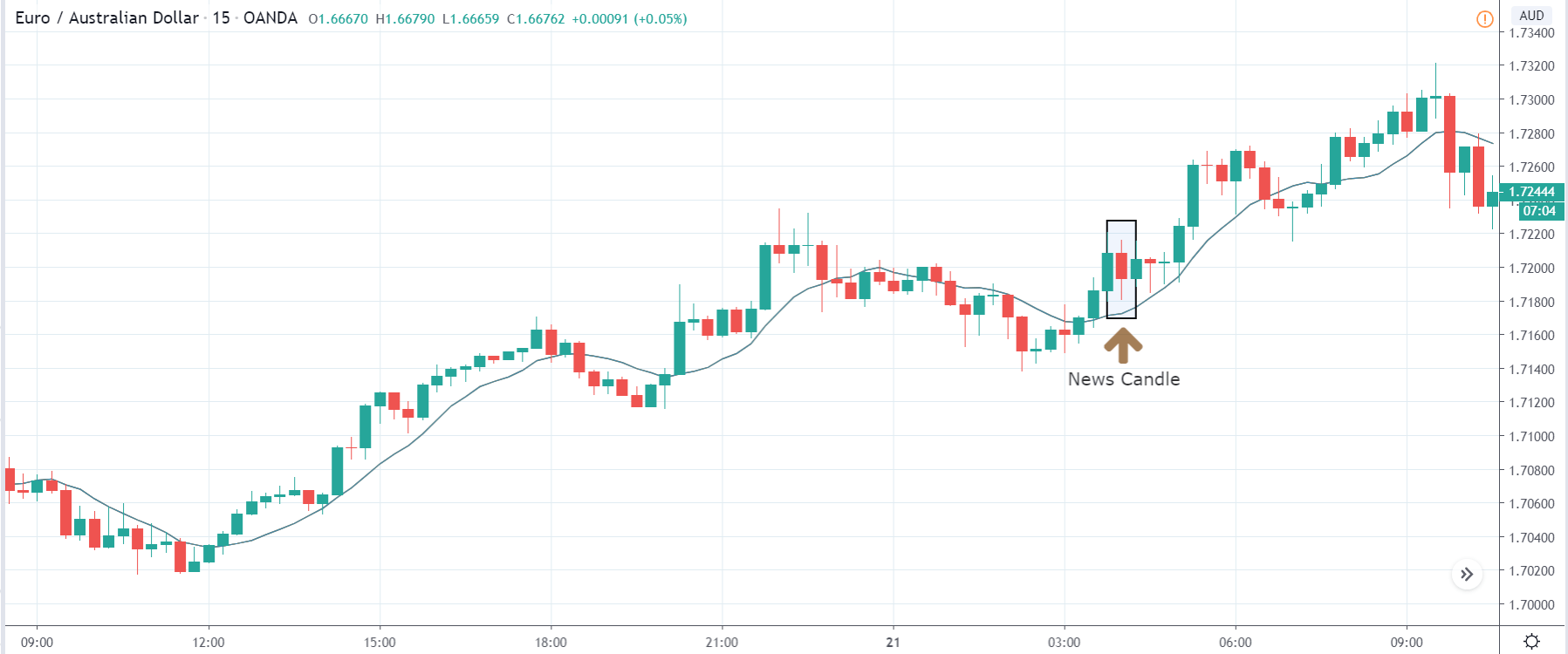
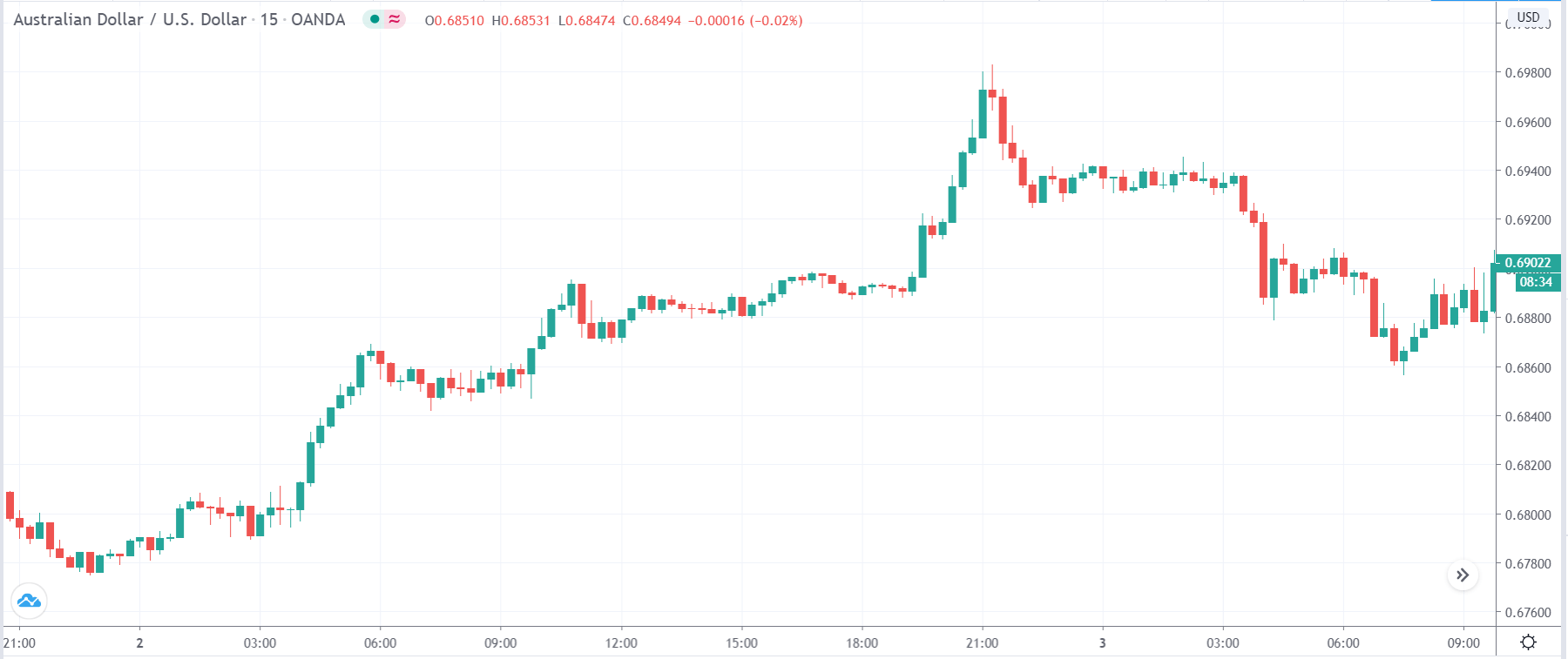
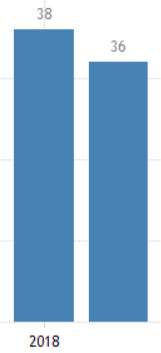
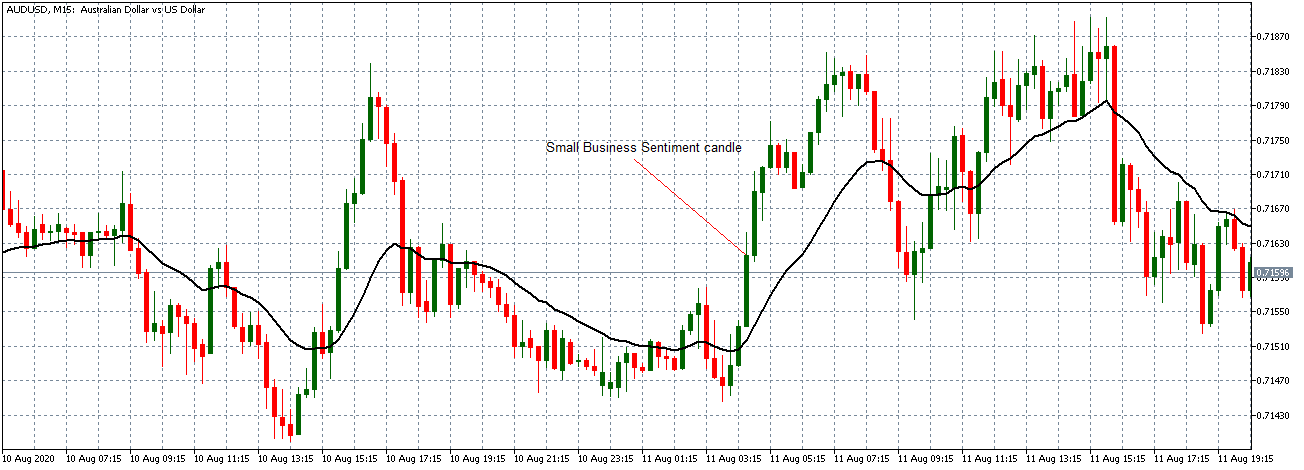
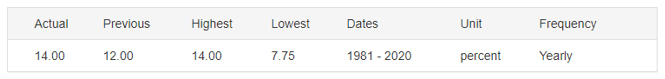
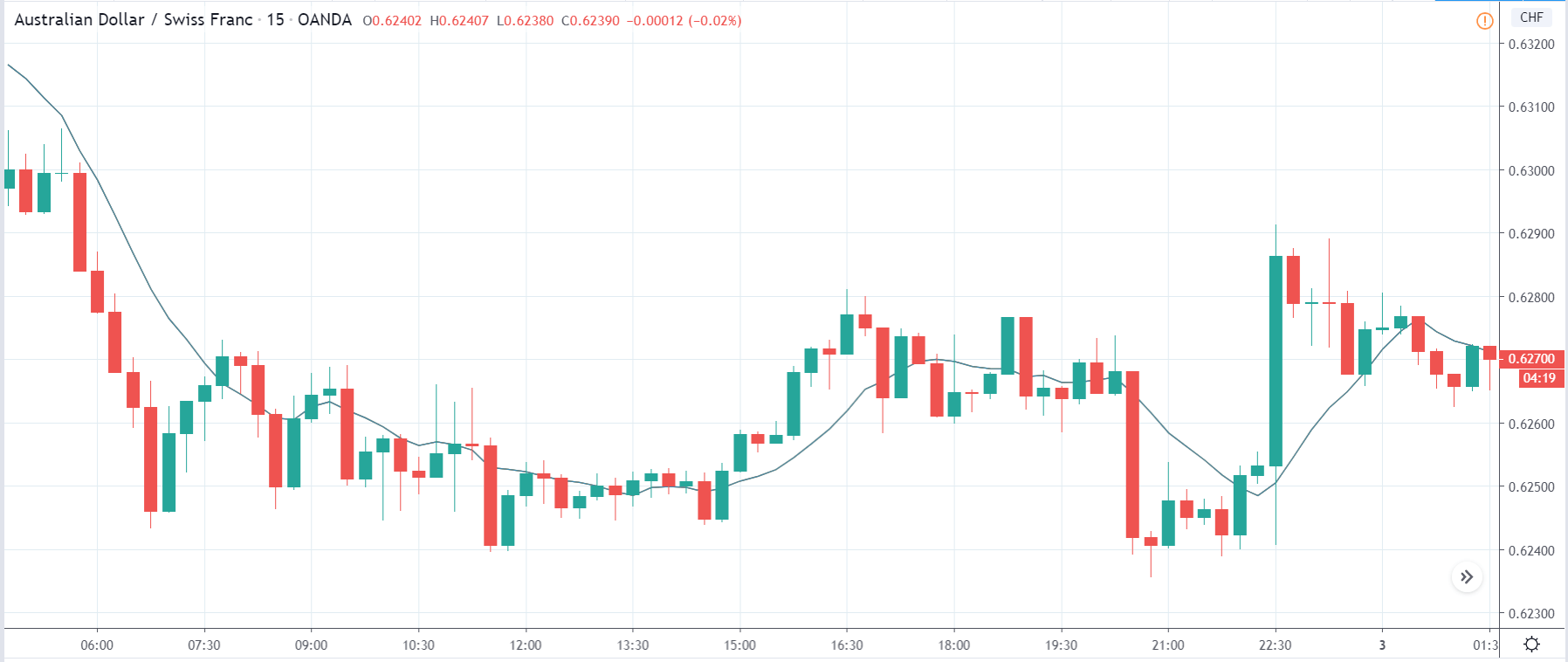
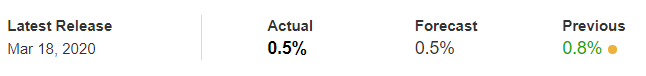
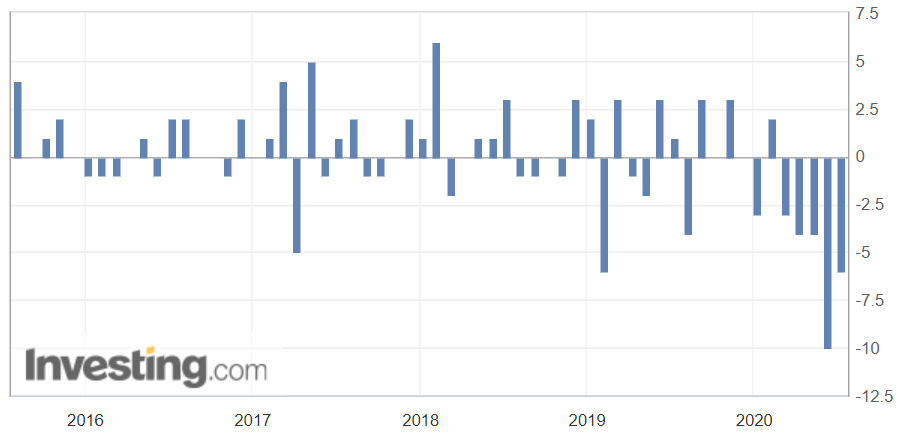
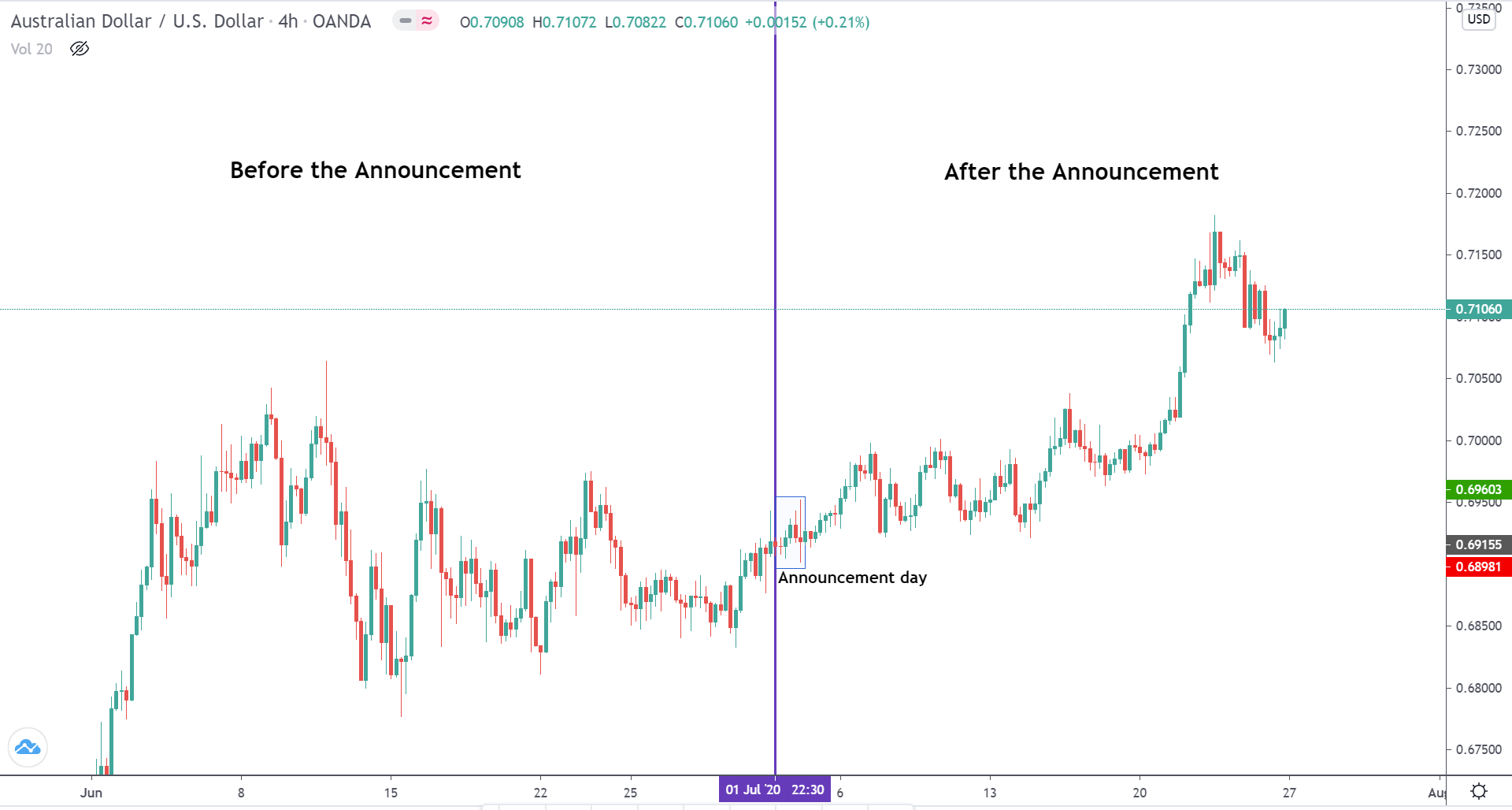
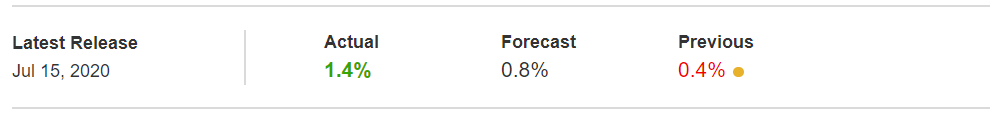
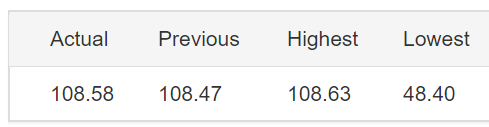
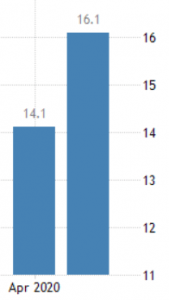
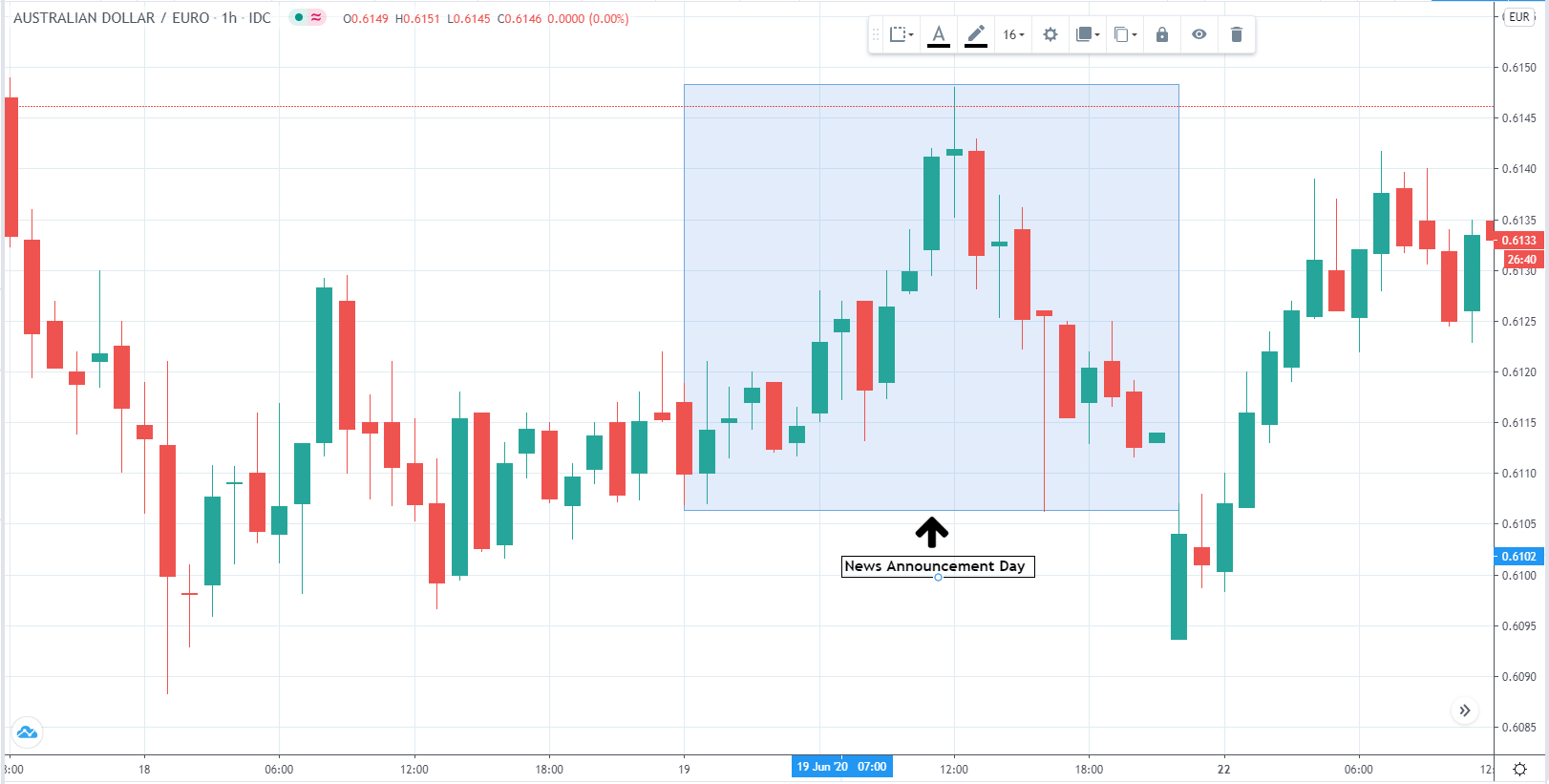
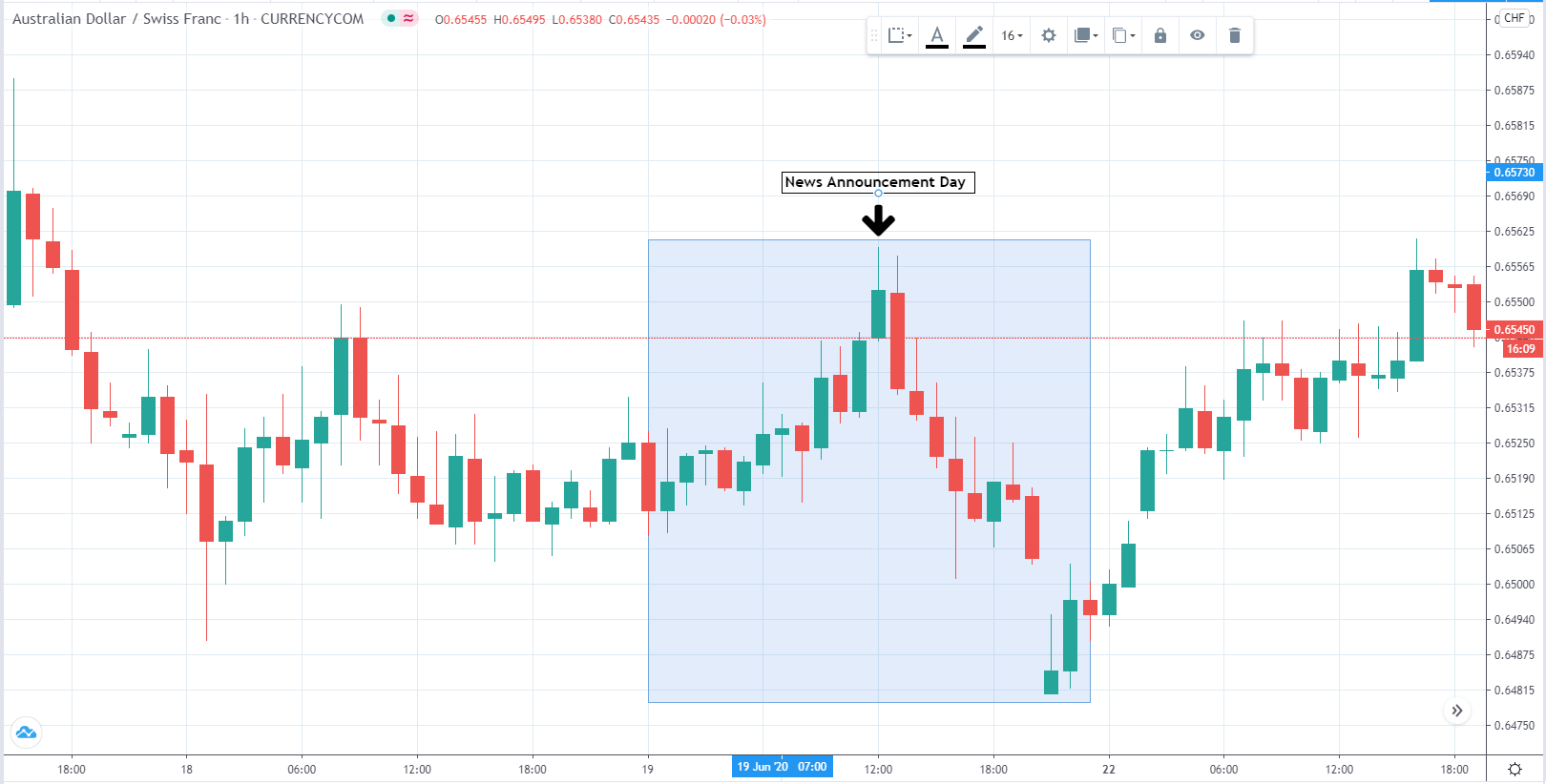
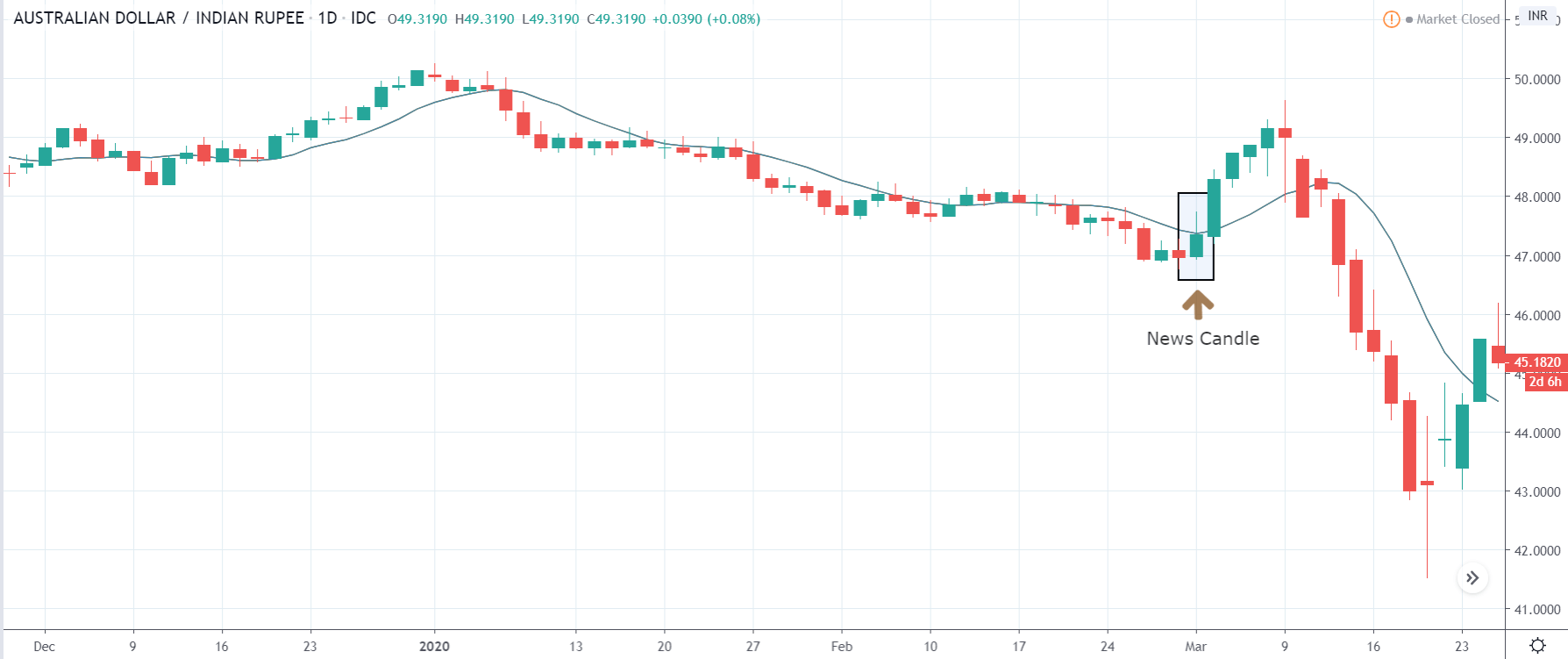
 The below image shows that the weekly wages were increased for Australian employees in 2020. Although the difference is not huge, it still is a positive step taken for the daily wage workers. Looking at the data, we should not expect significant volatility in the currency pairs during the announcement.
The below image shows that the weekly wages were increased for Australian employees in 2020. Although the difference is not huge, it still is a positive step taken for the daily wage workers. Looking at the data, we should not expect significant volatility in the currency pairs during the announcement.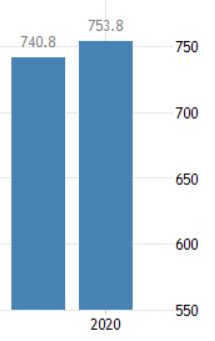



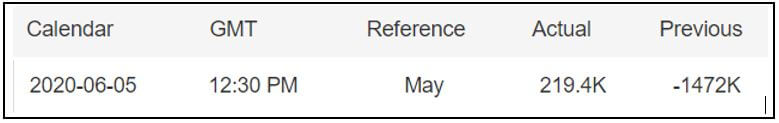
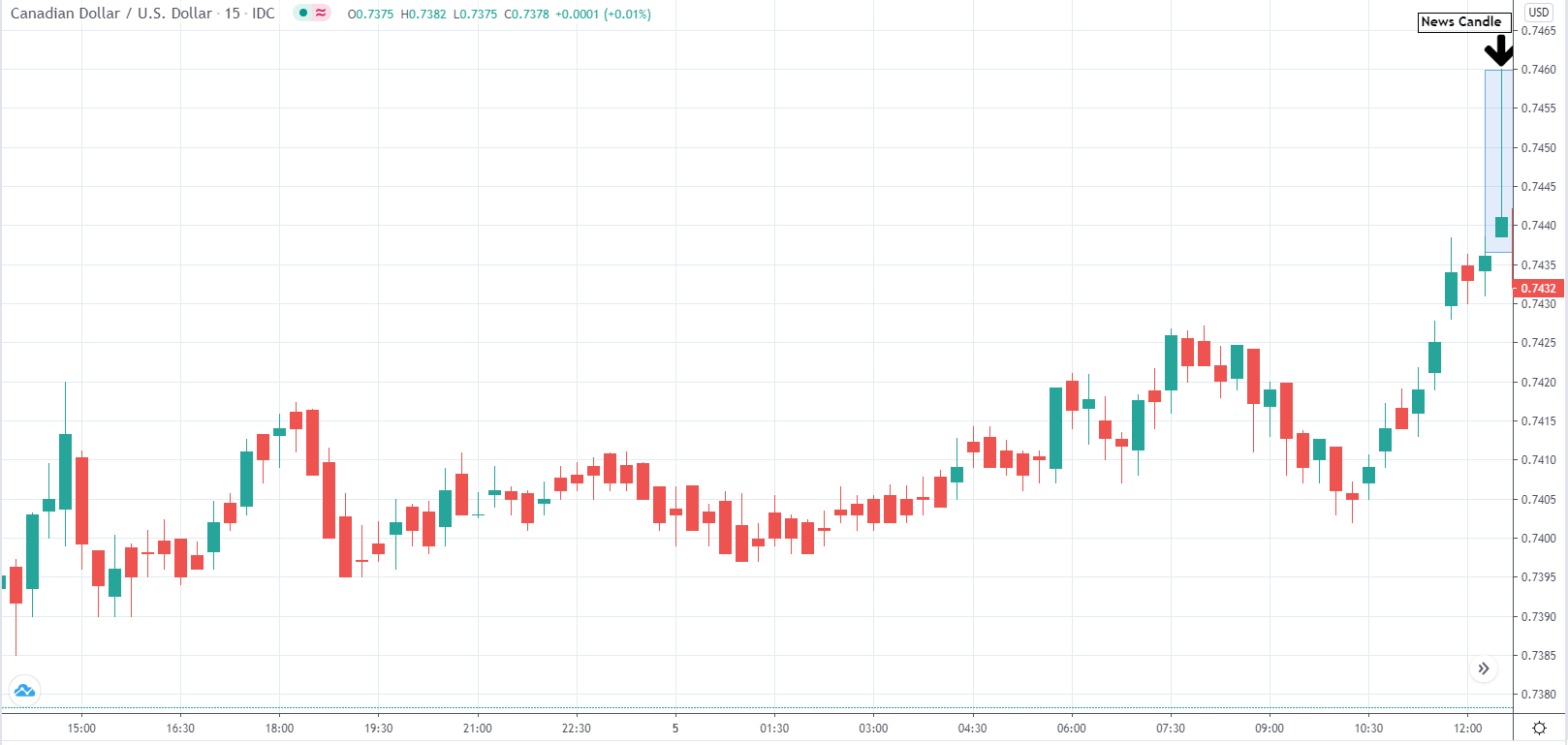
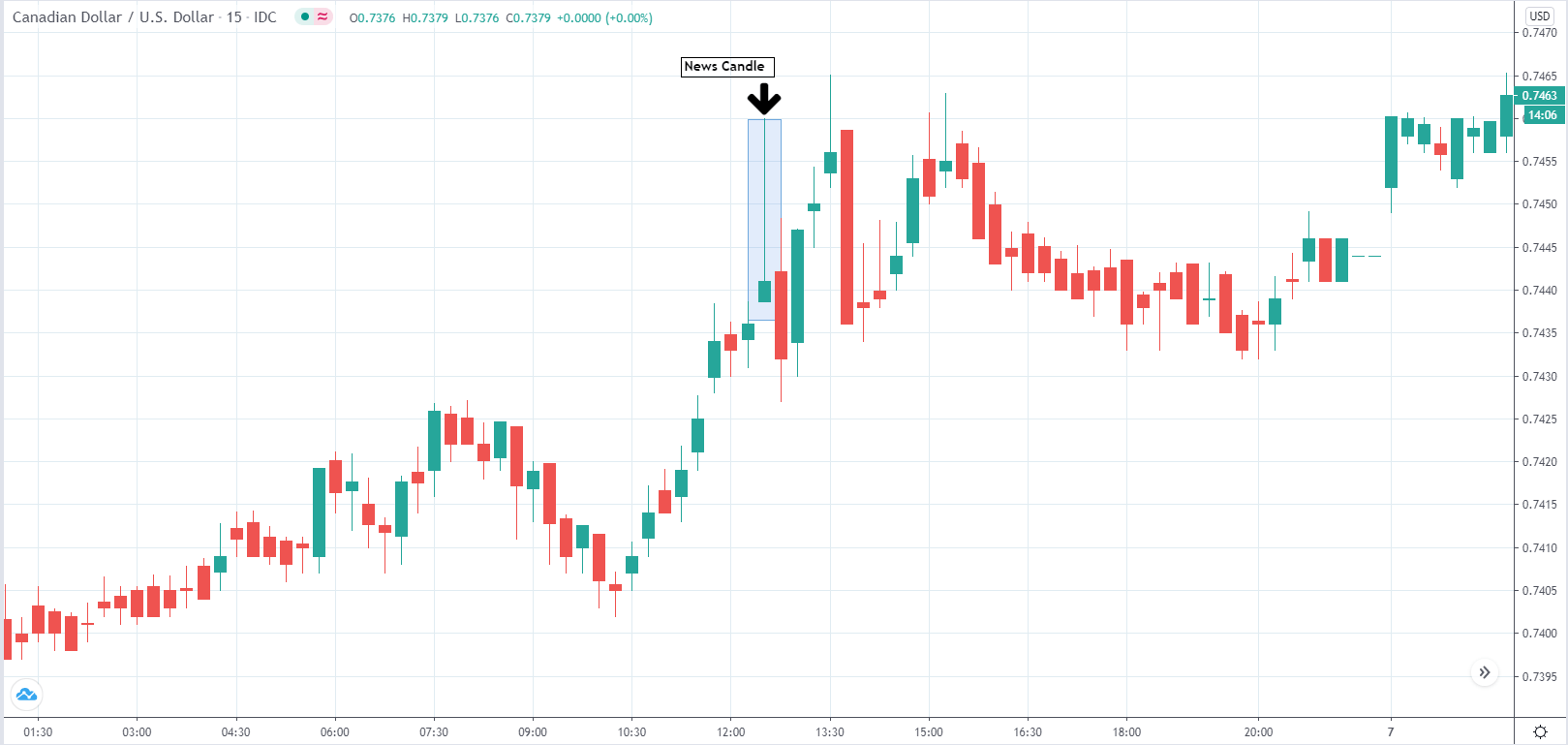
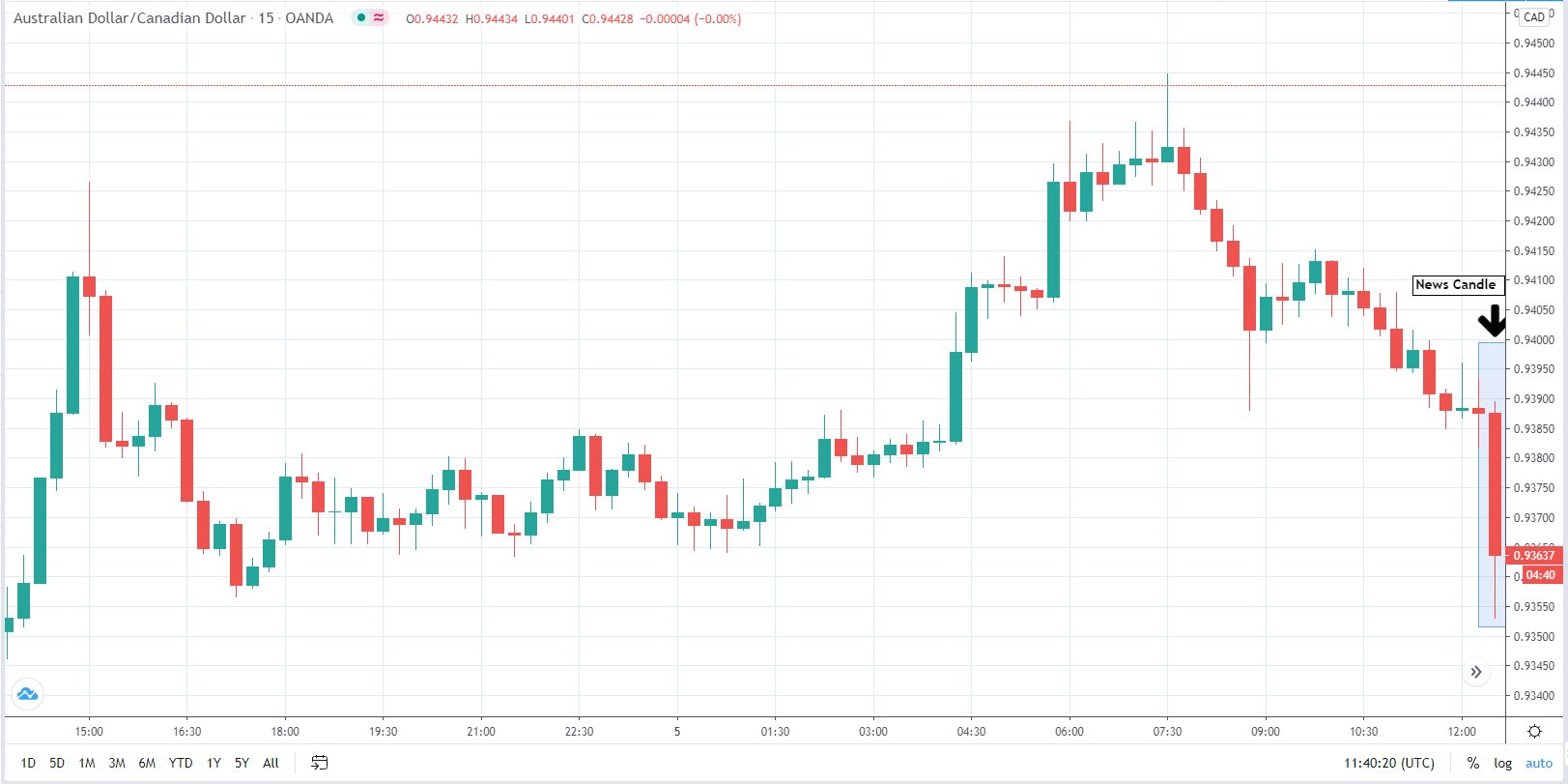
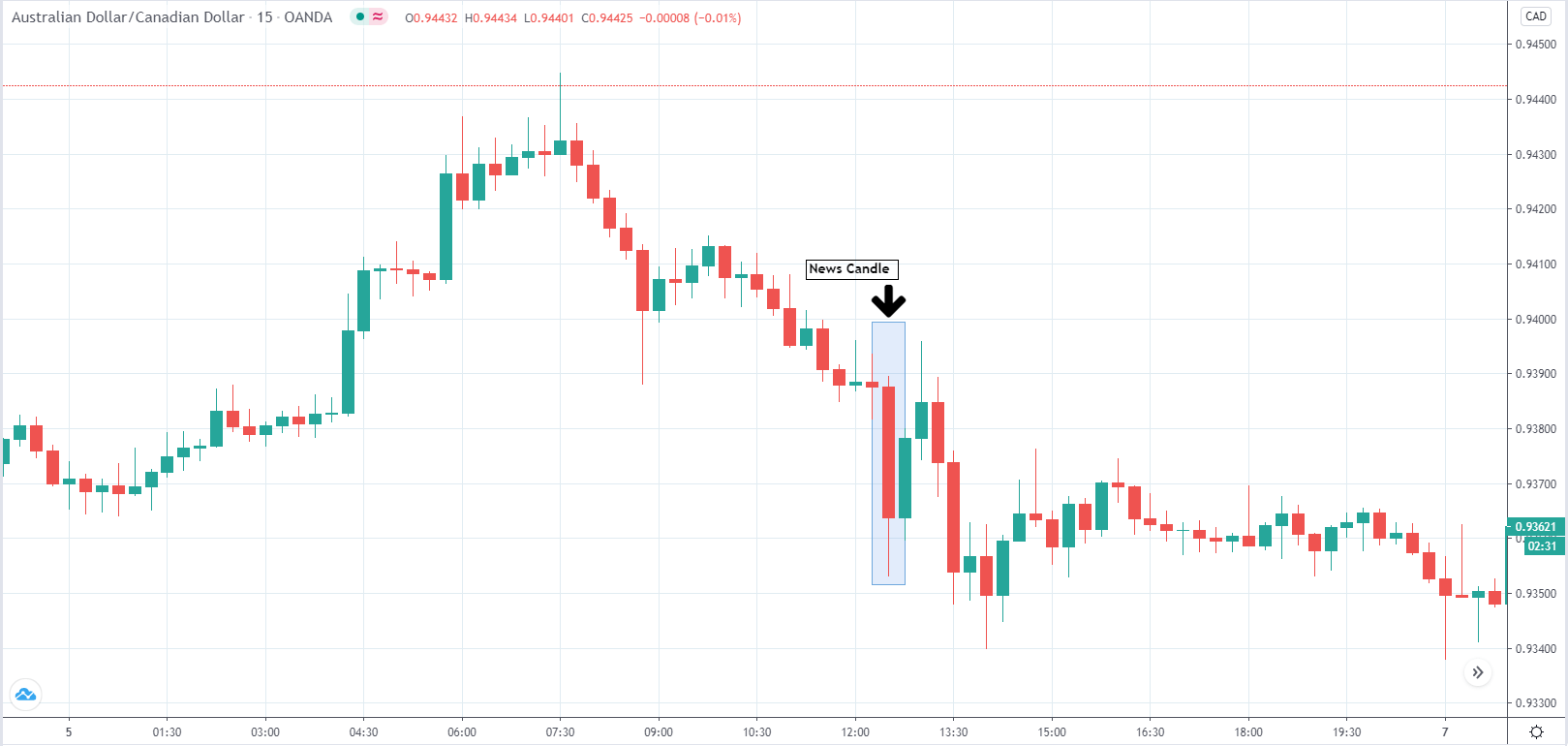
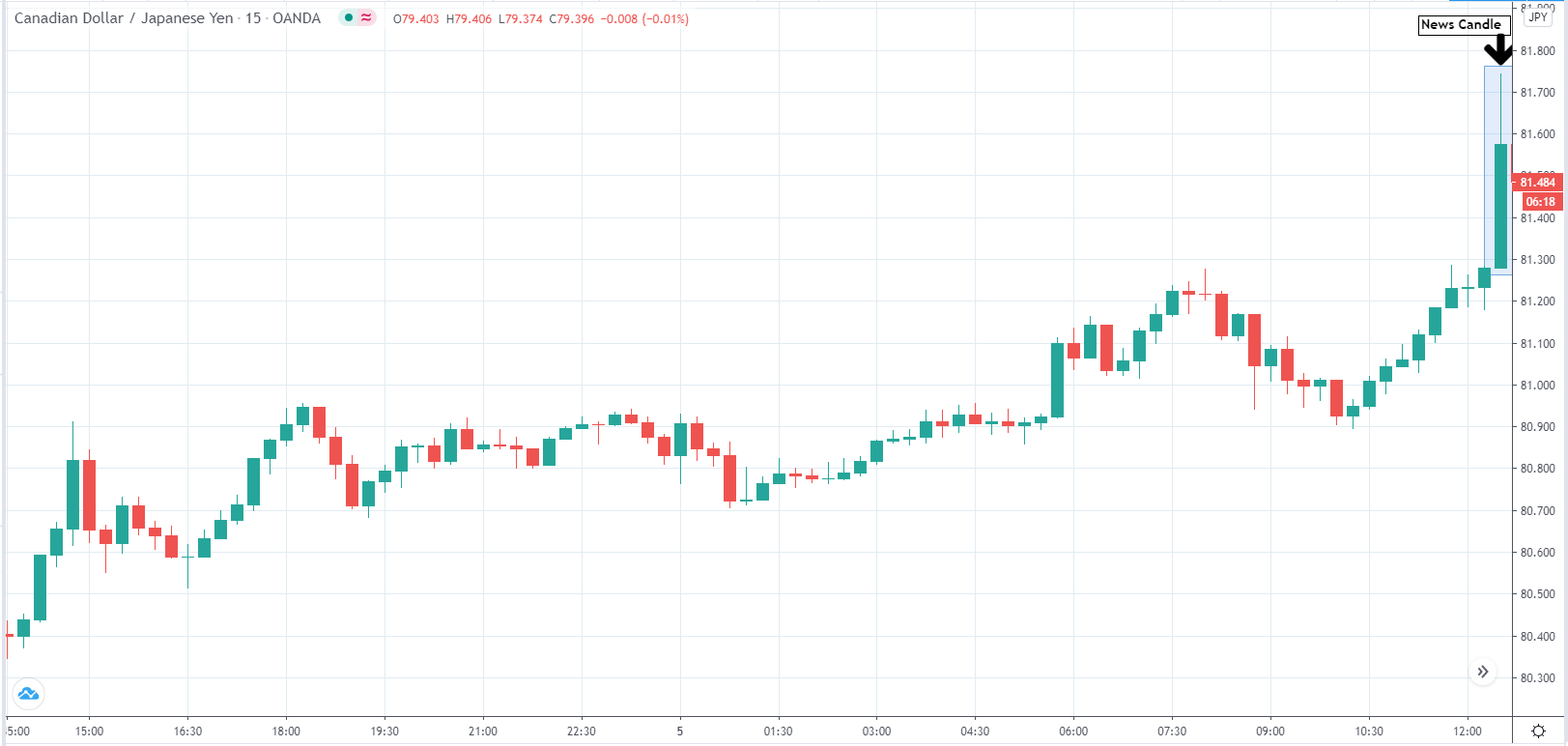
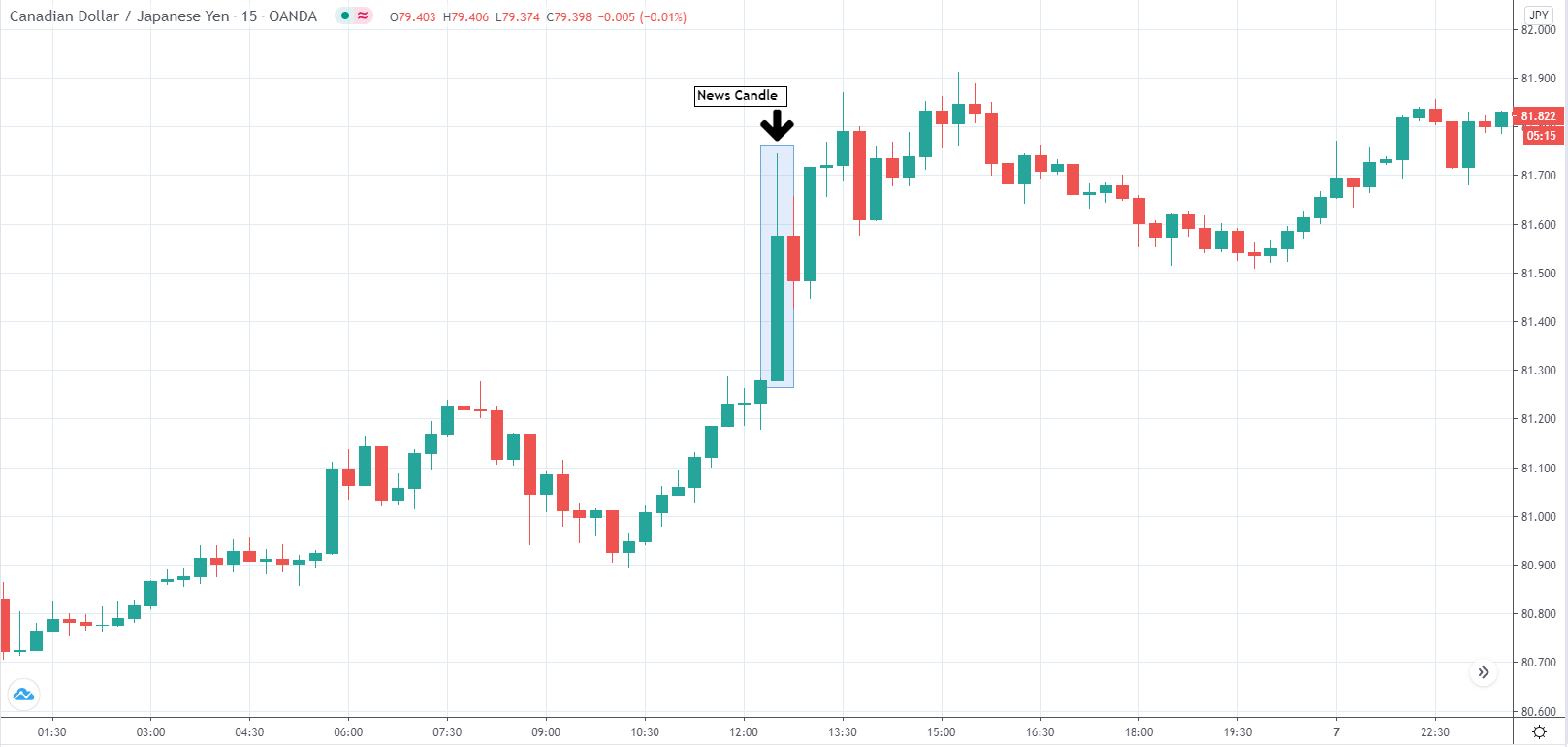


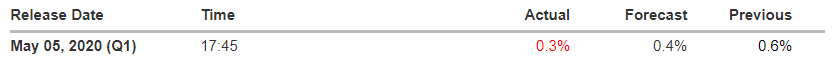
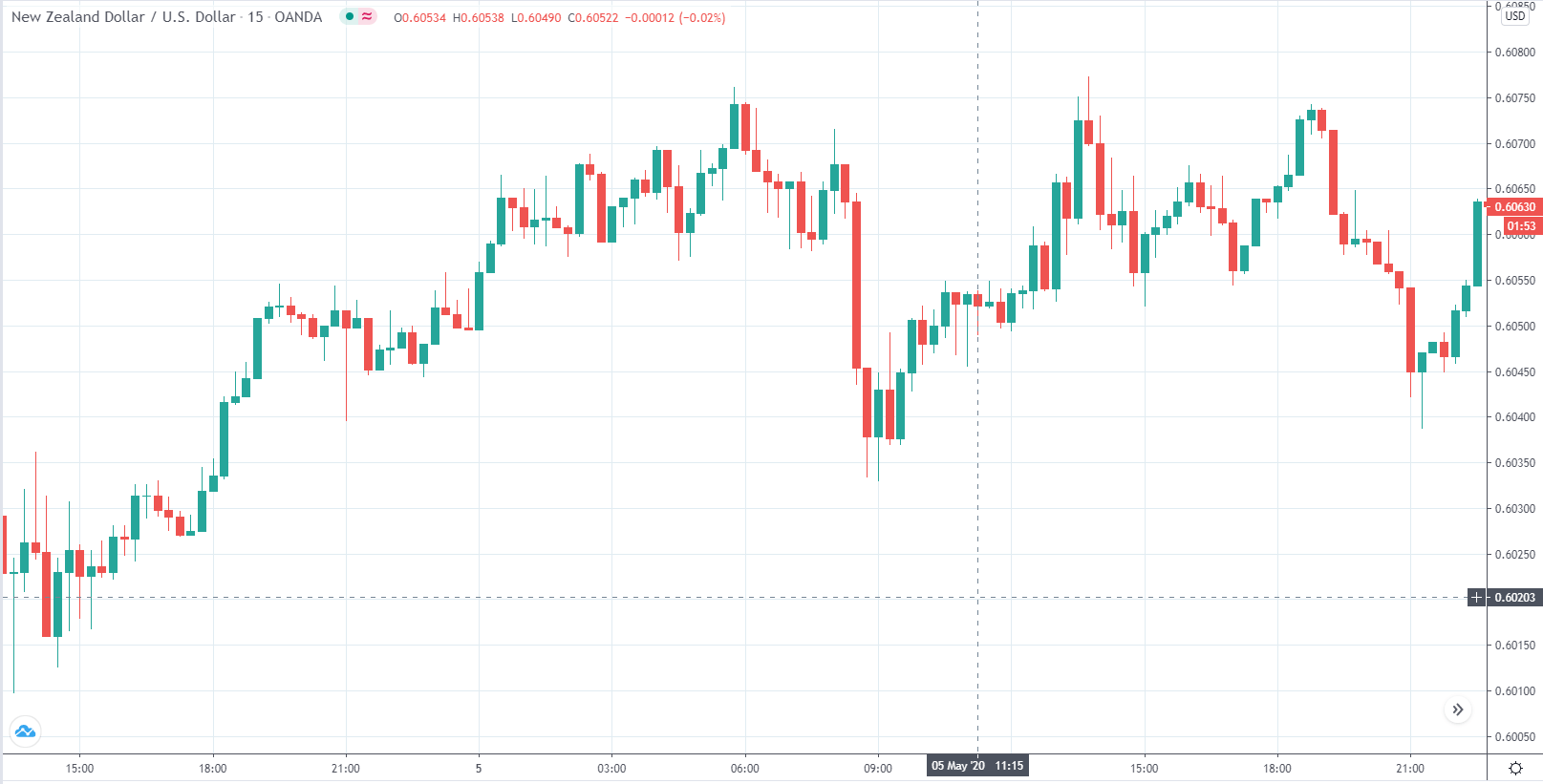
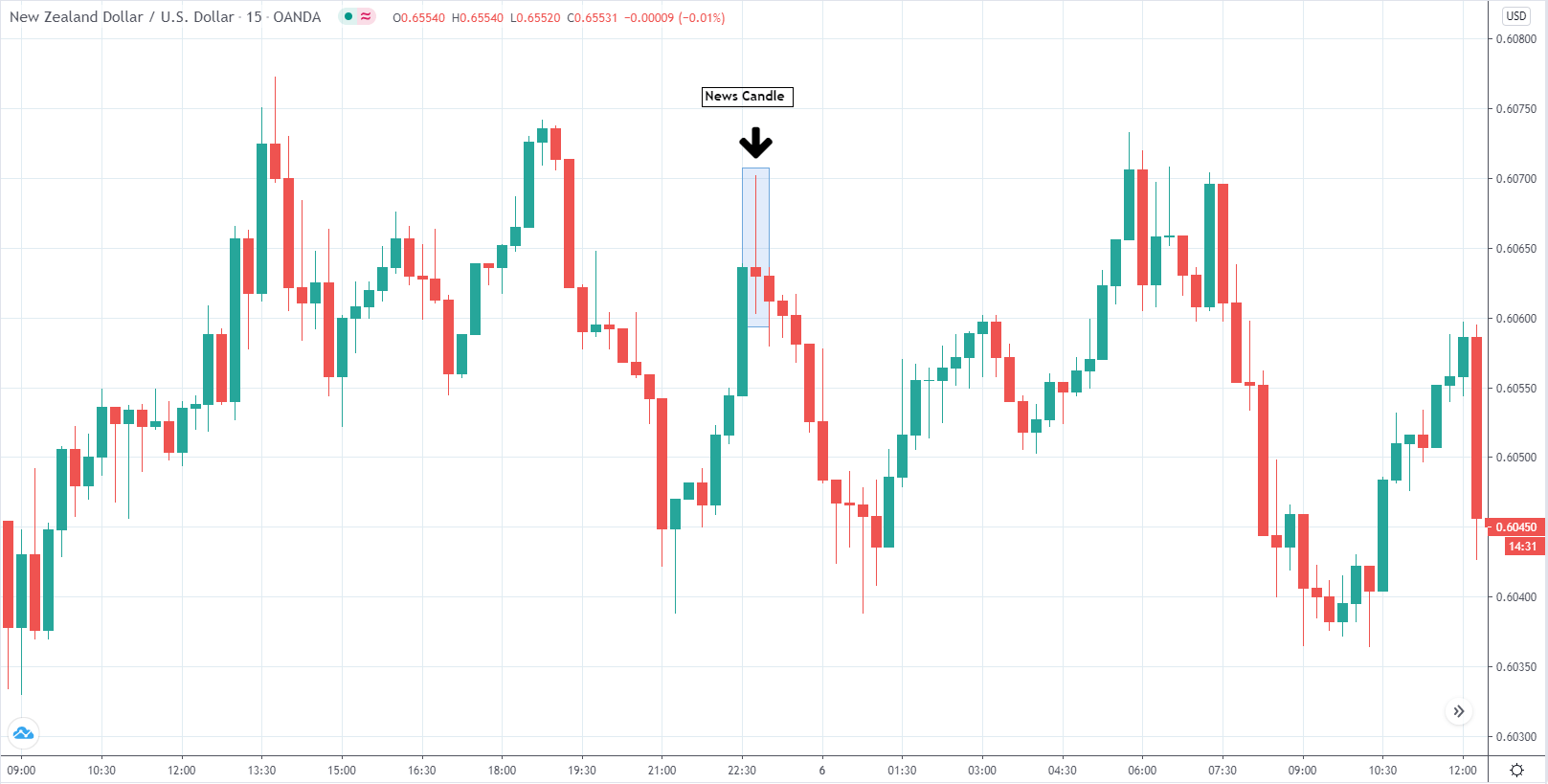

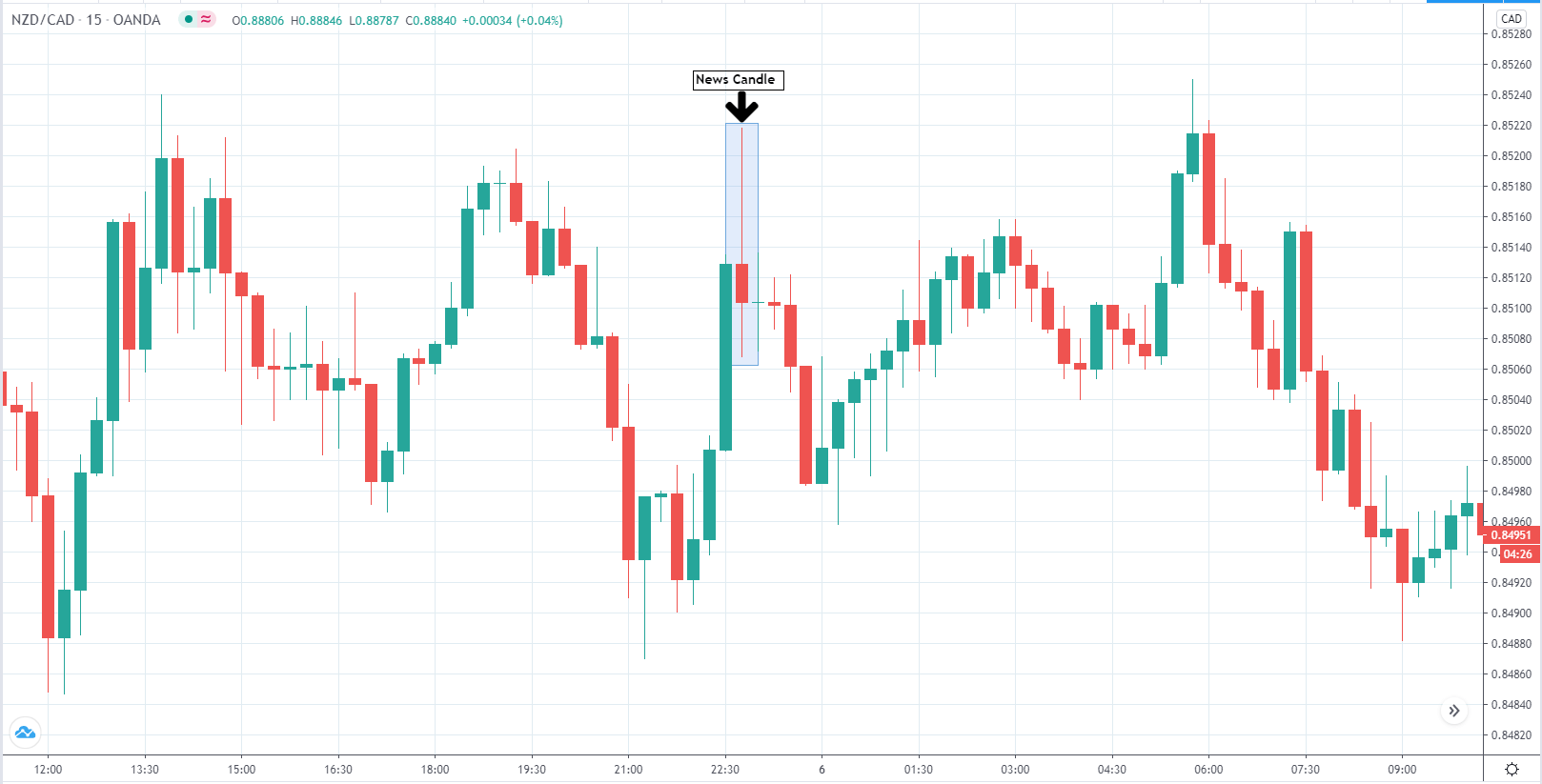
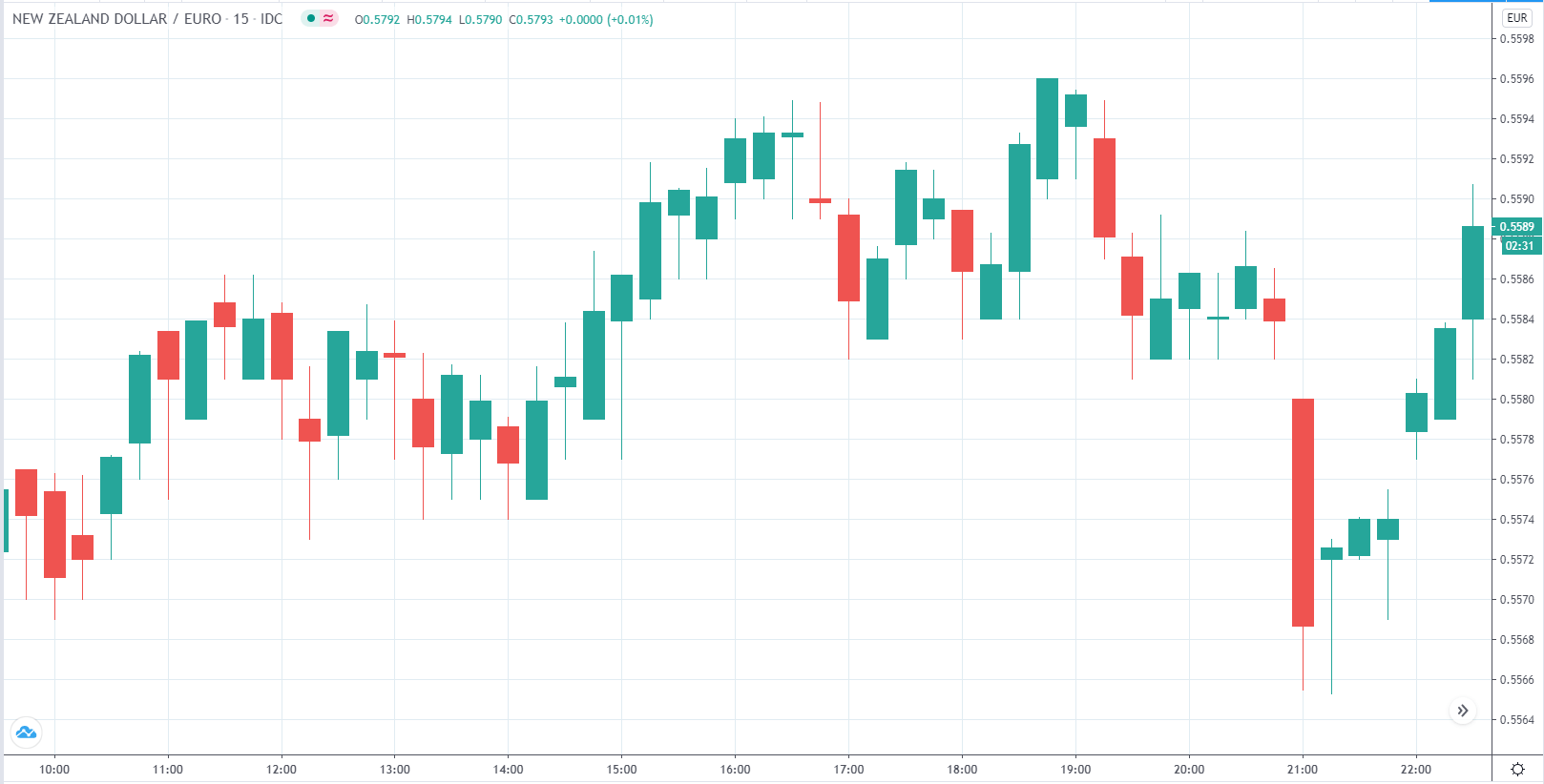



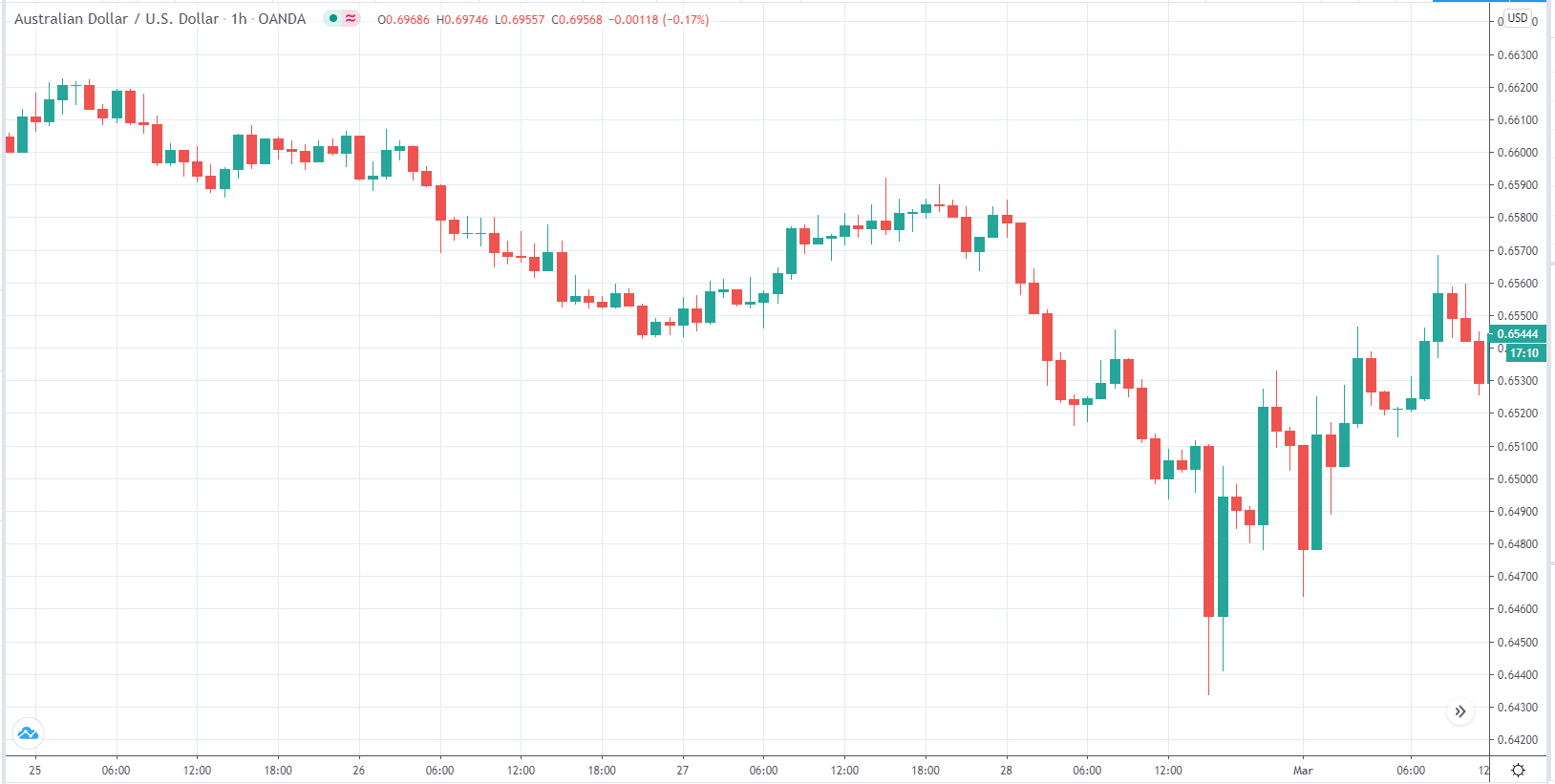
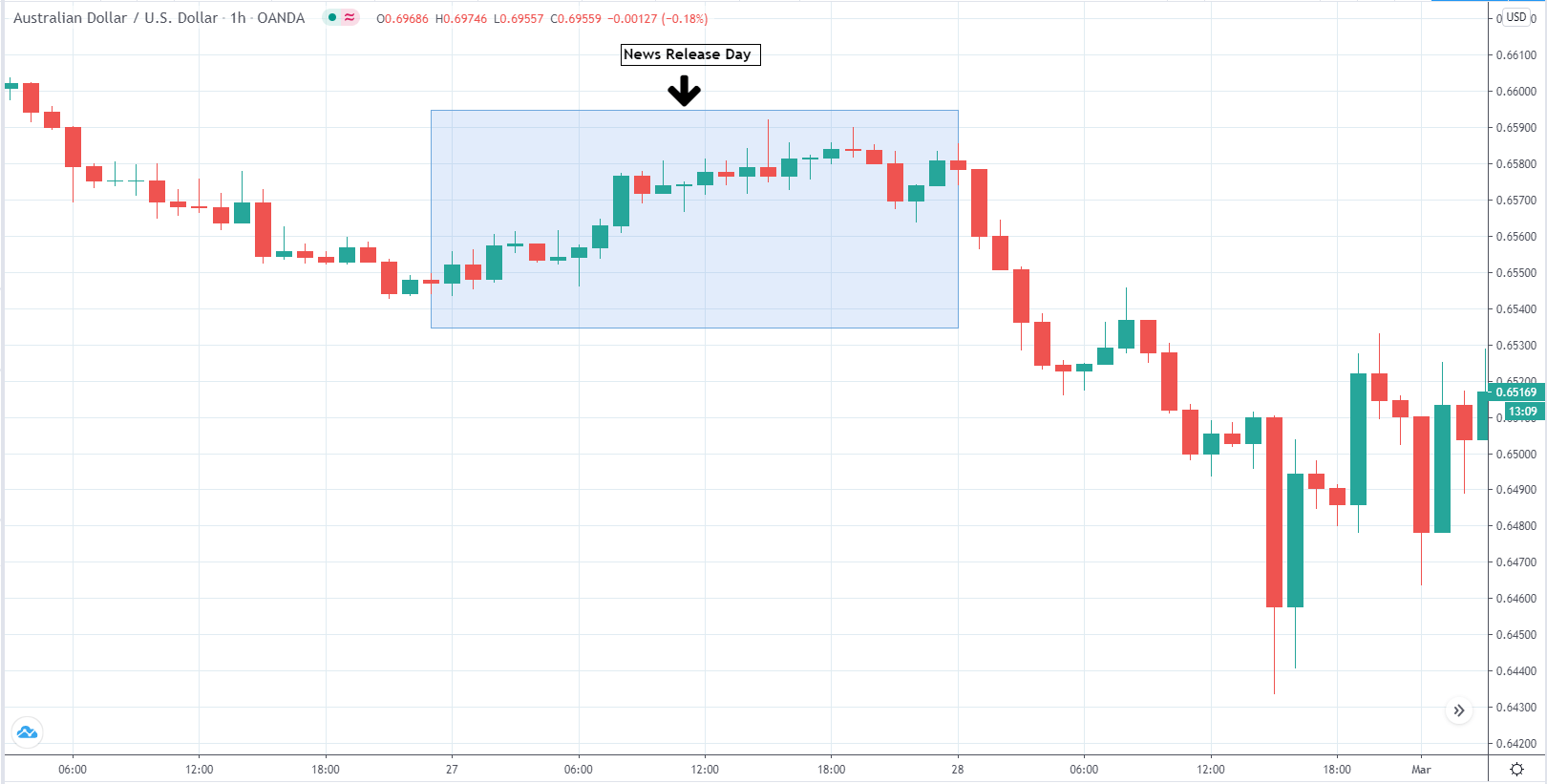
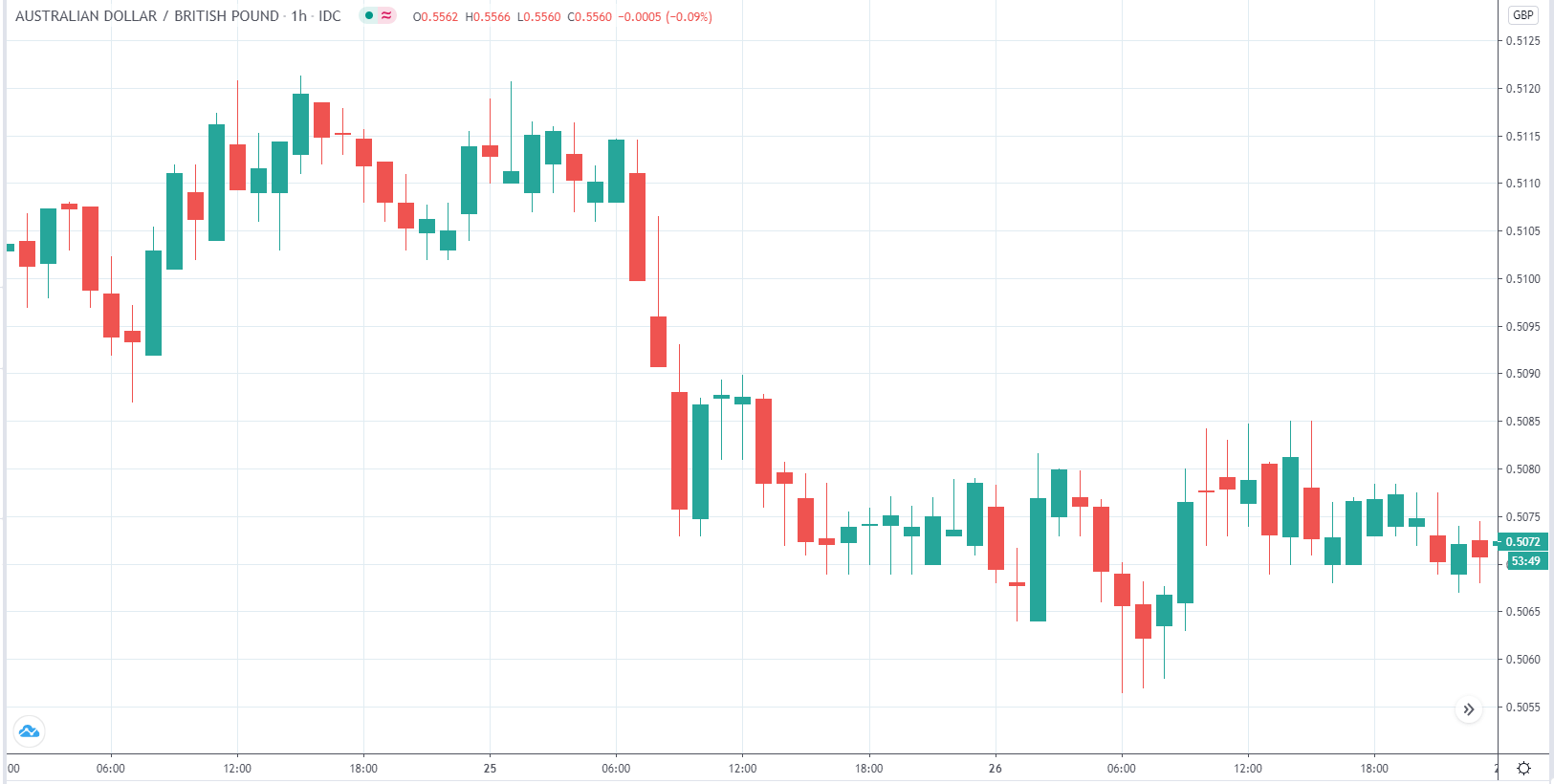

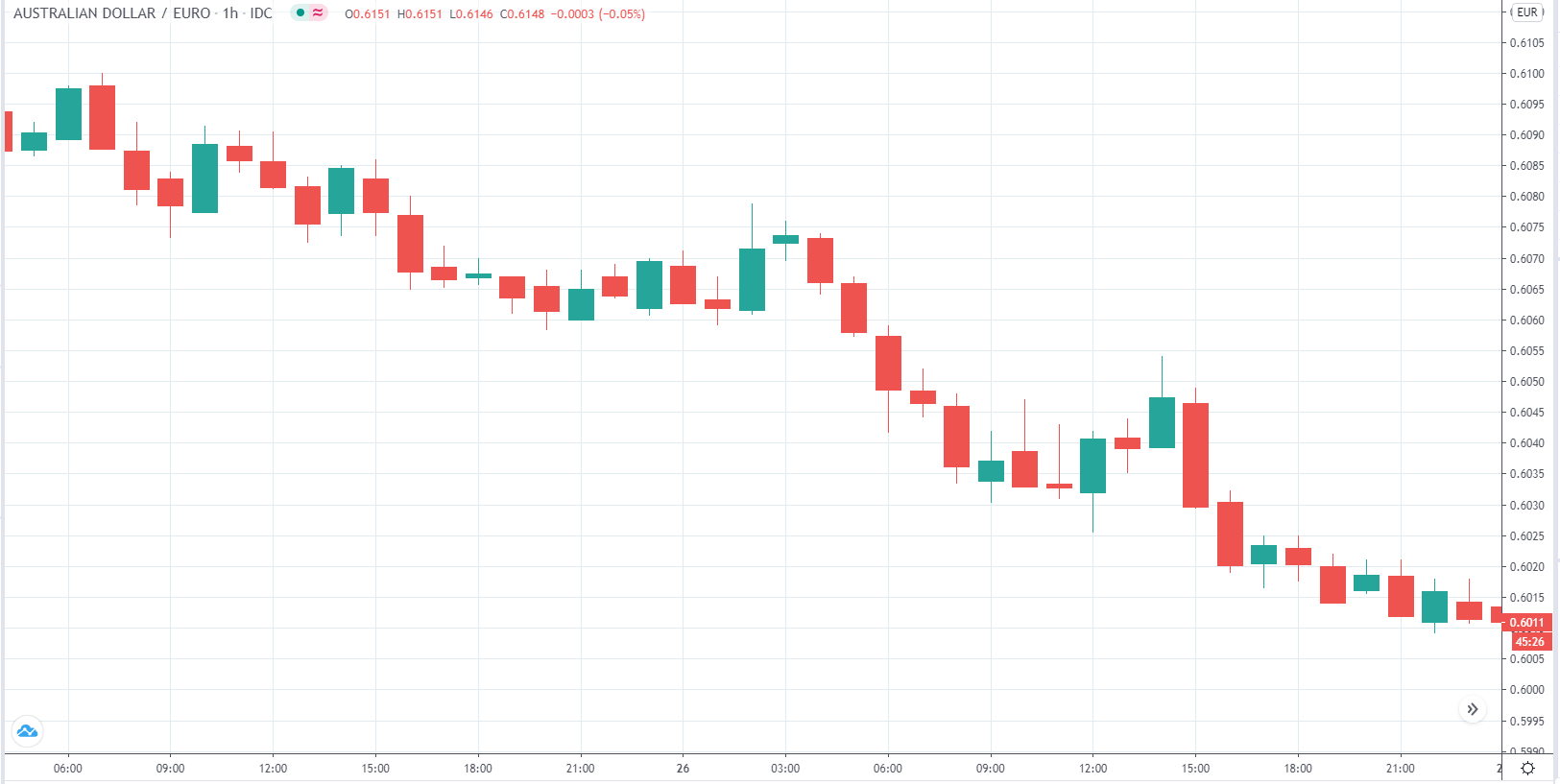
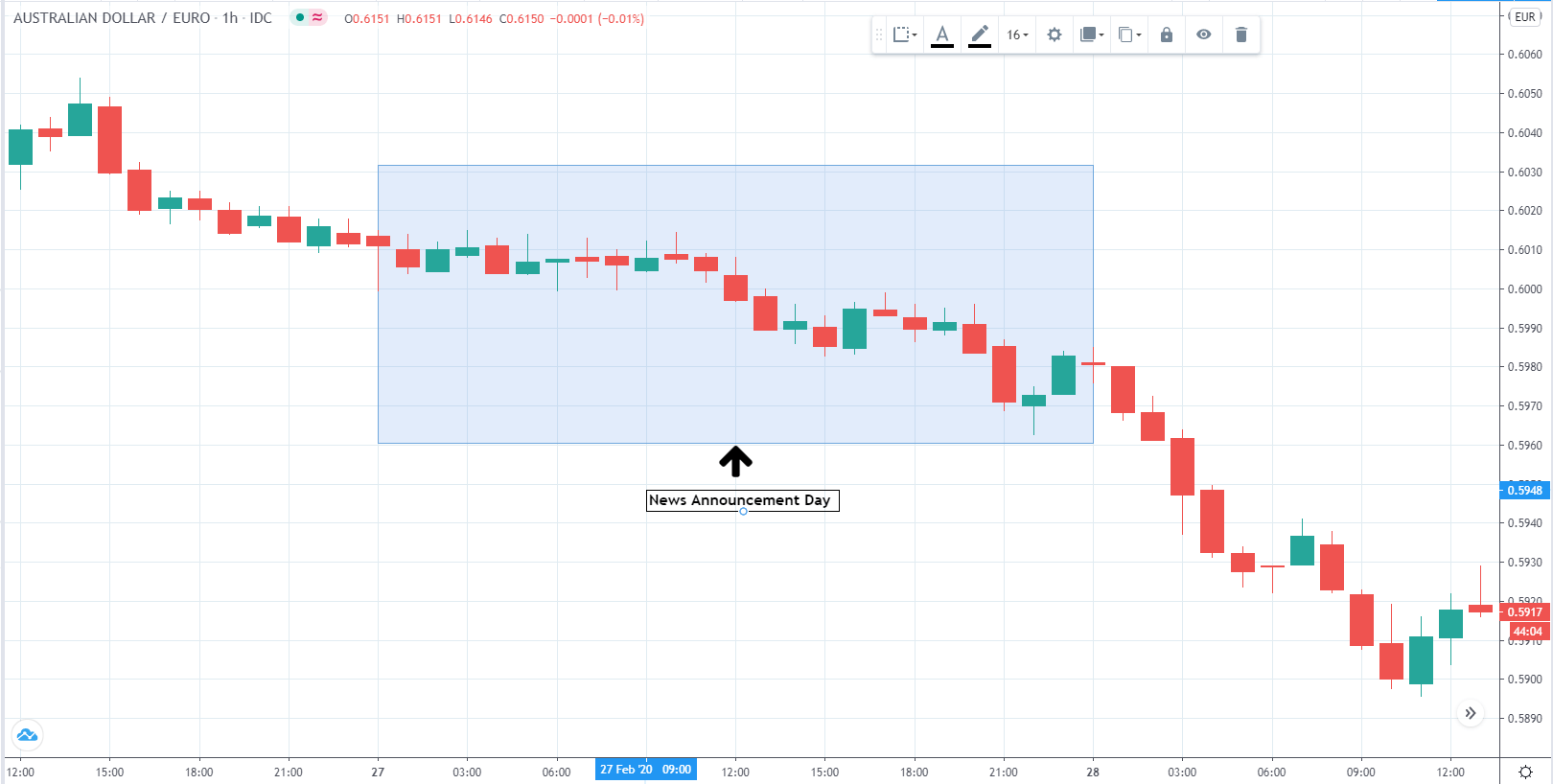



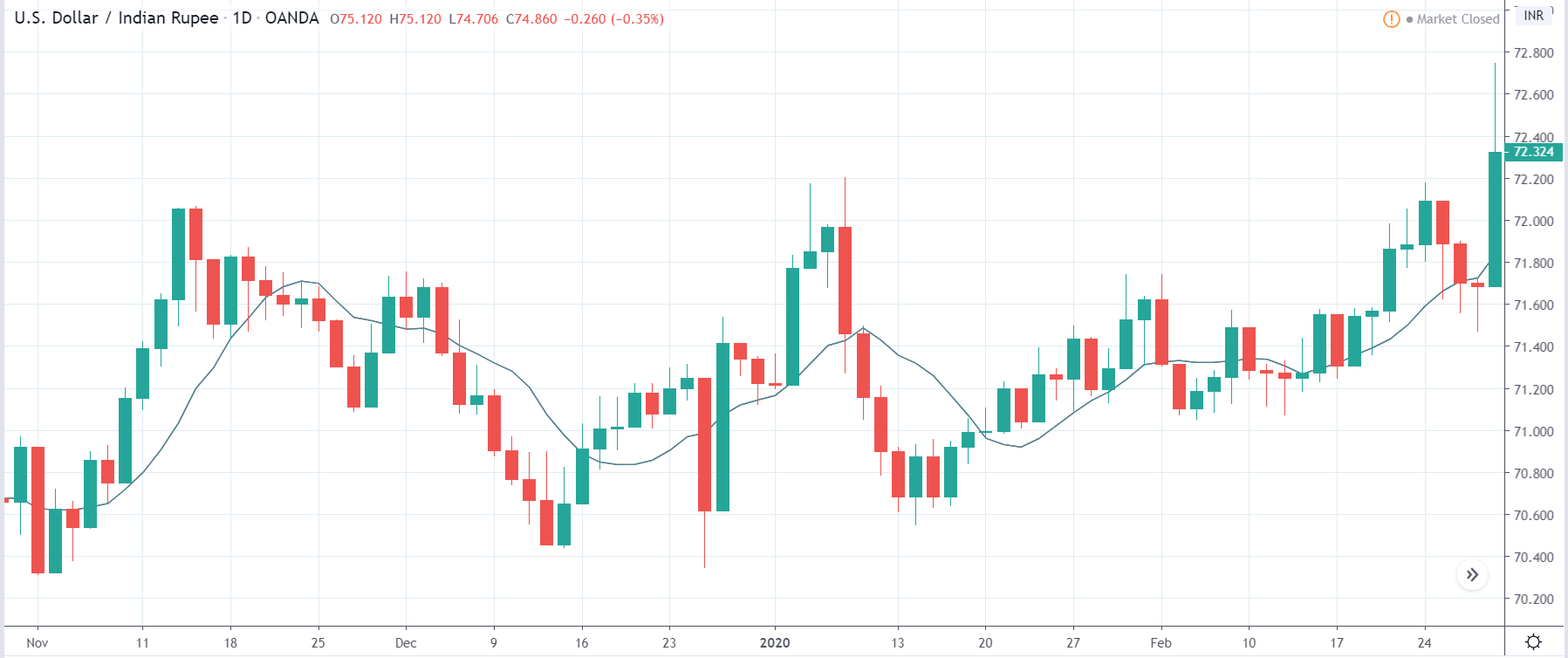
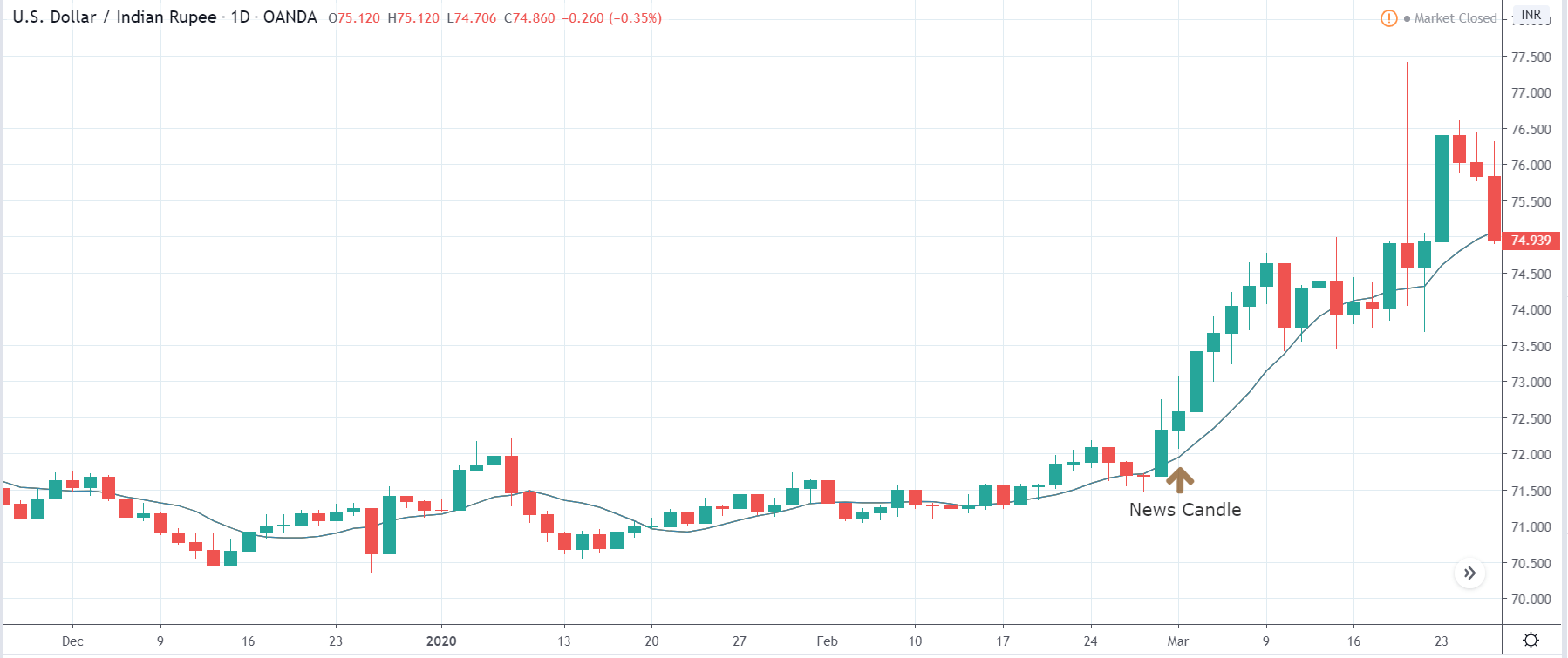
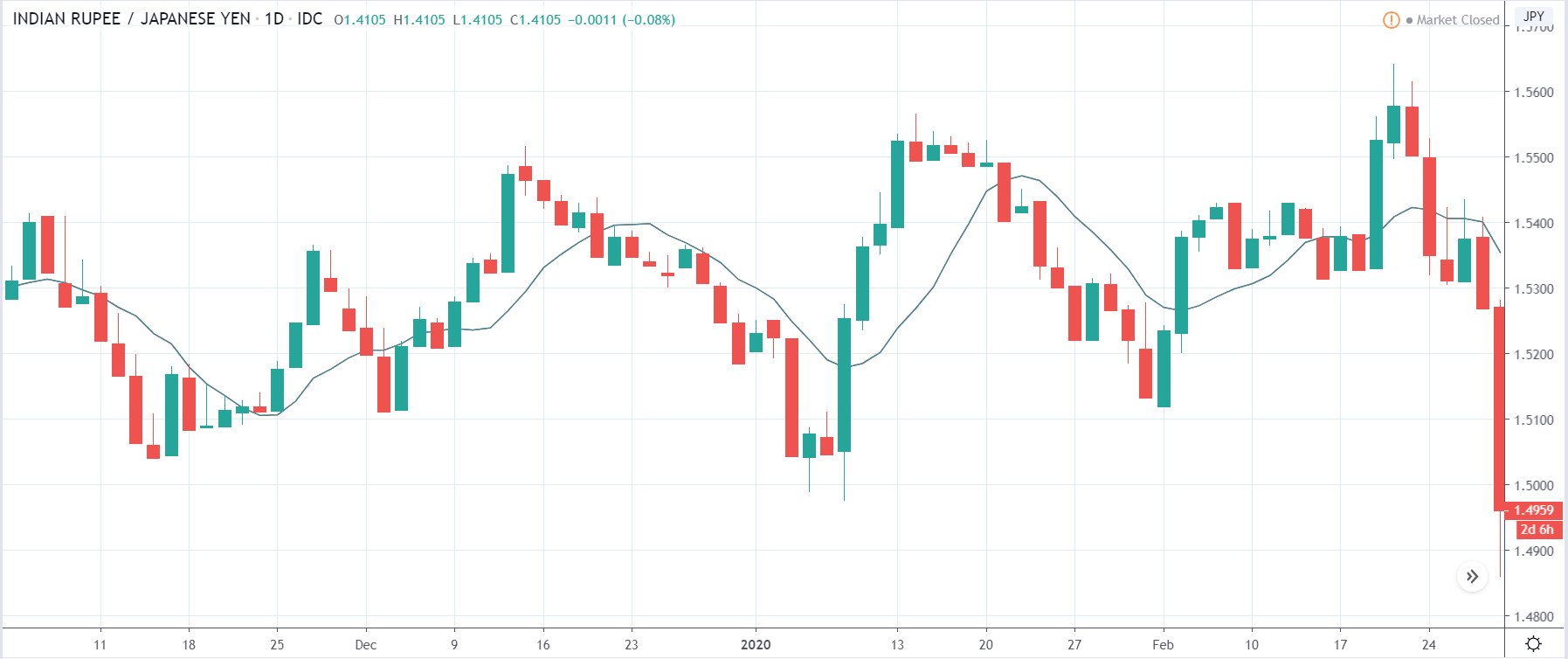

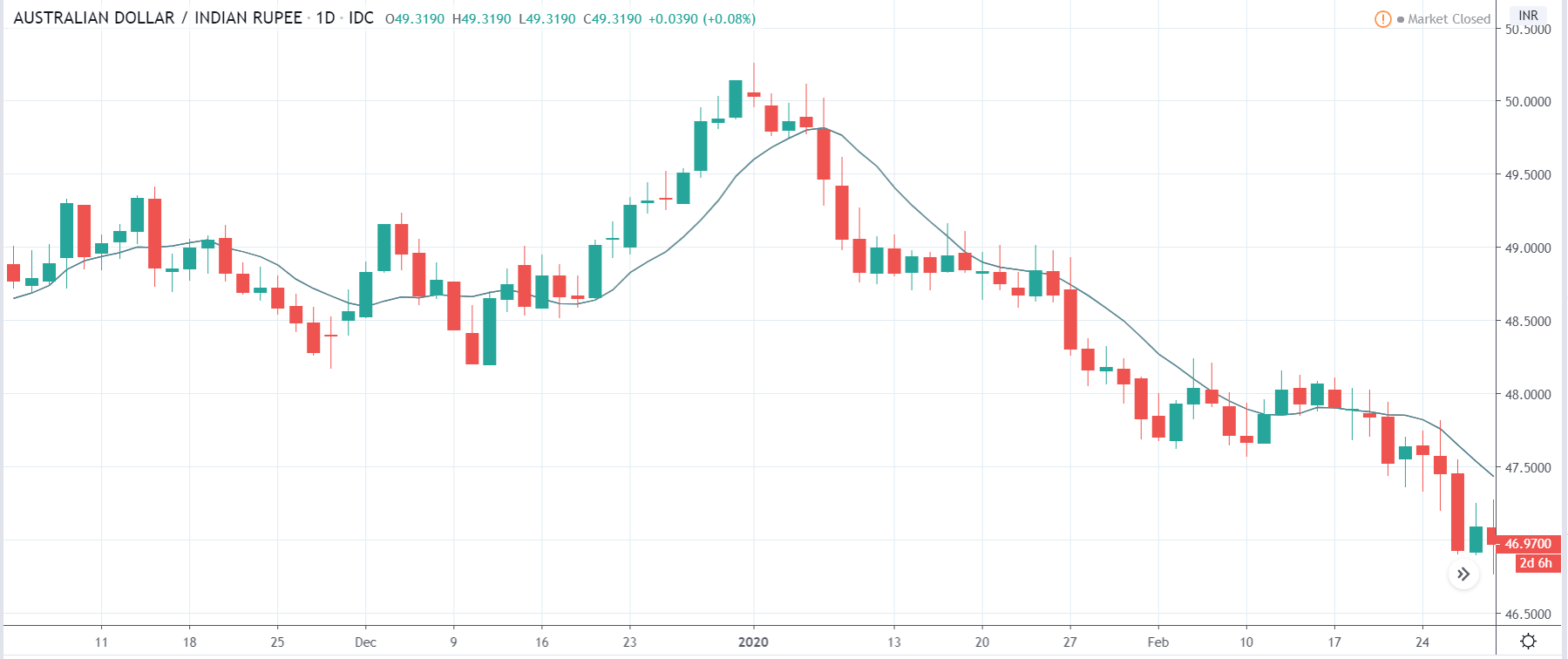


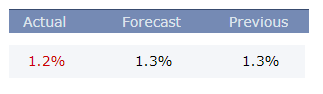
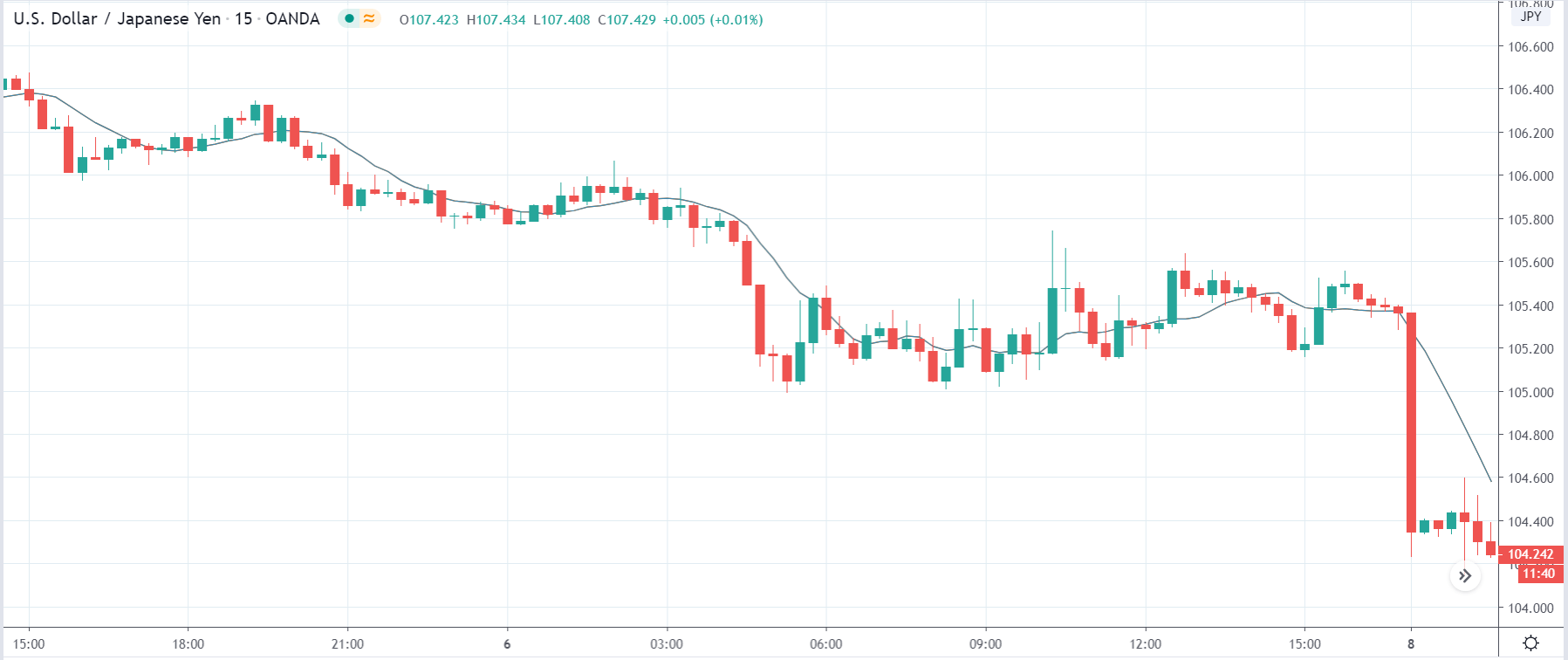
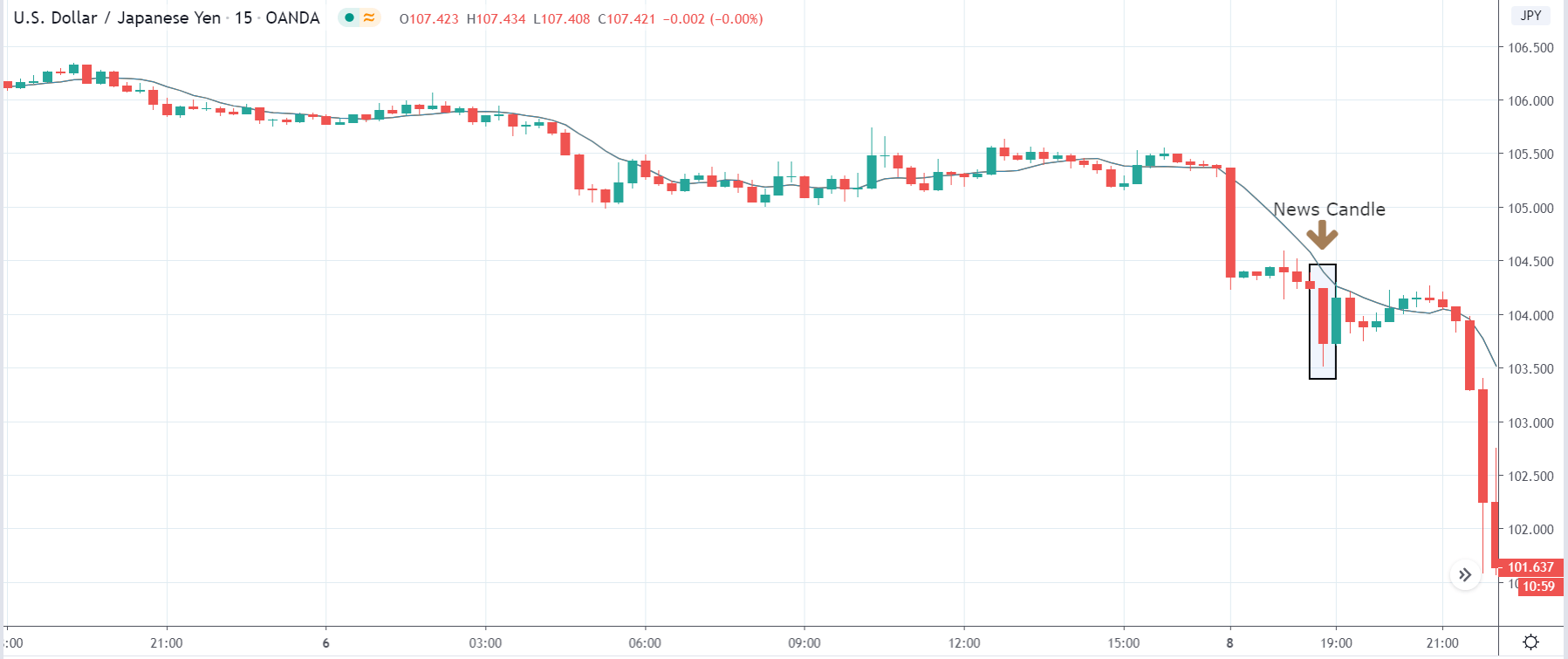
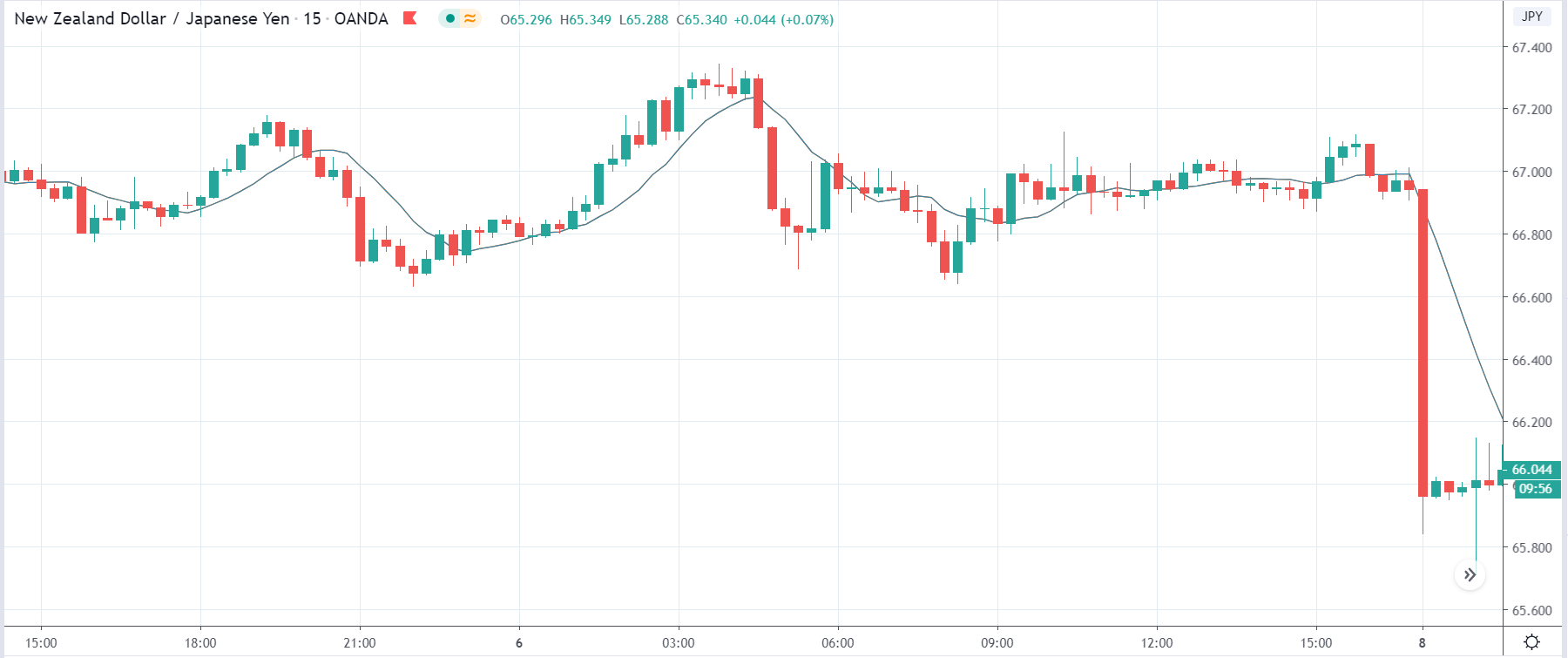
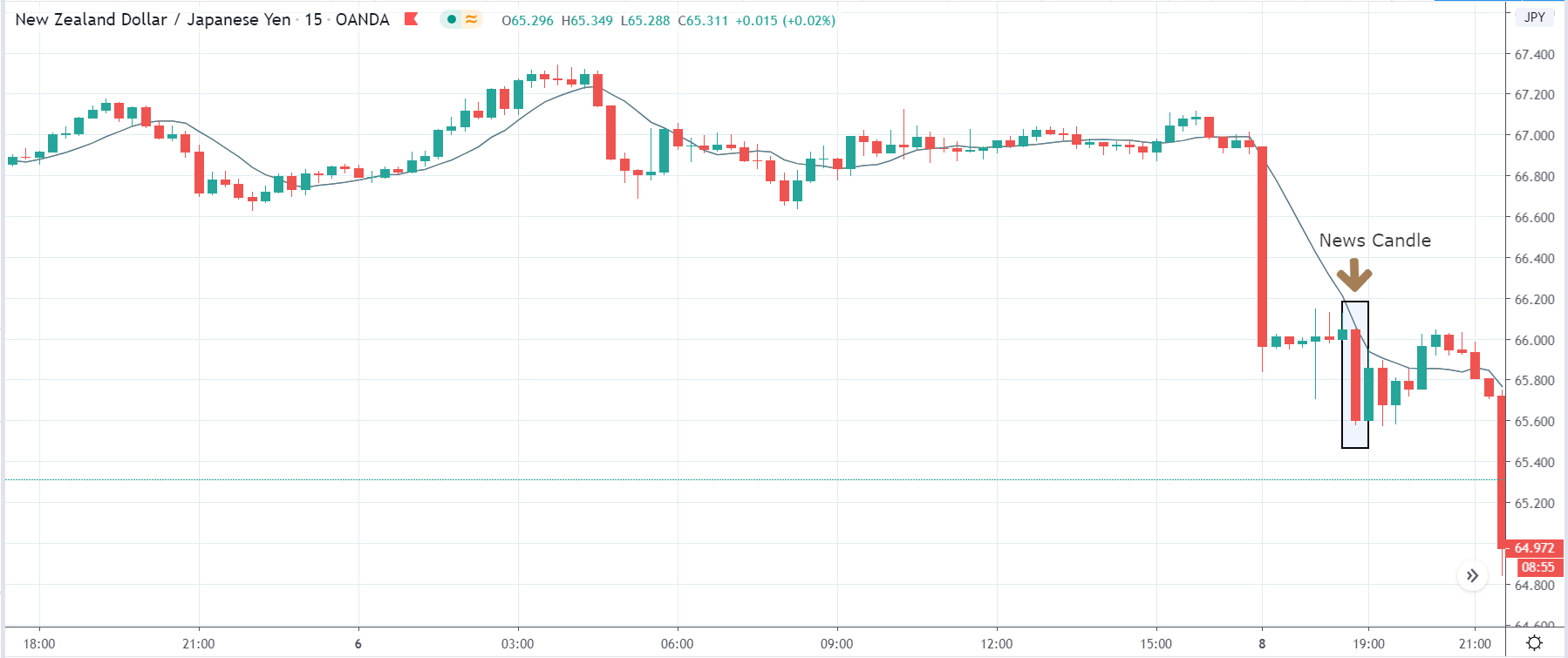

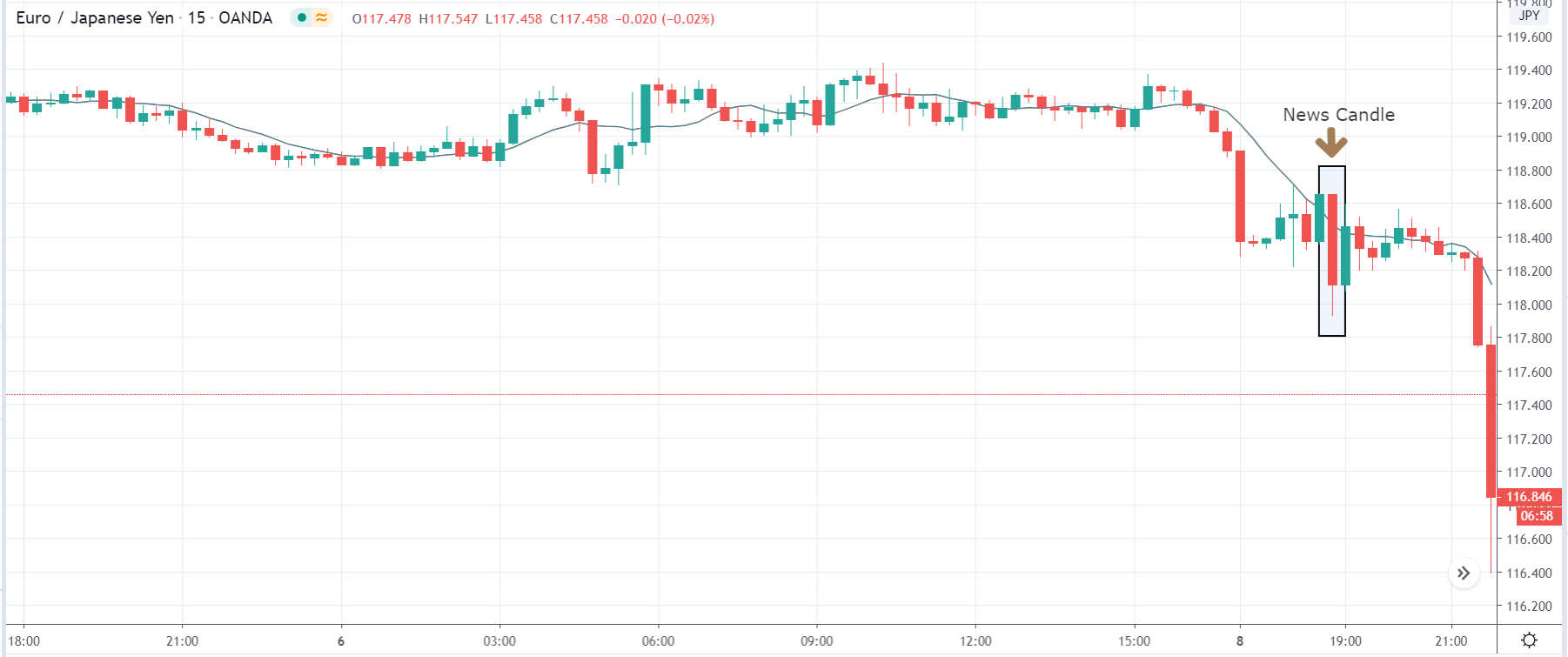




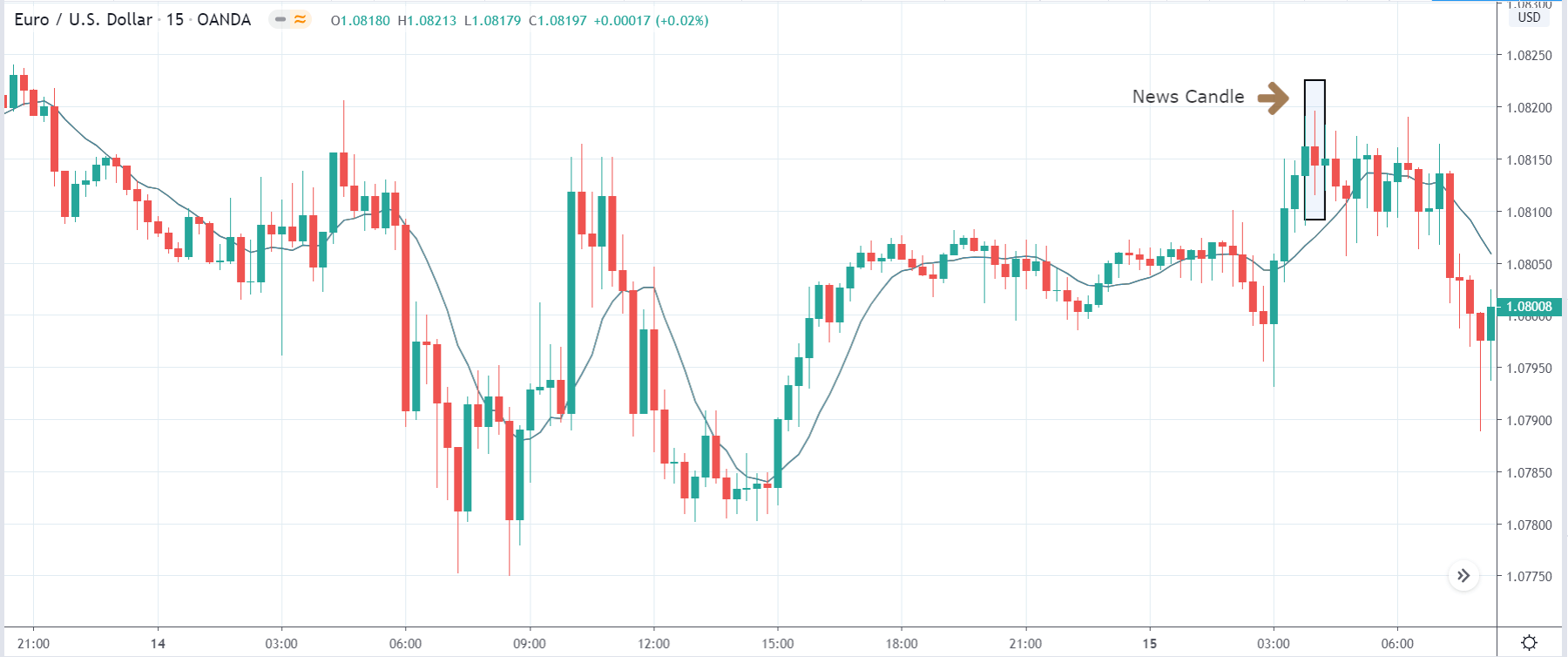
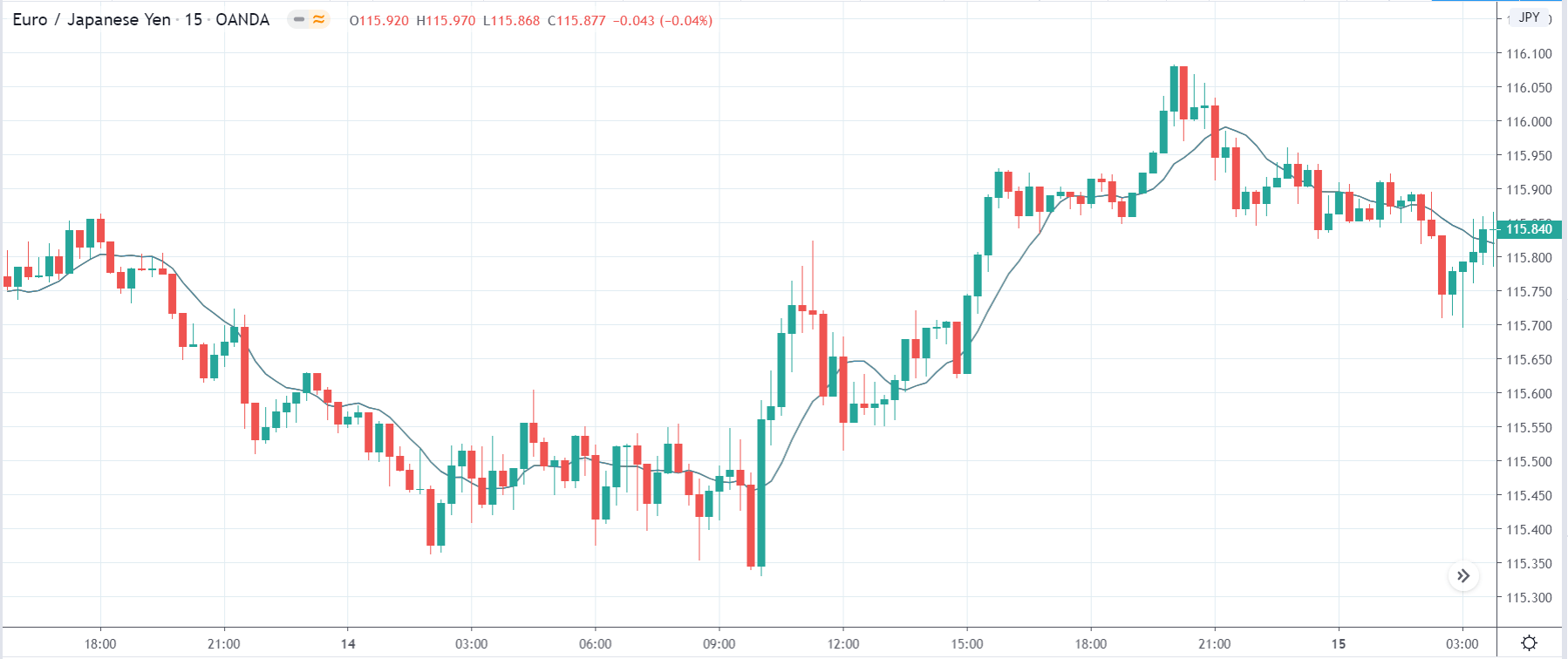
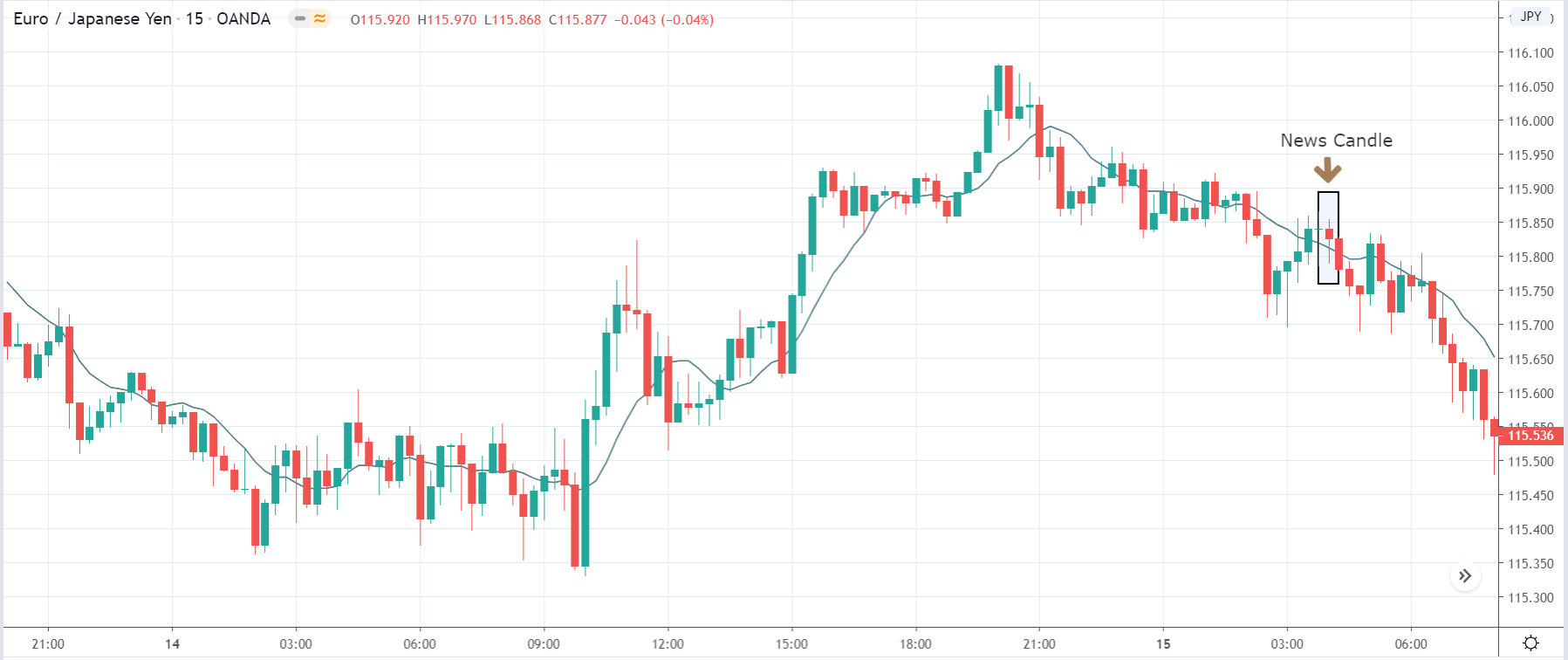
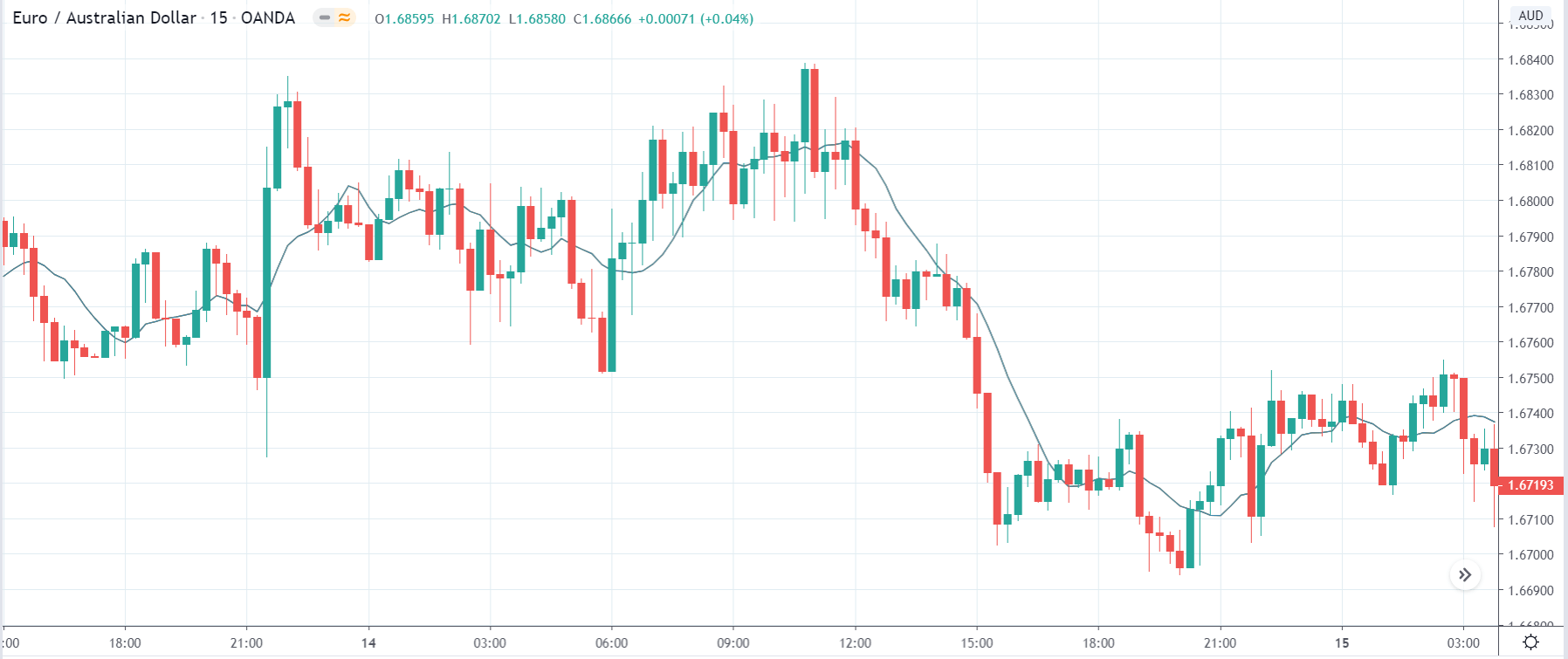




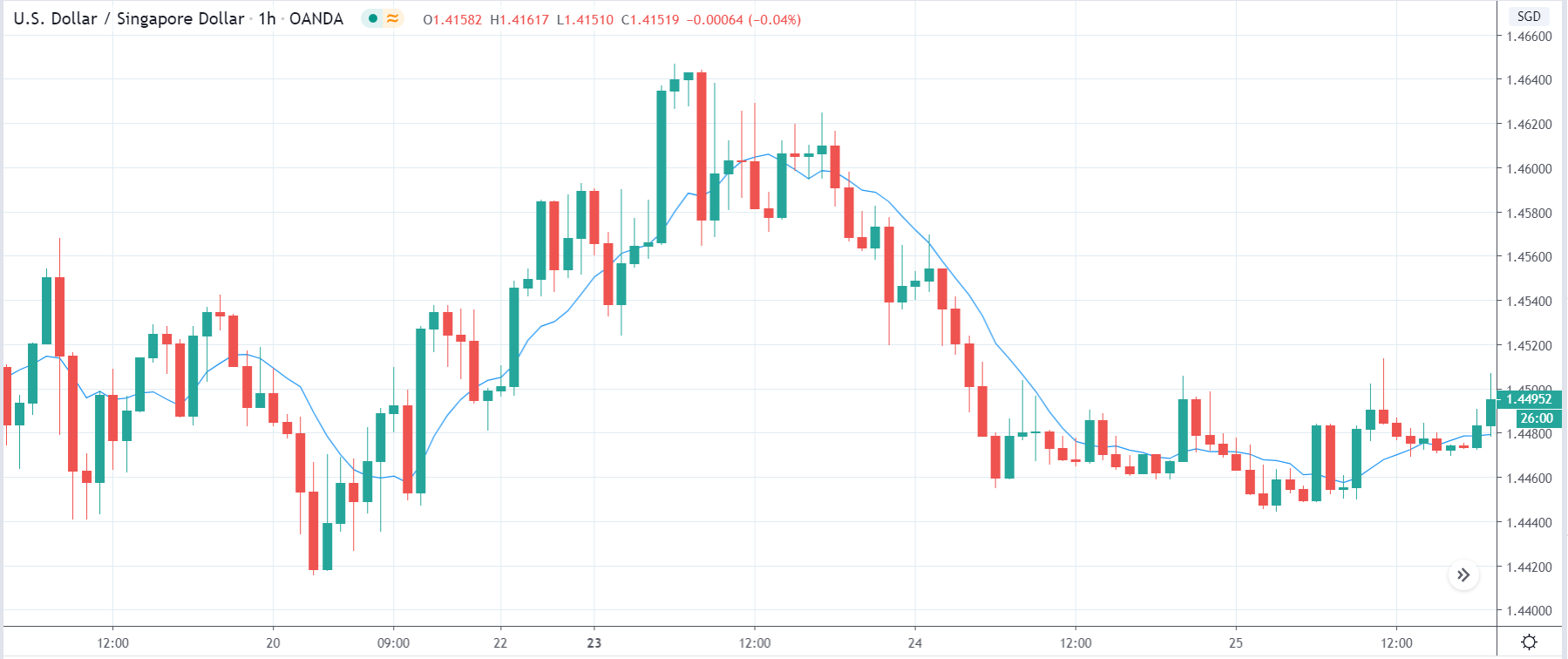





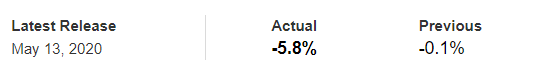
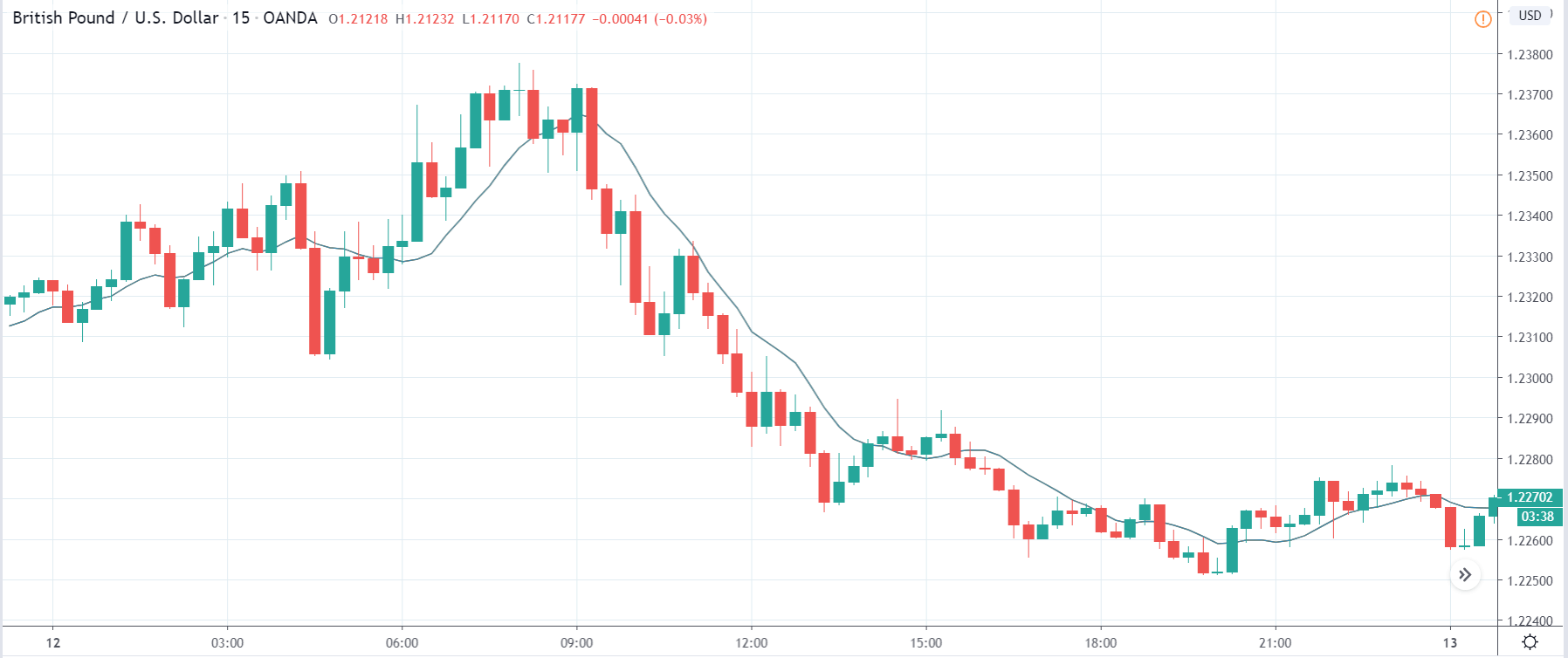
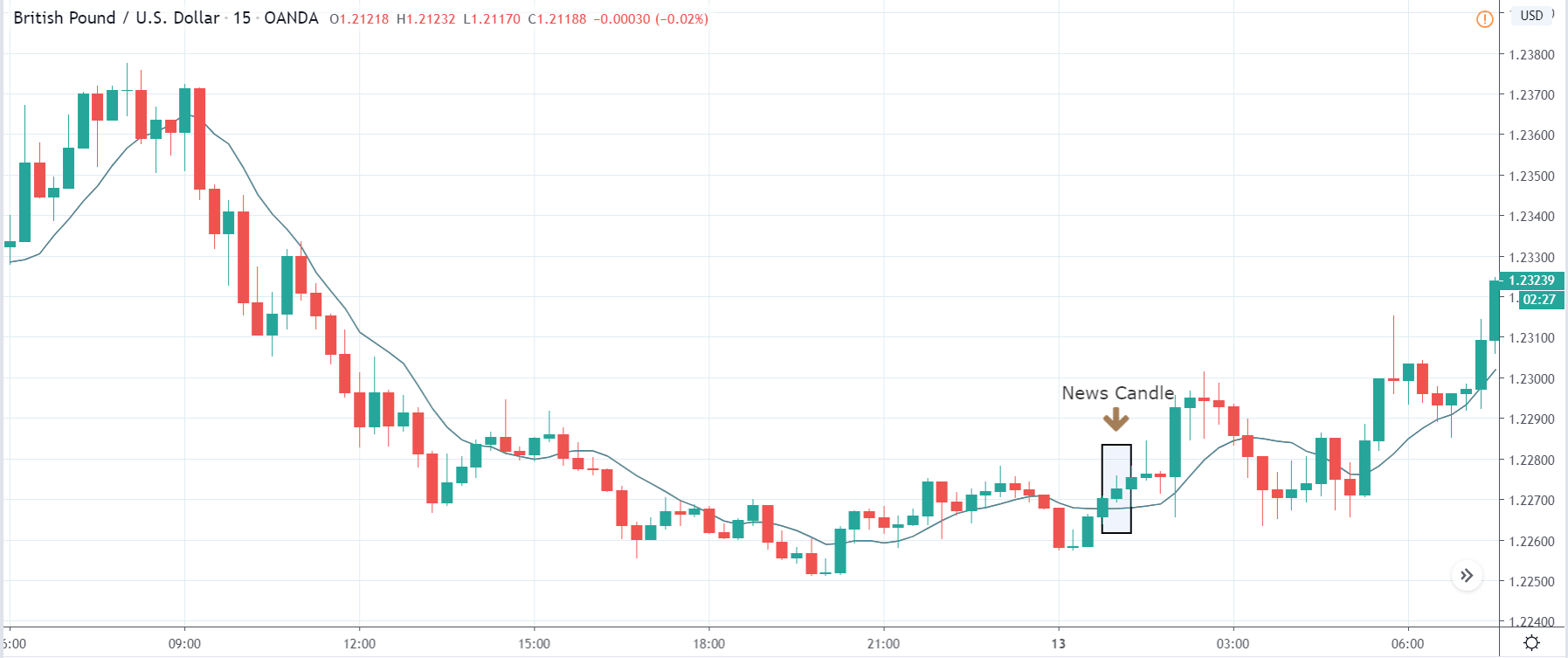

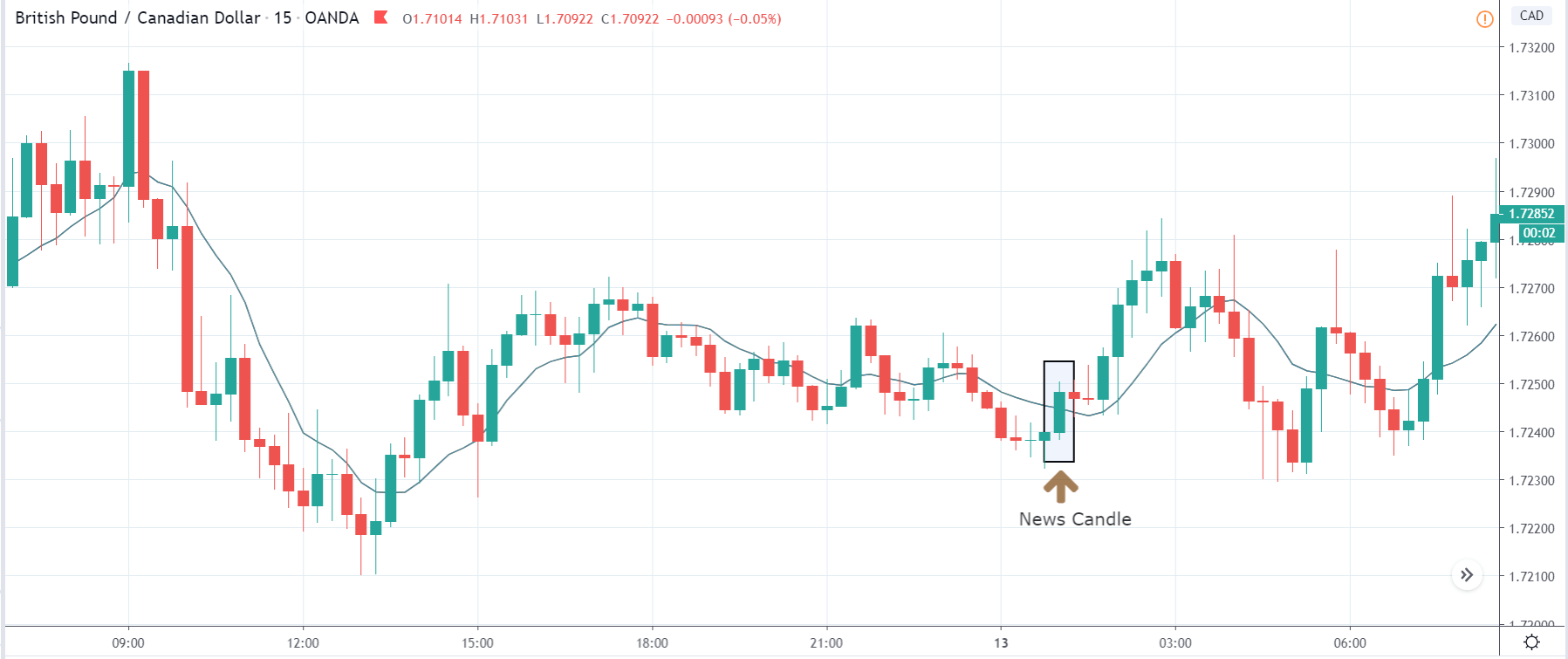
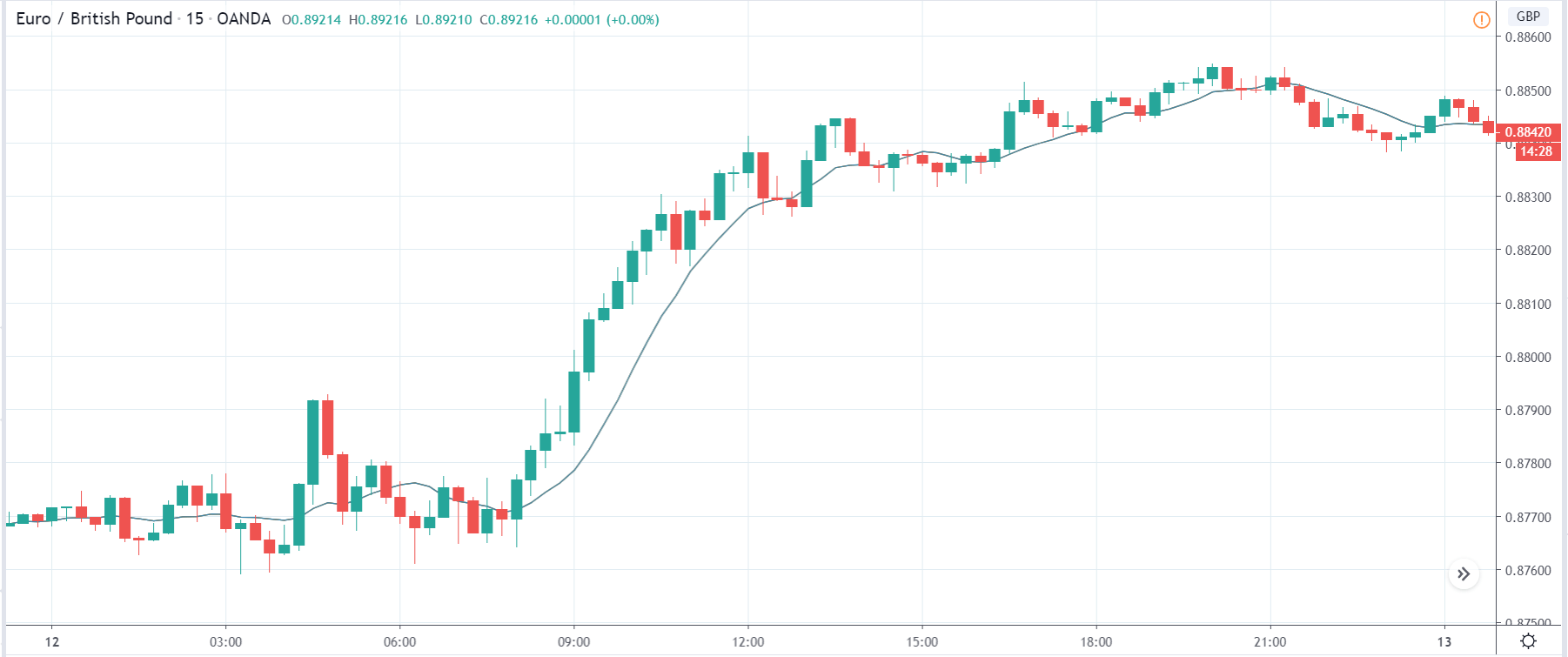
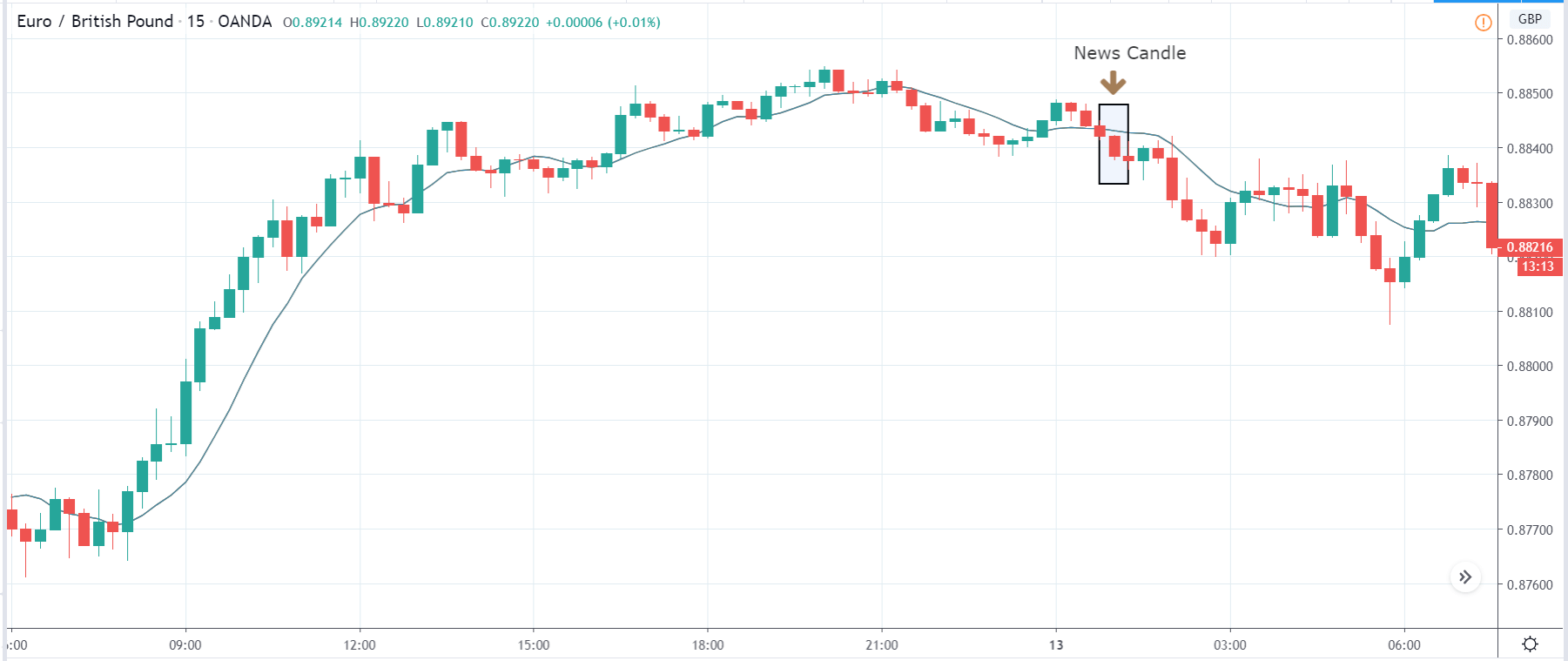

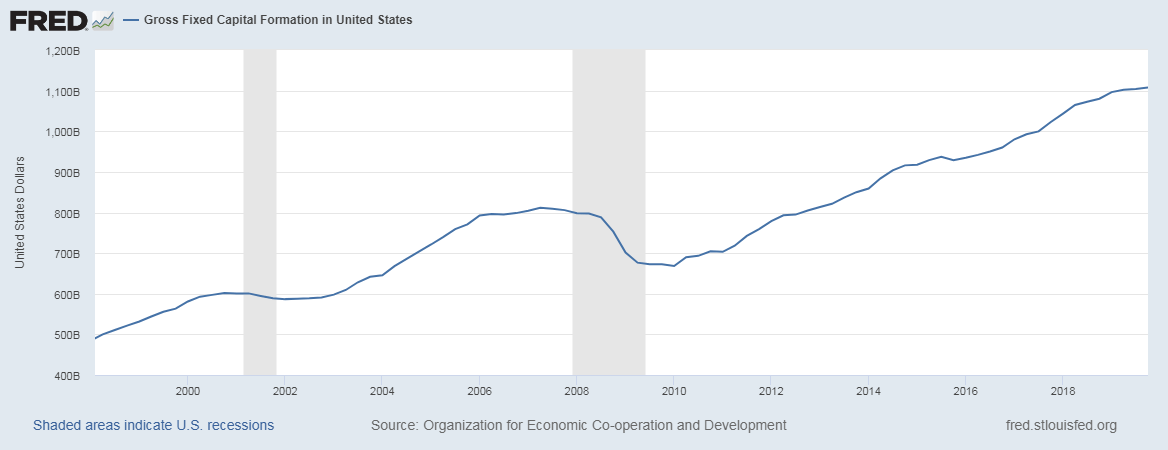


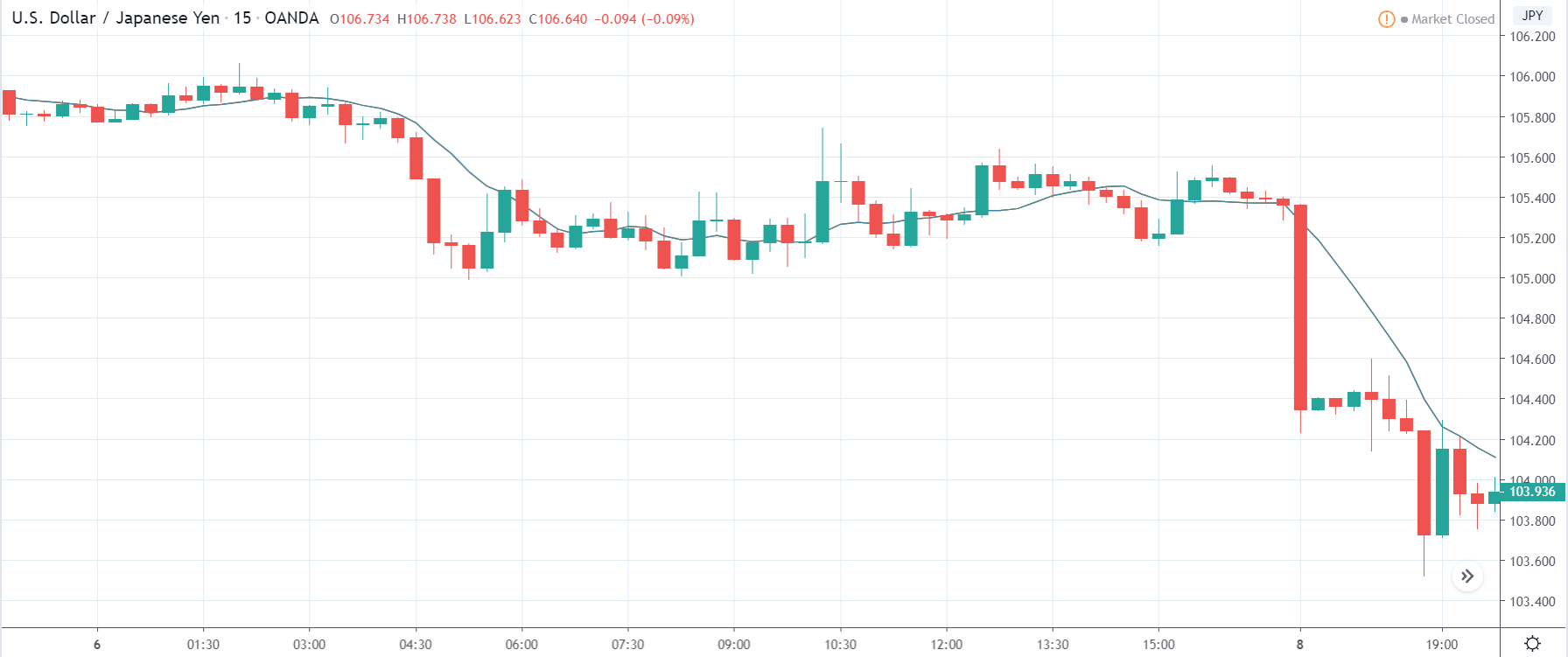
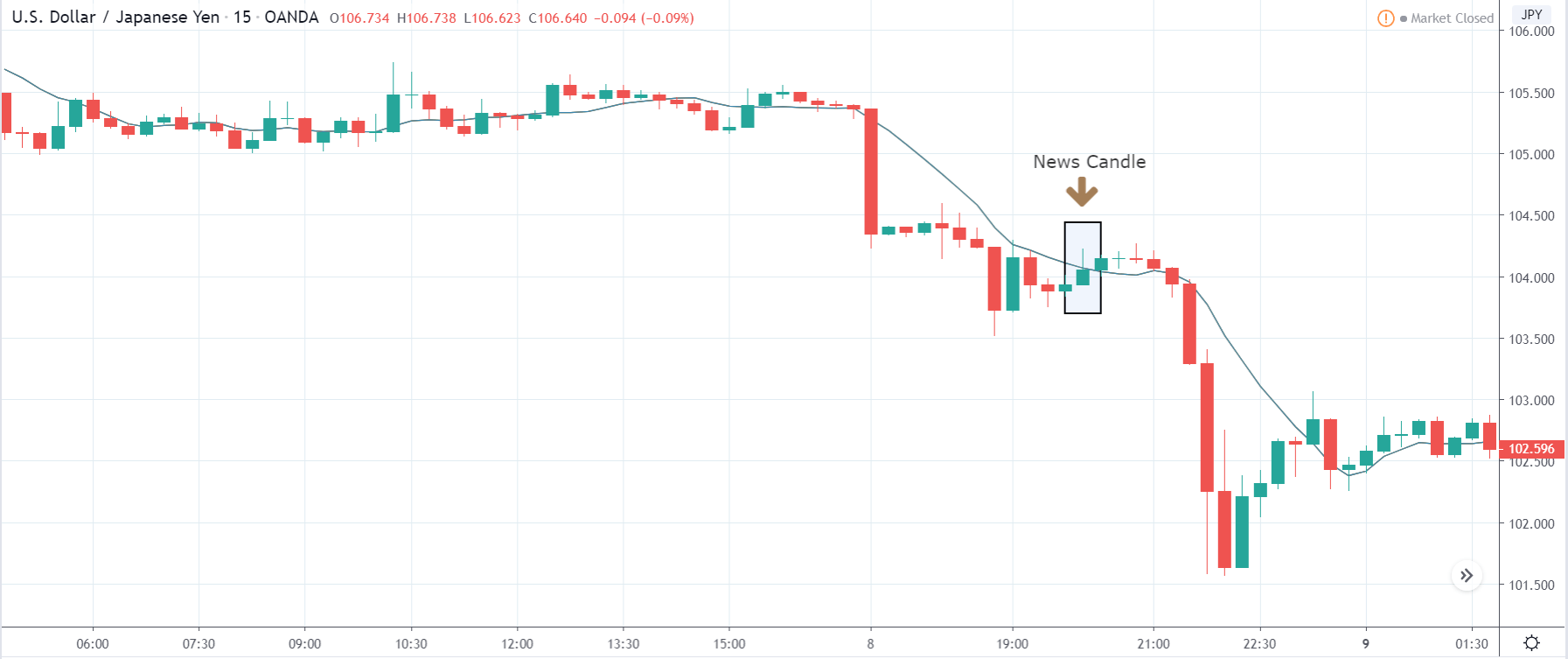
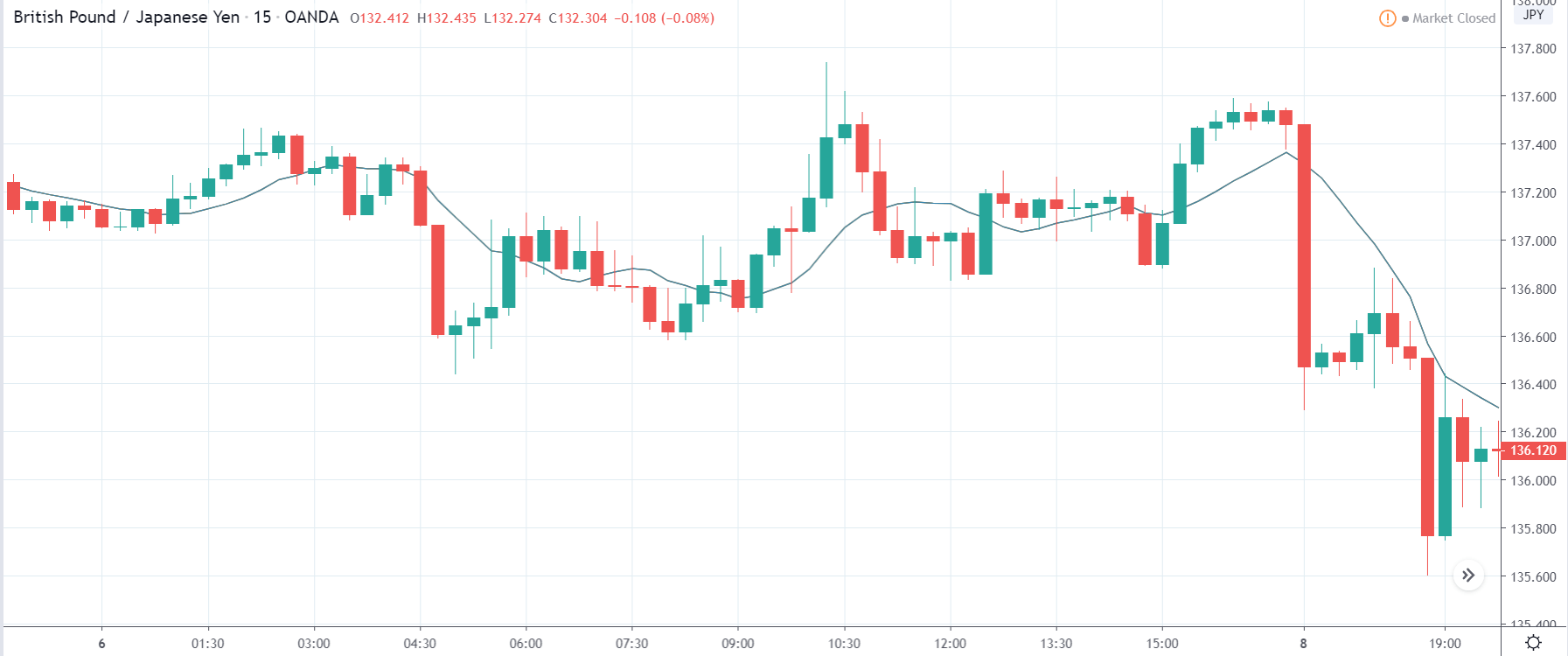
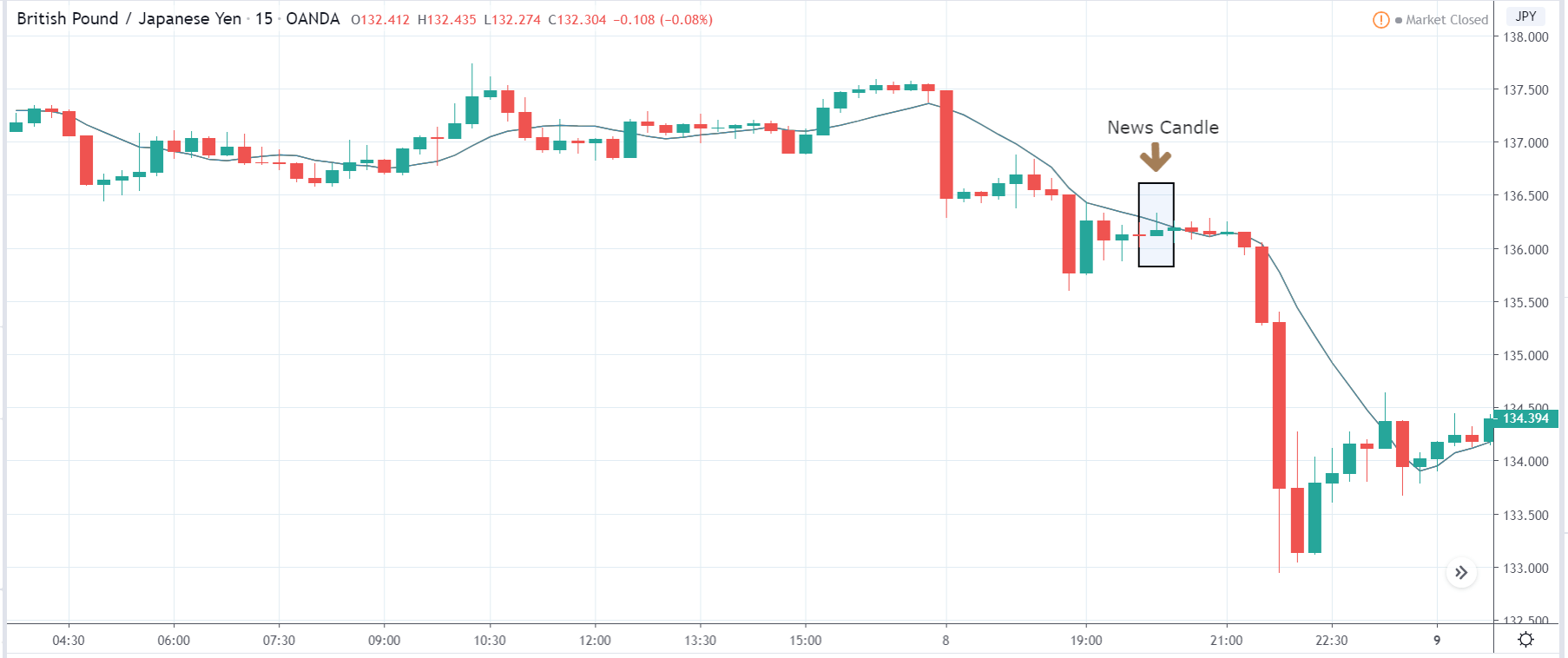

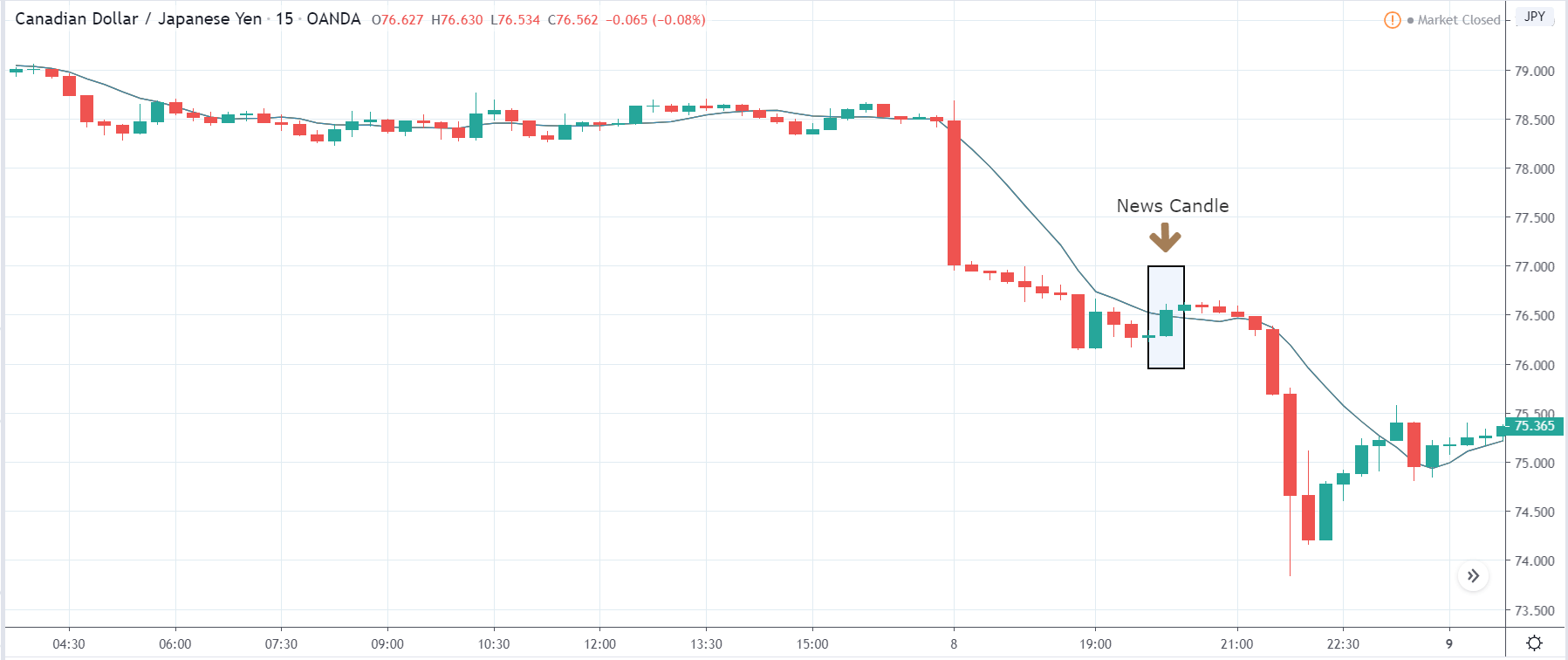


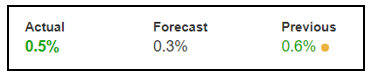
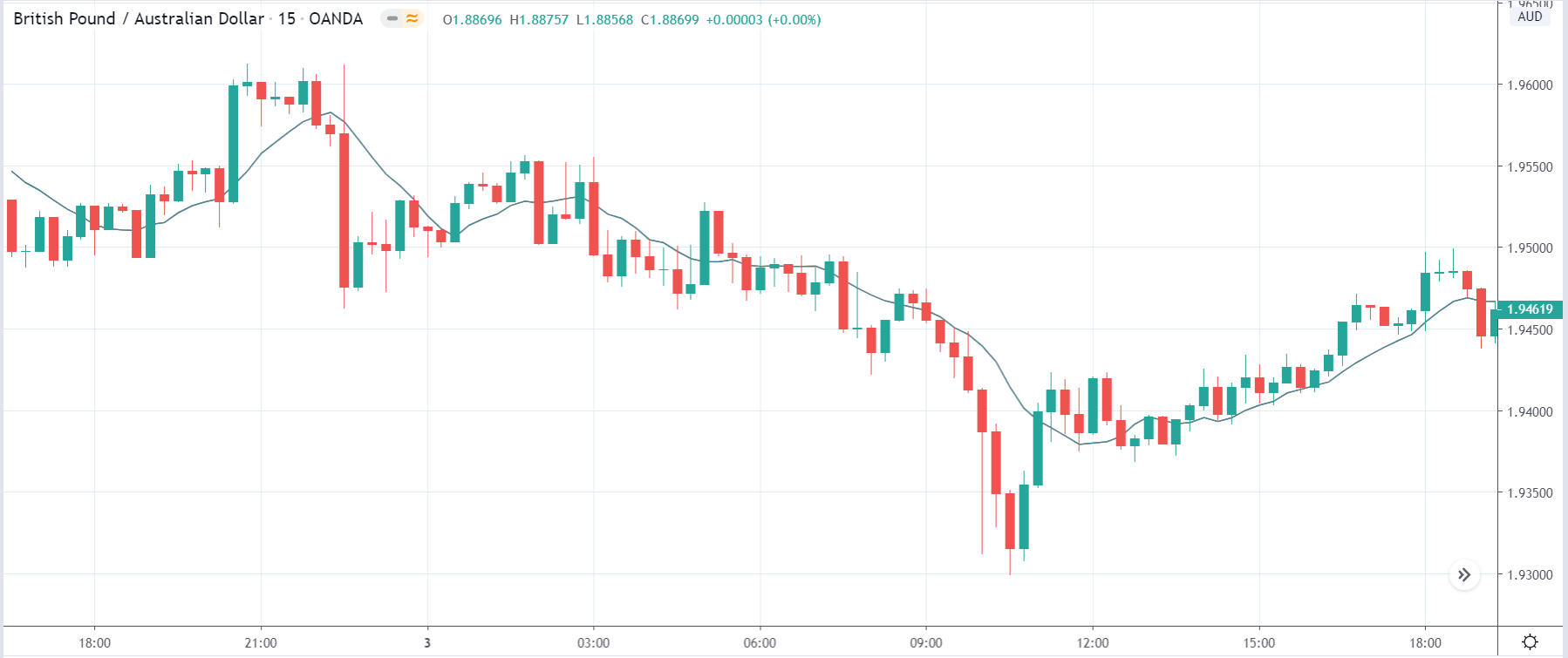
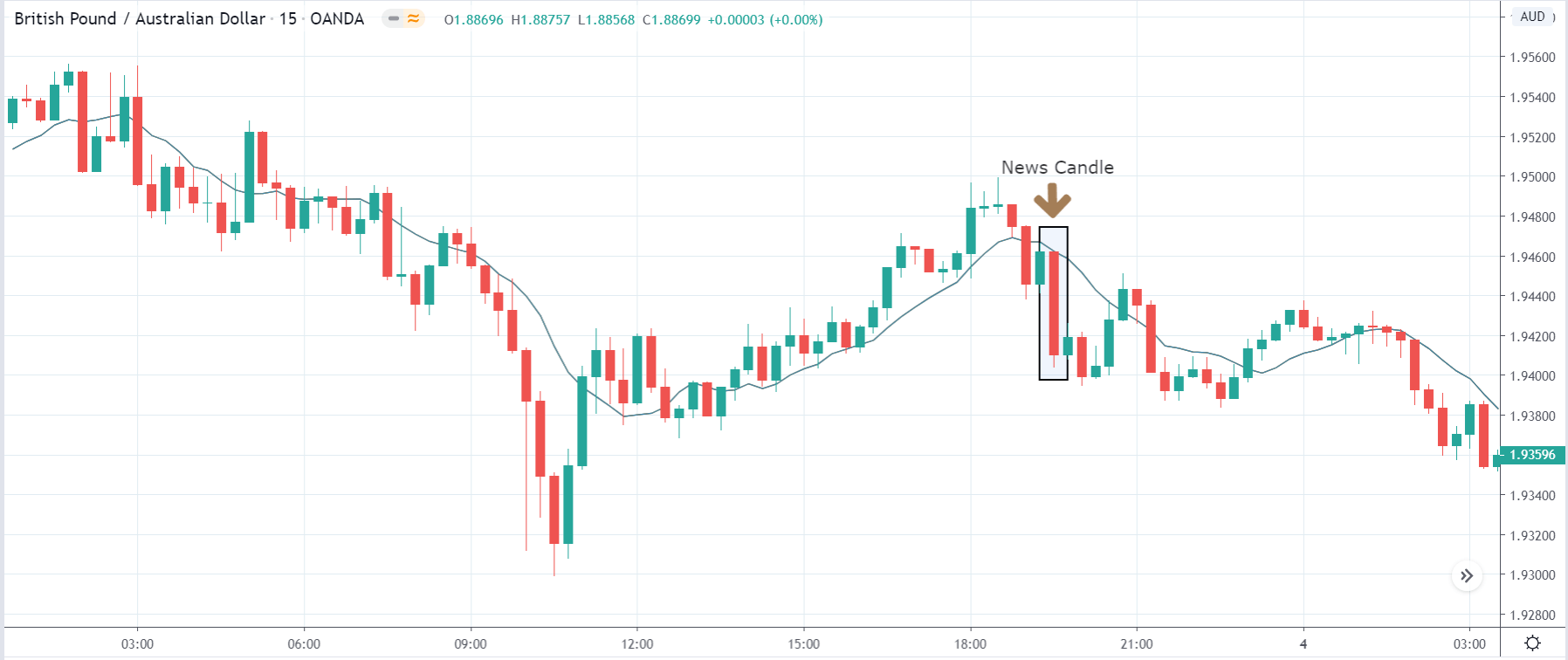

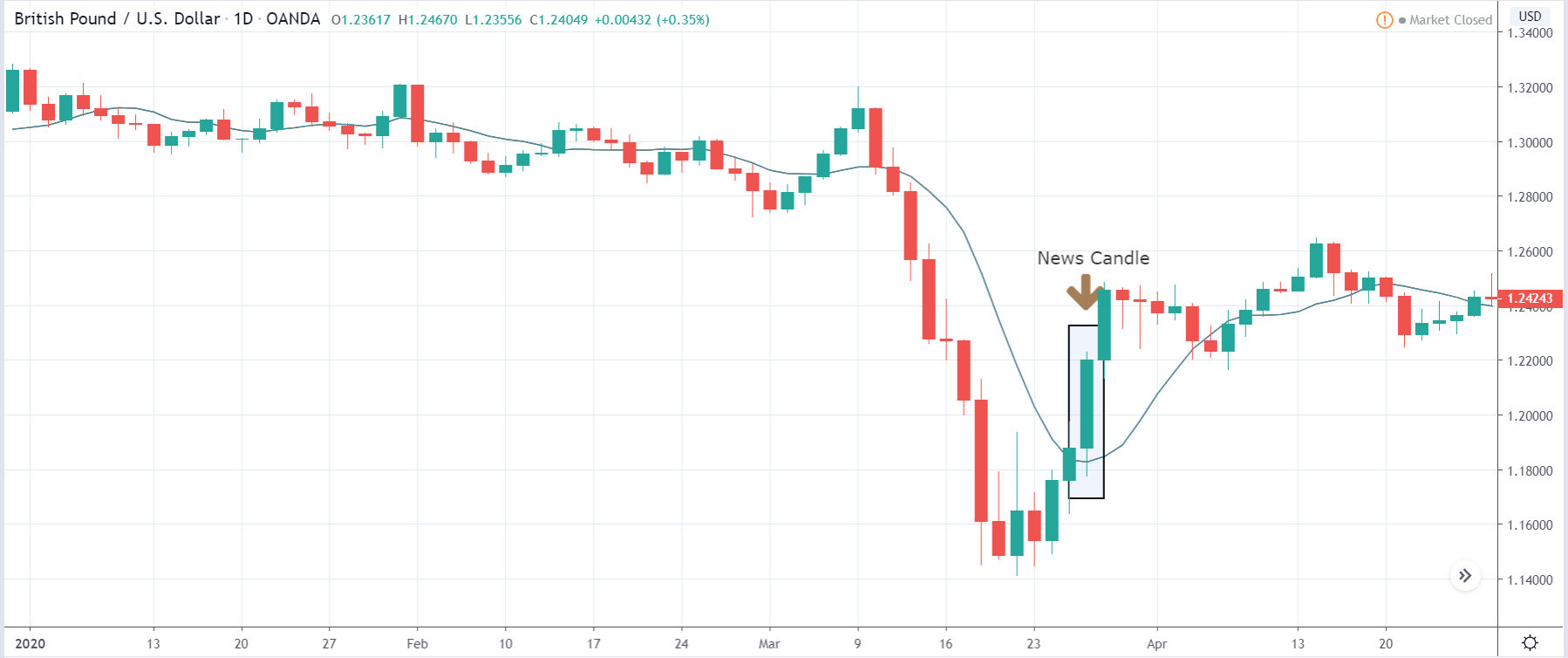
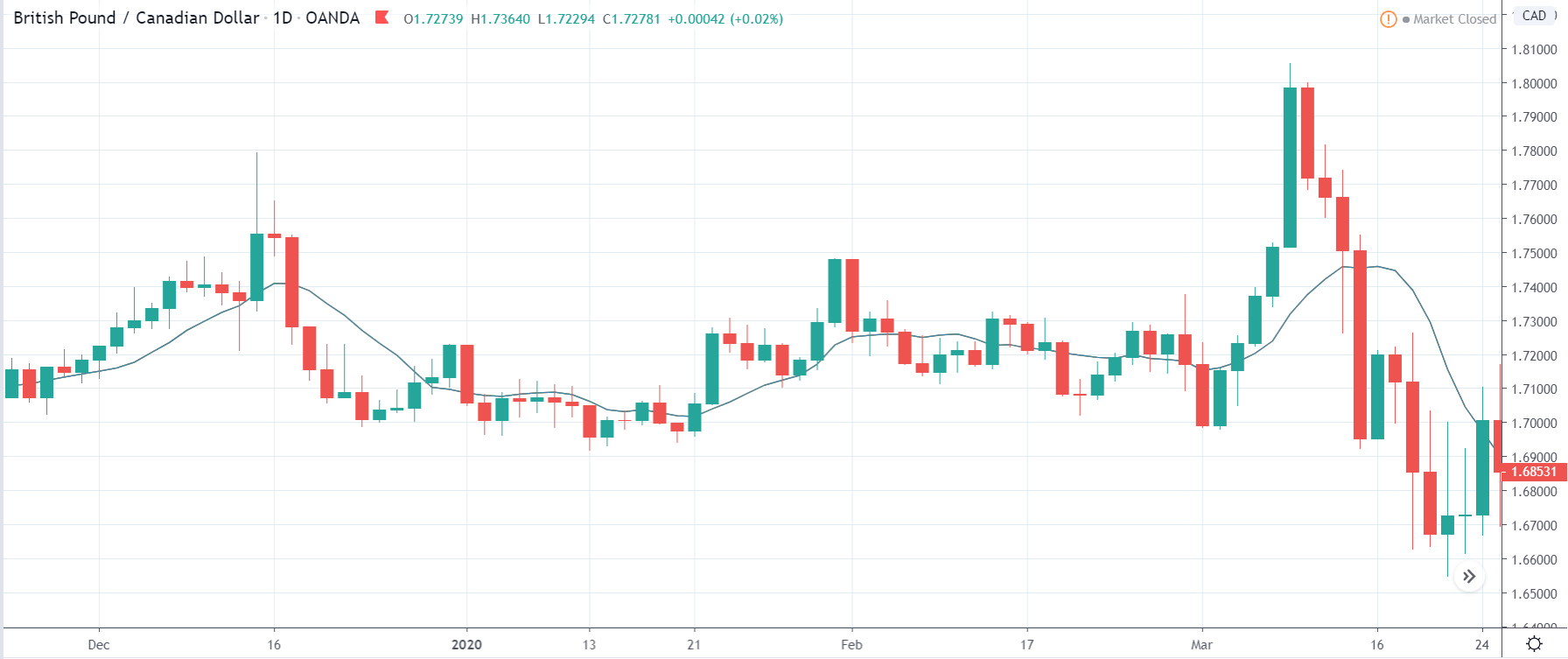
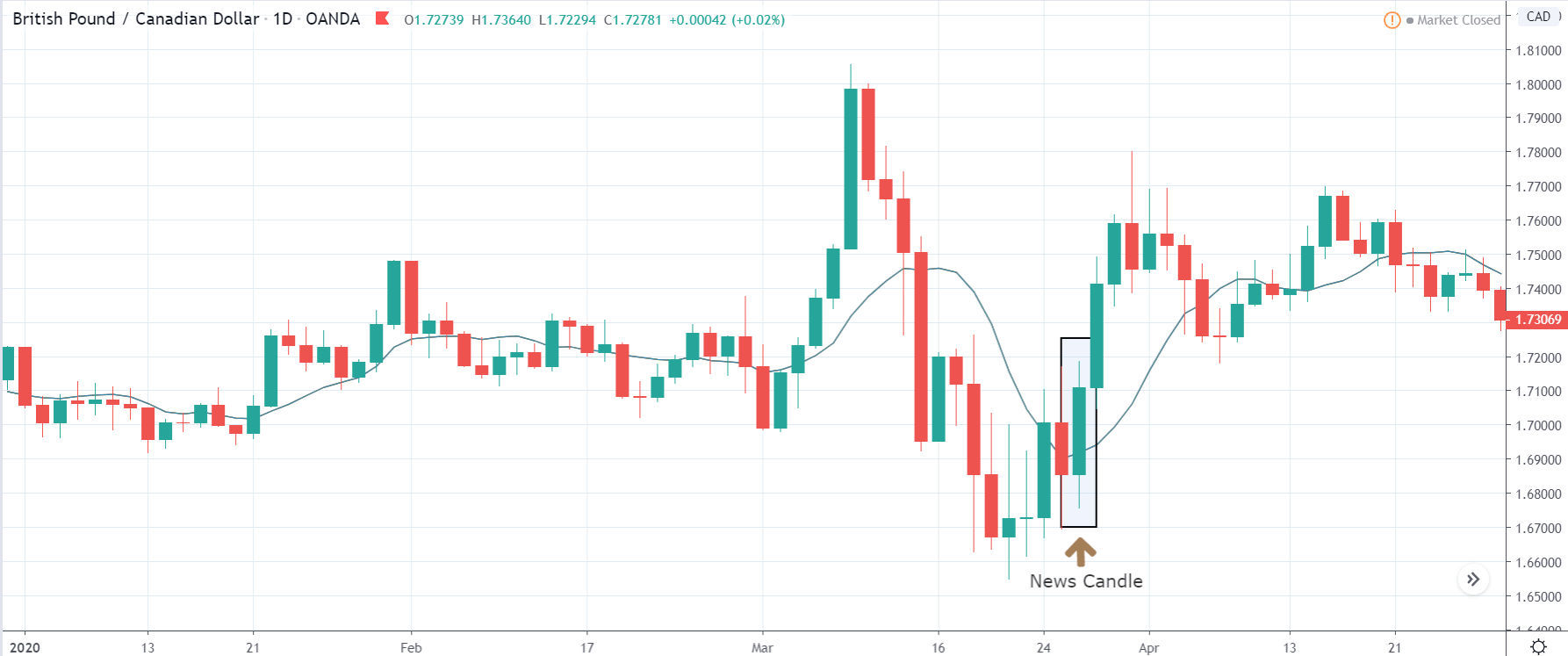
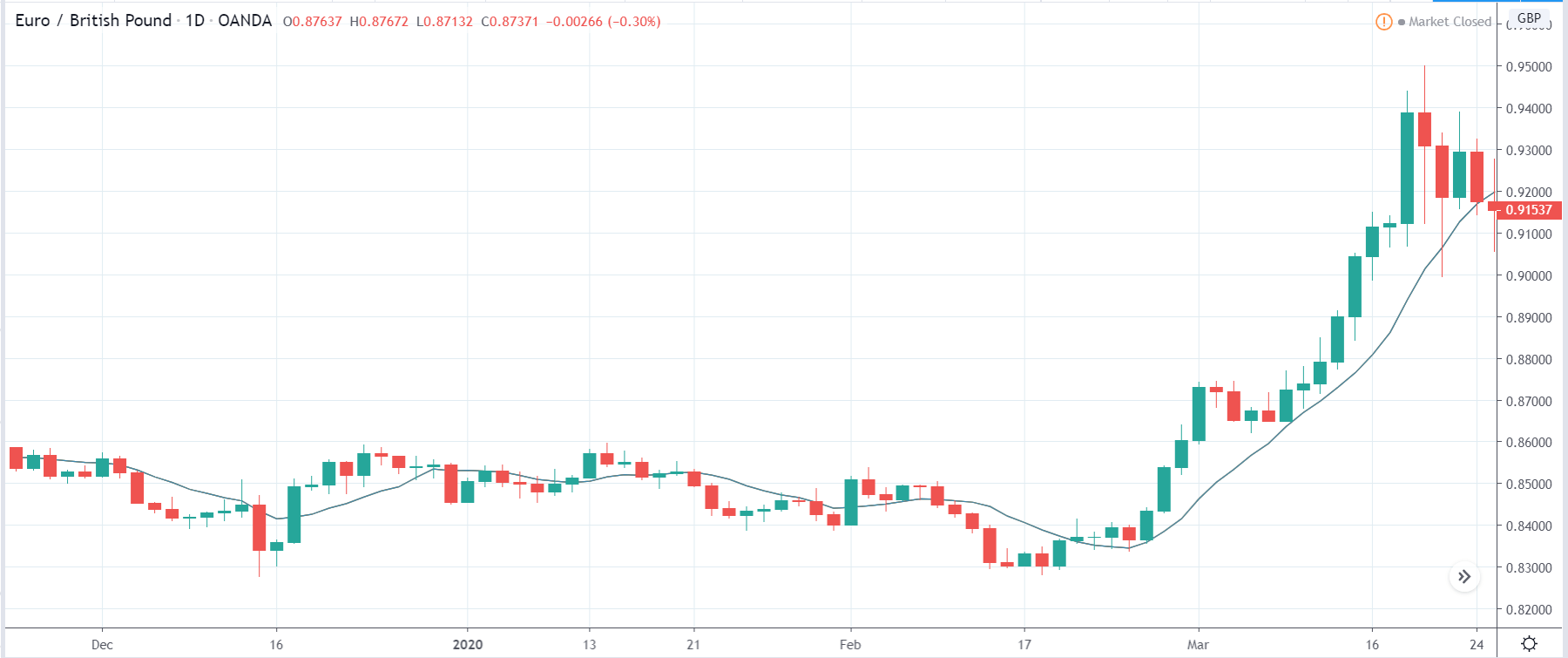
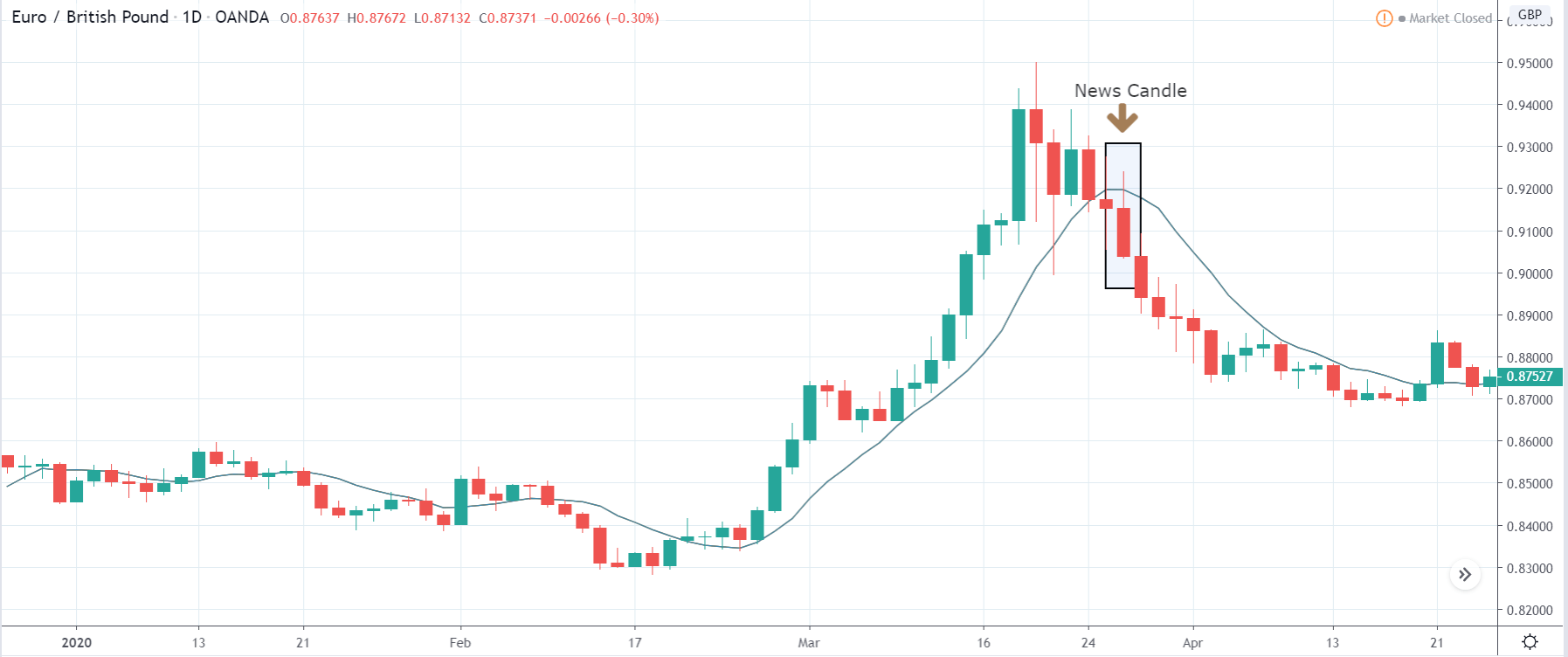


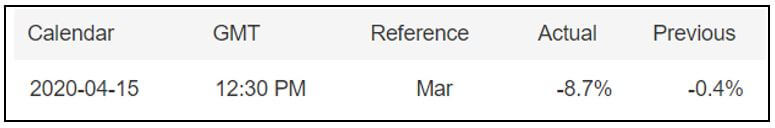
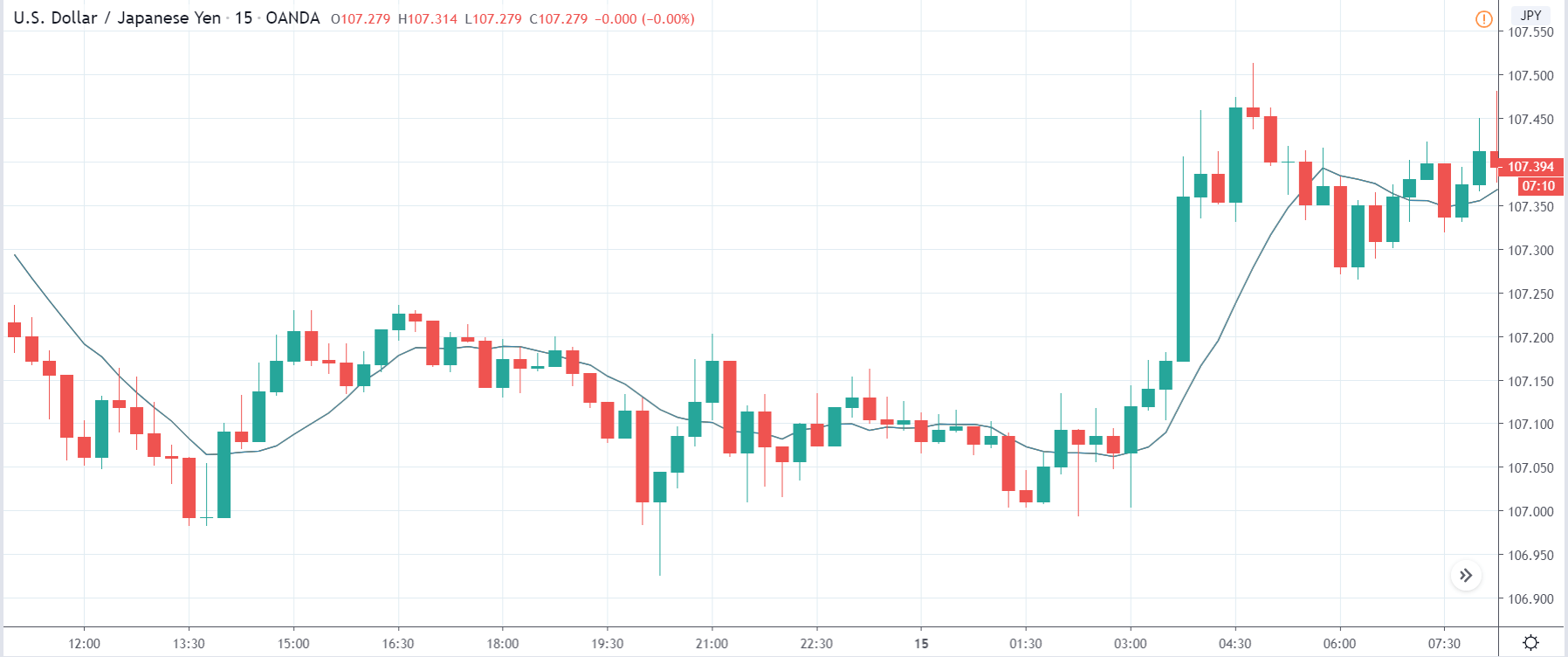
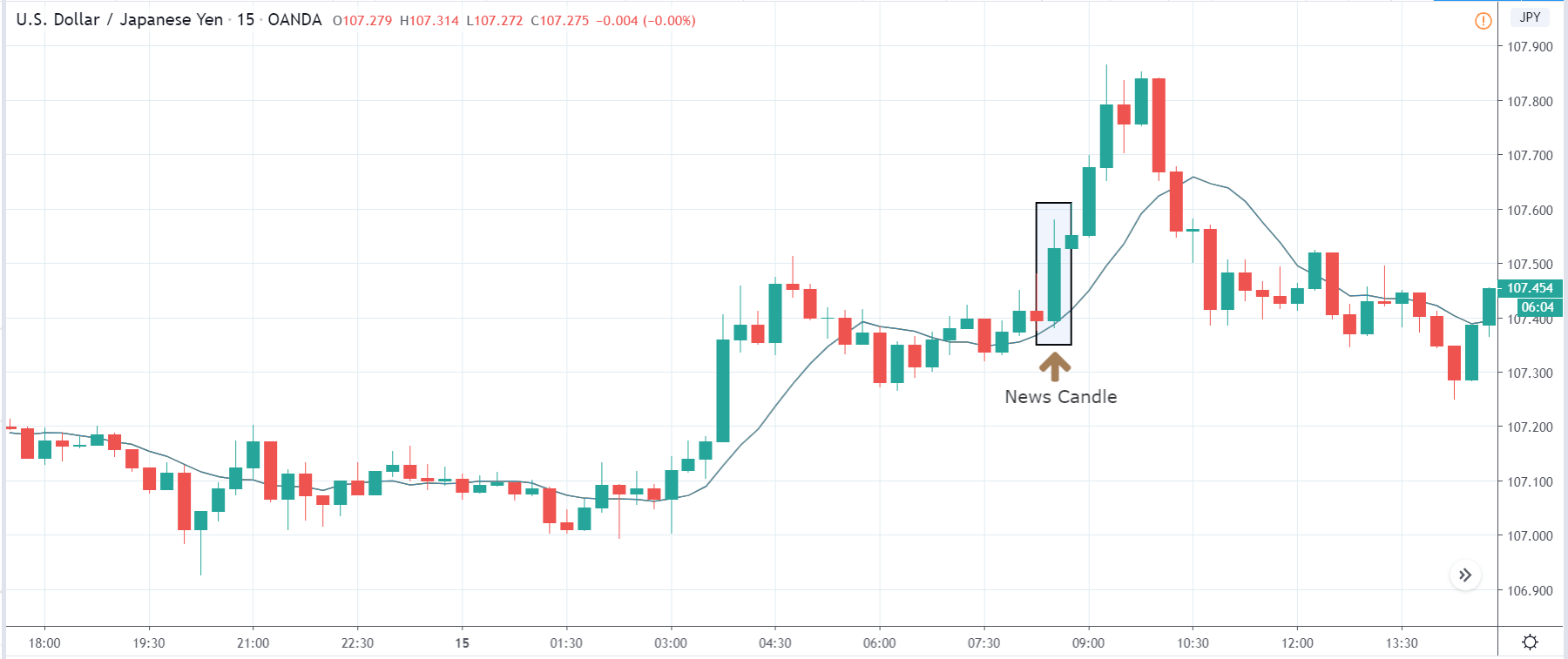
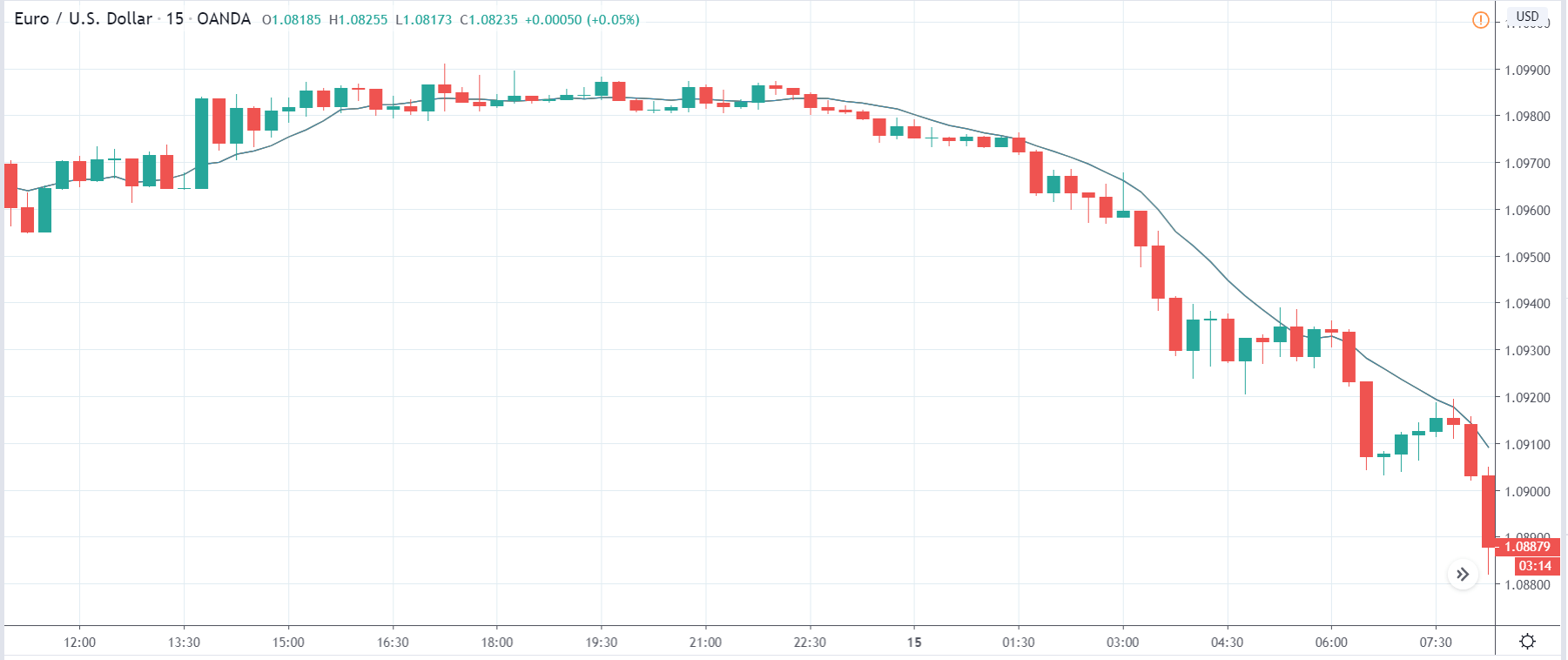
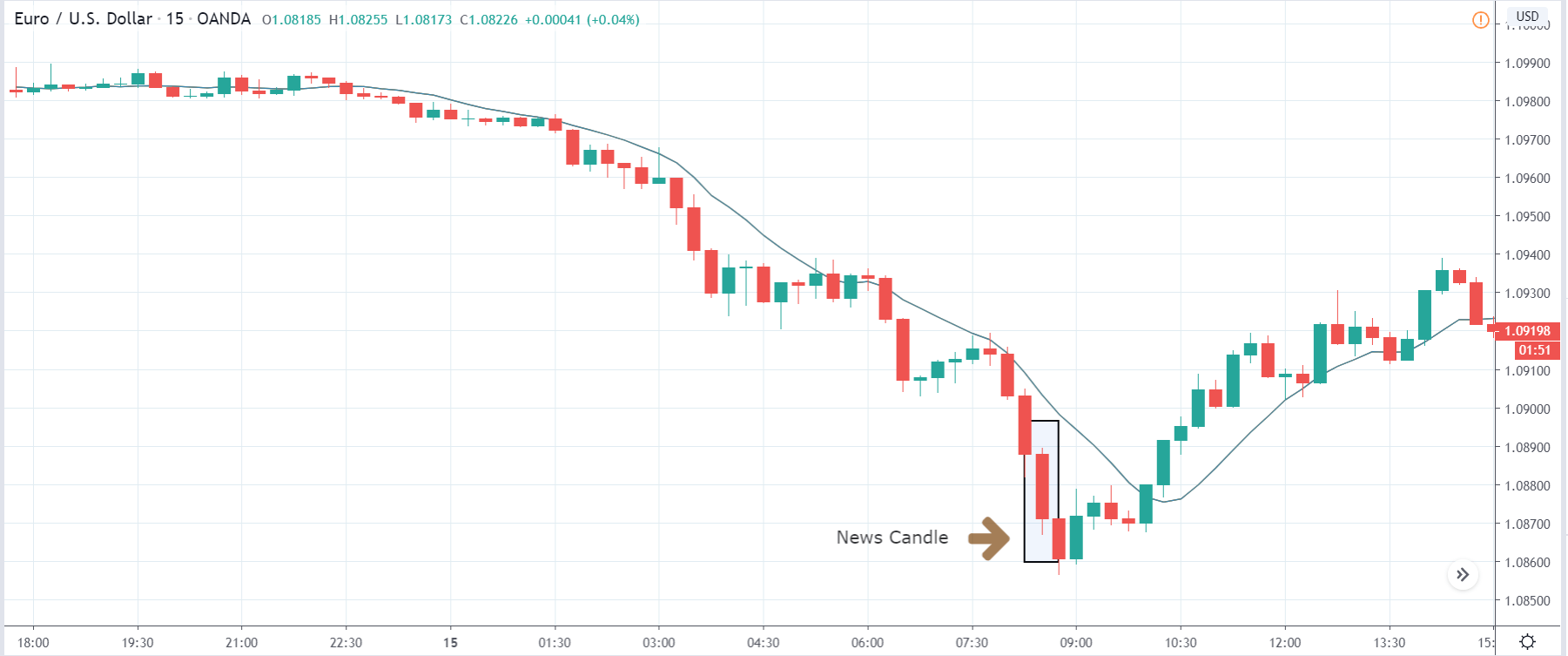
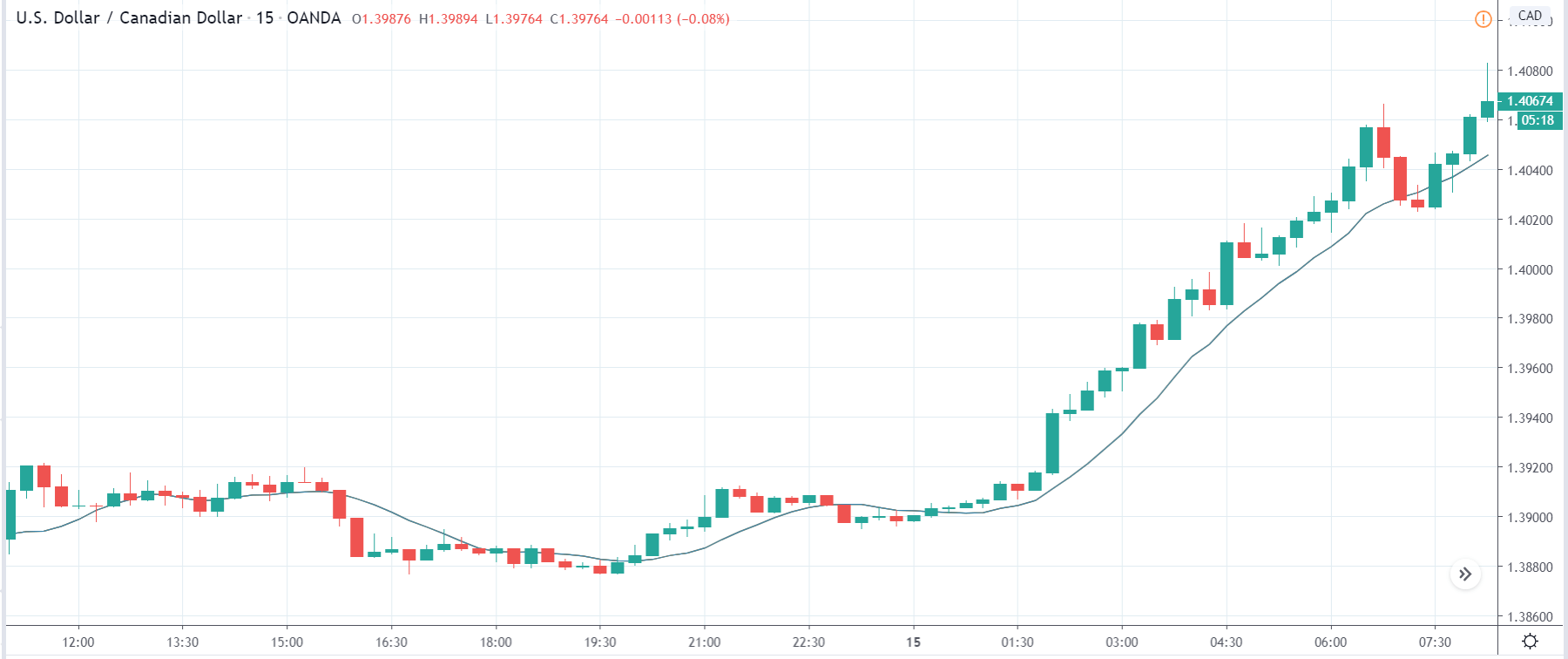
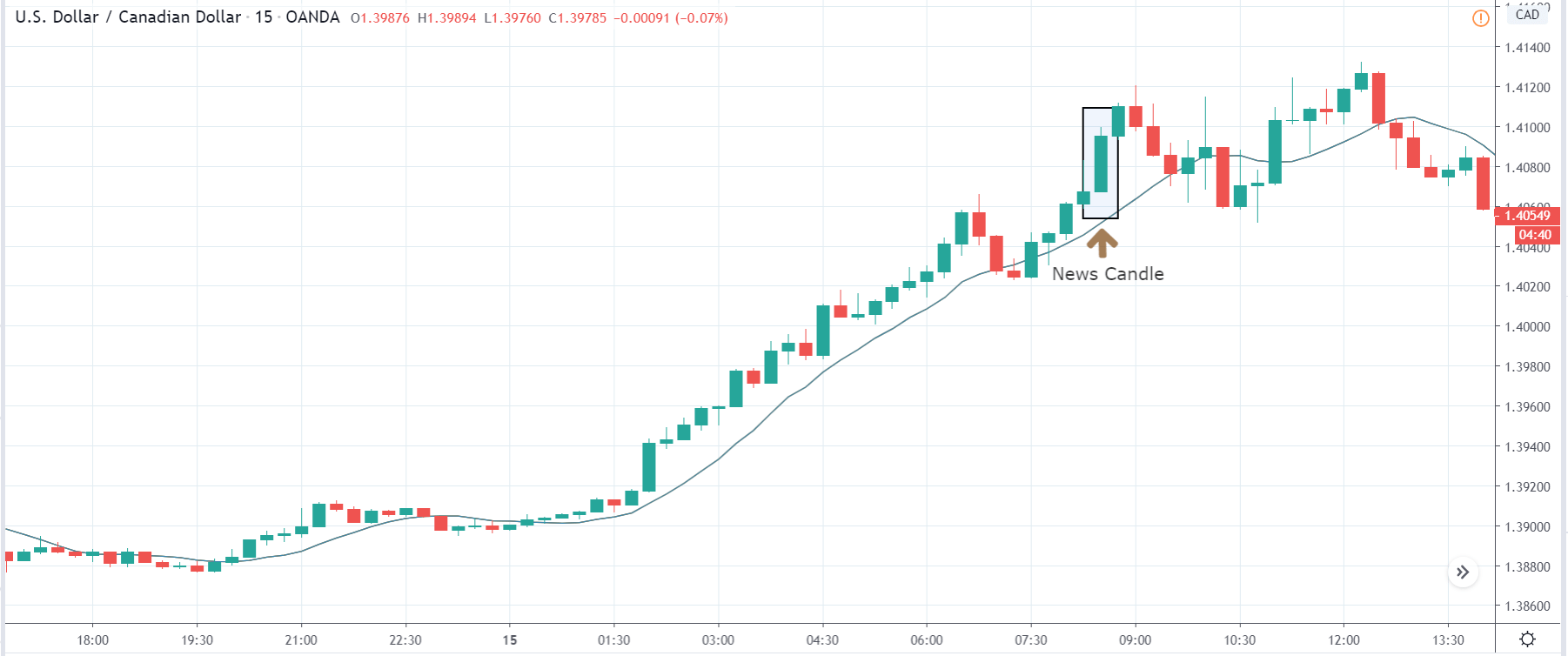

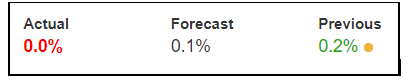
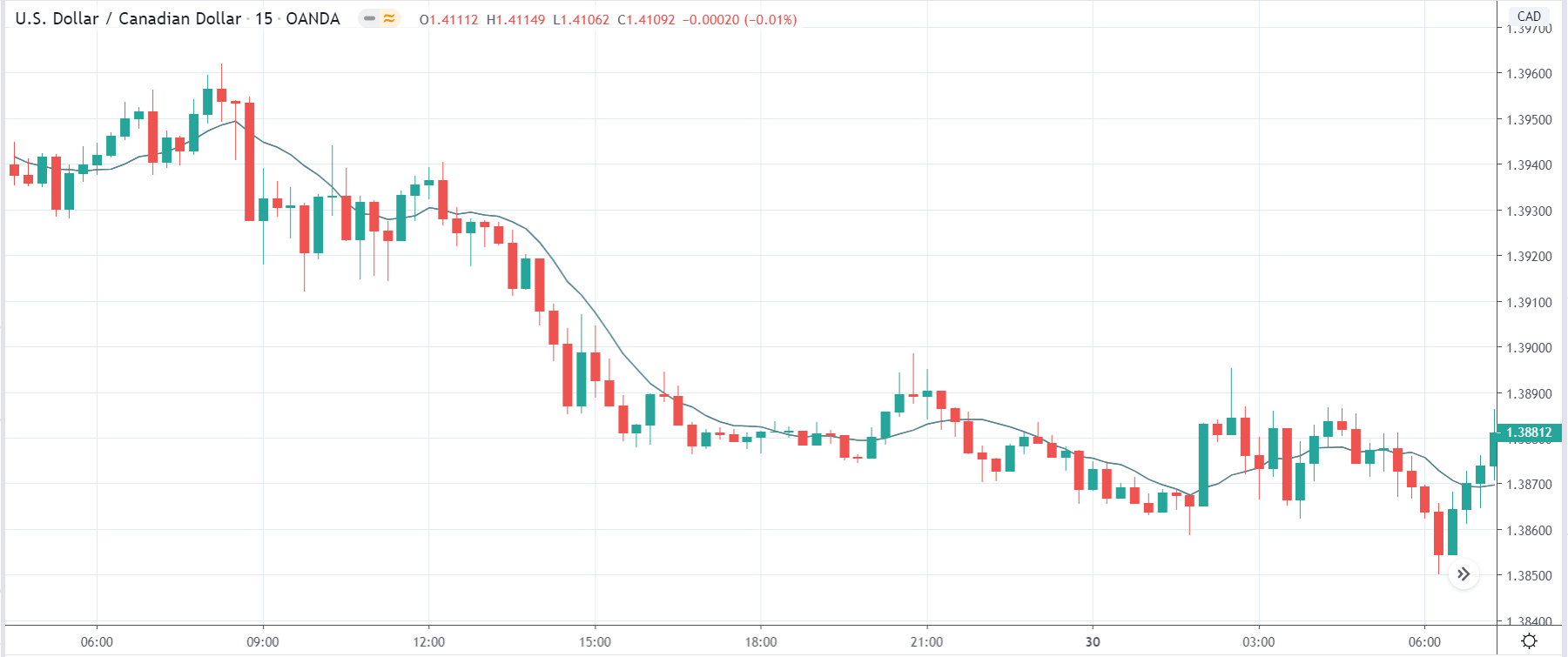
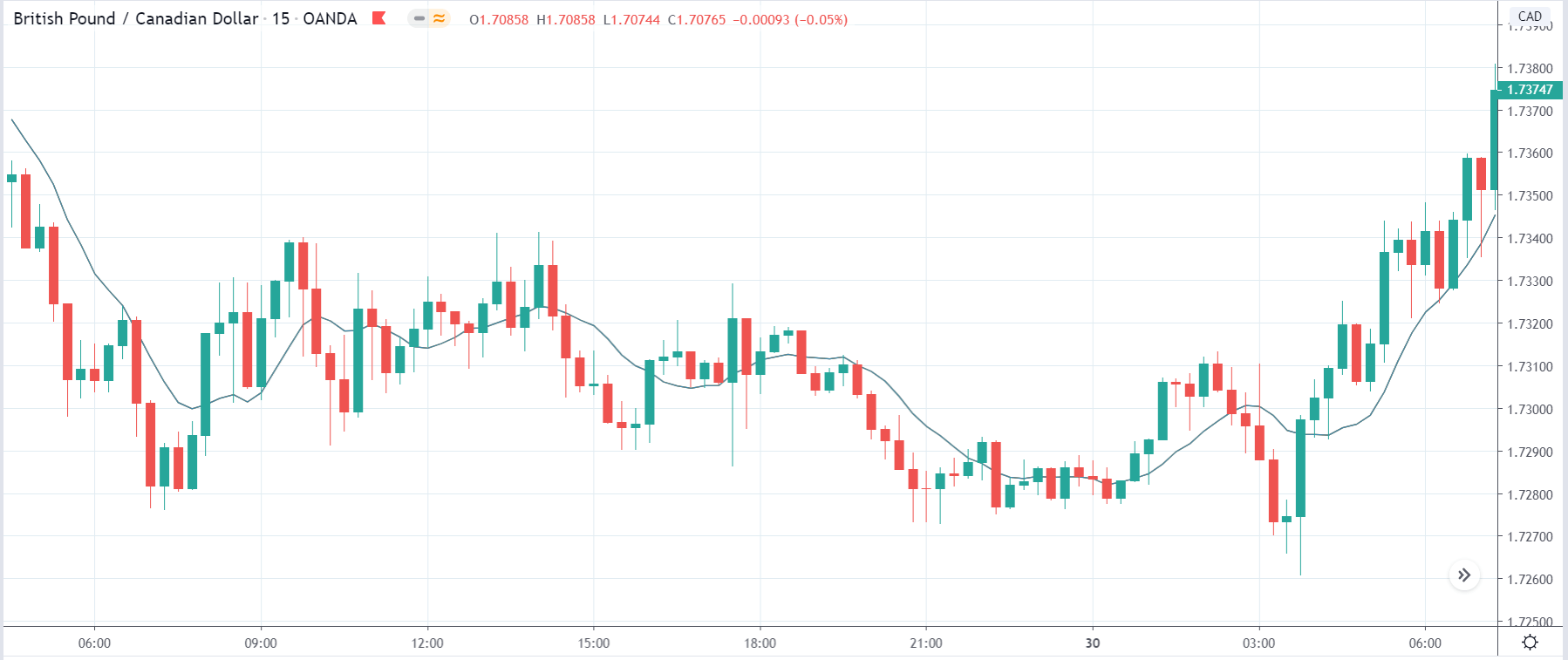
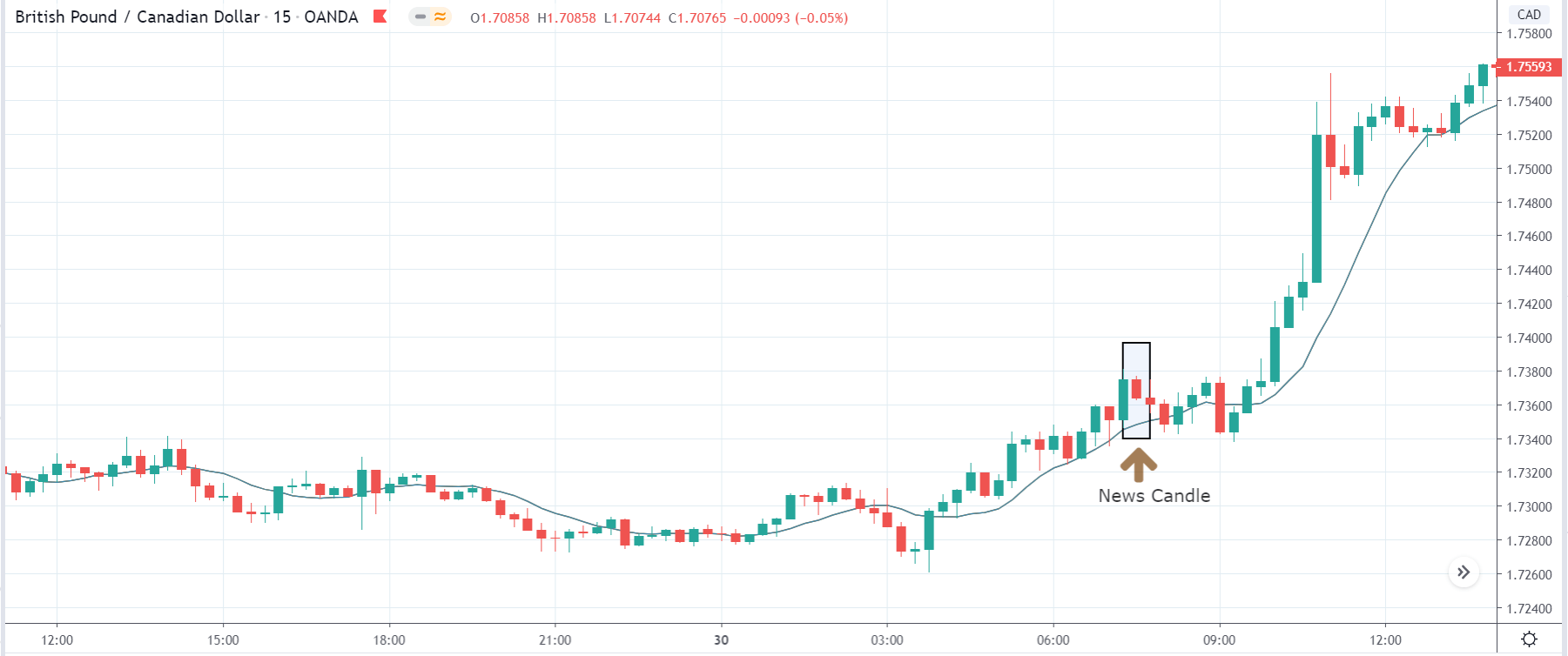
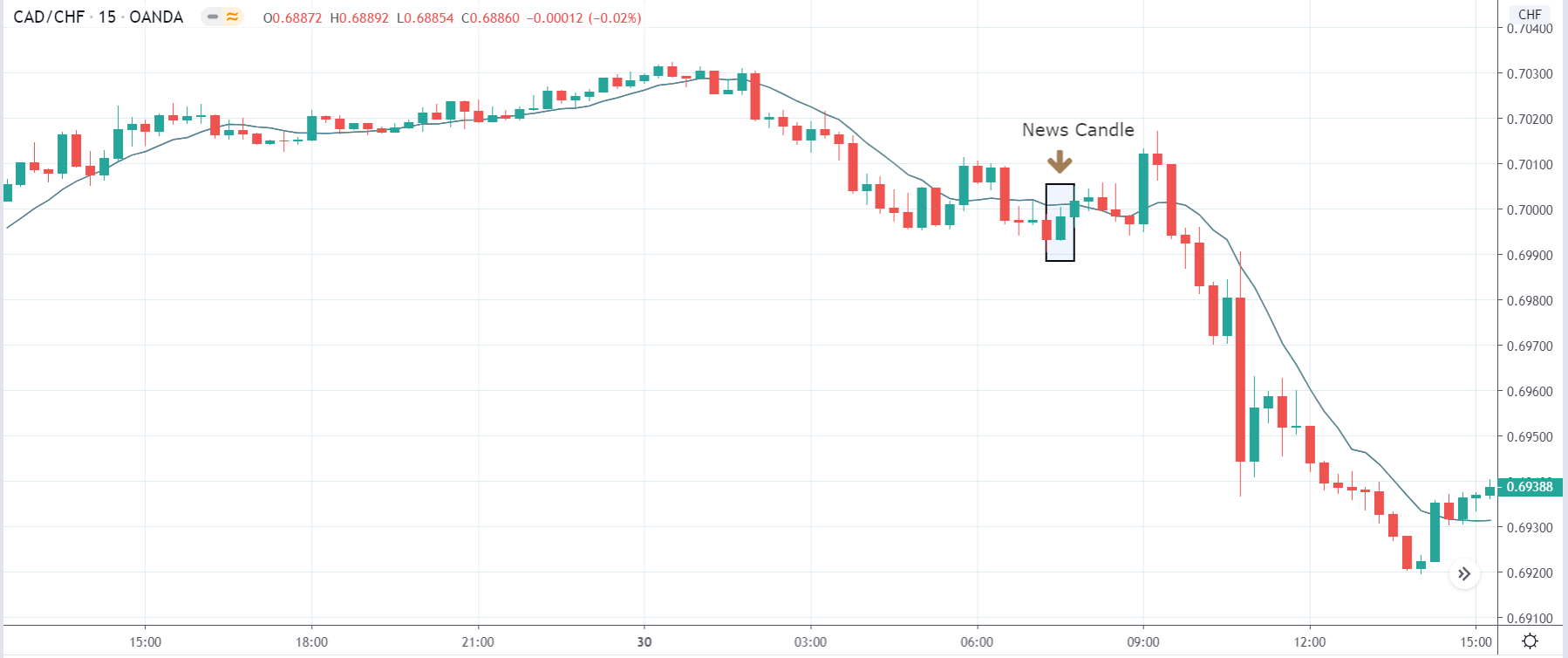
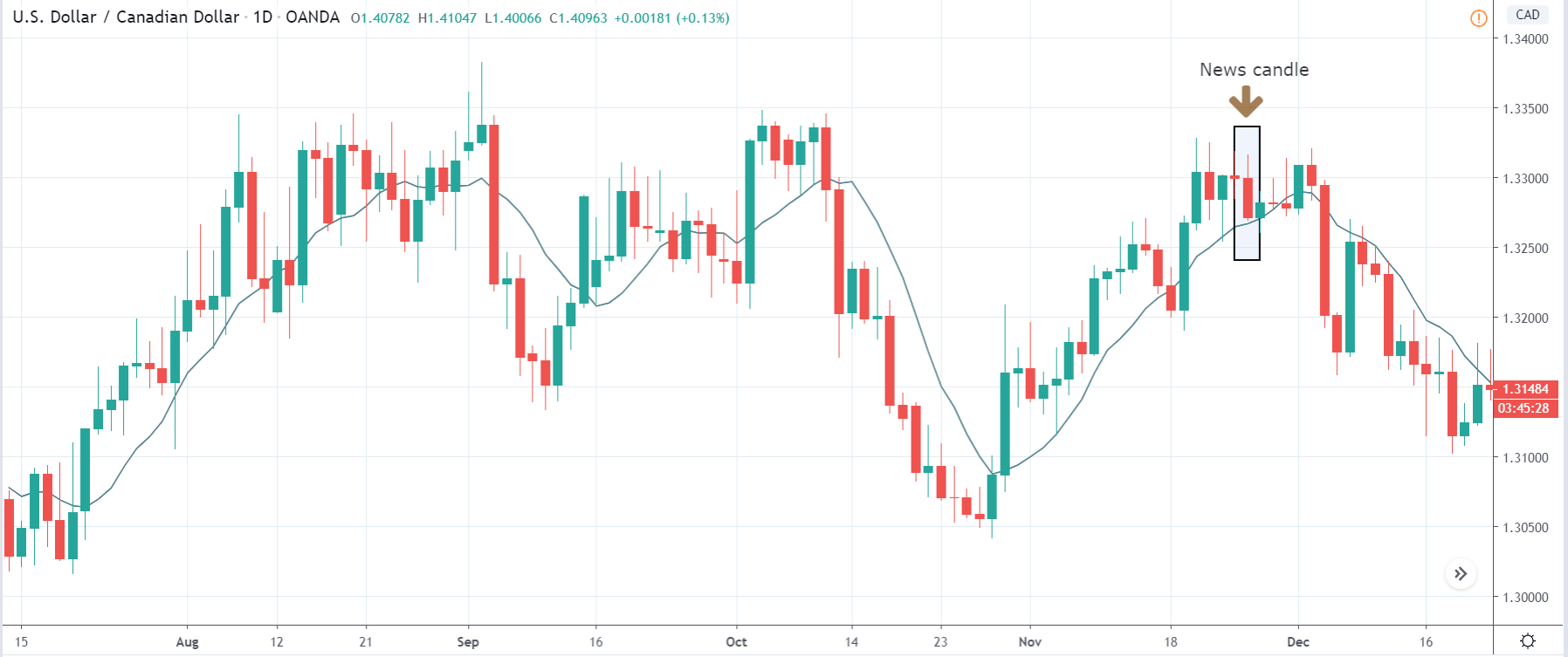
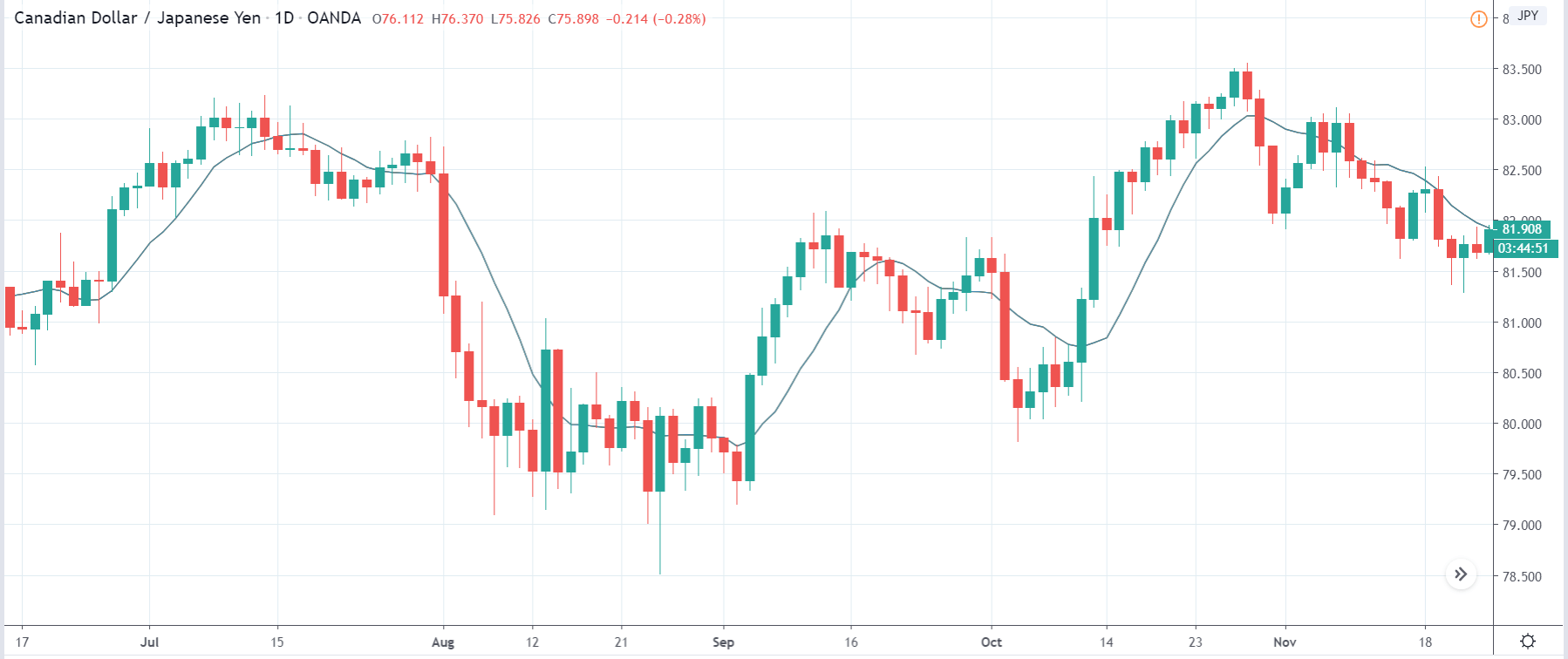
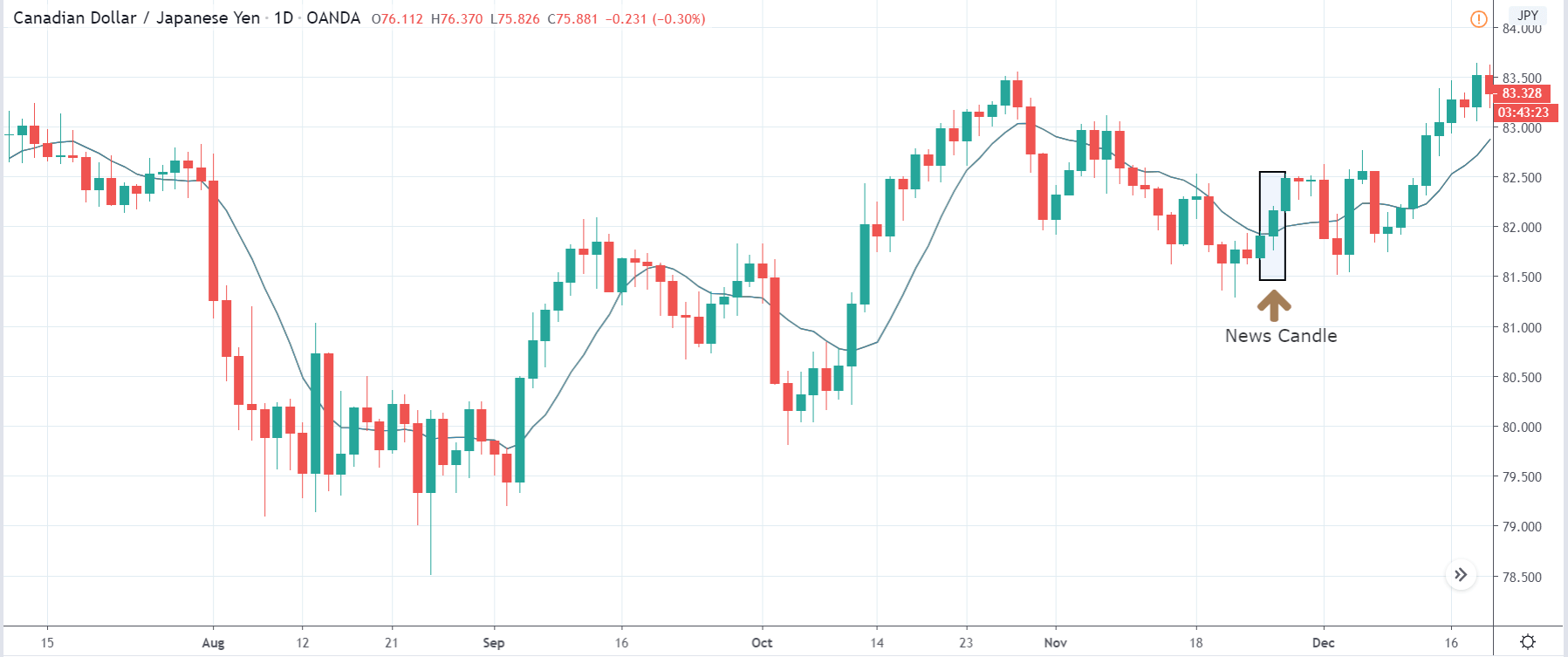
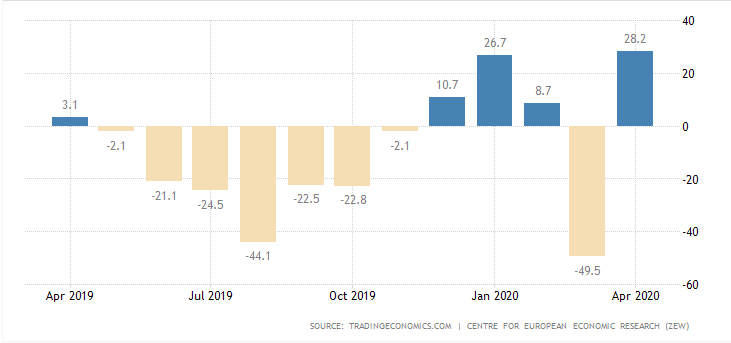
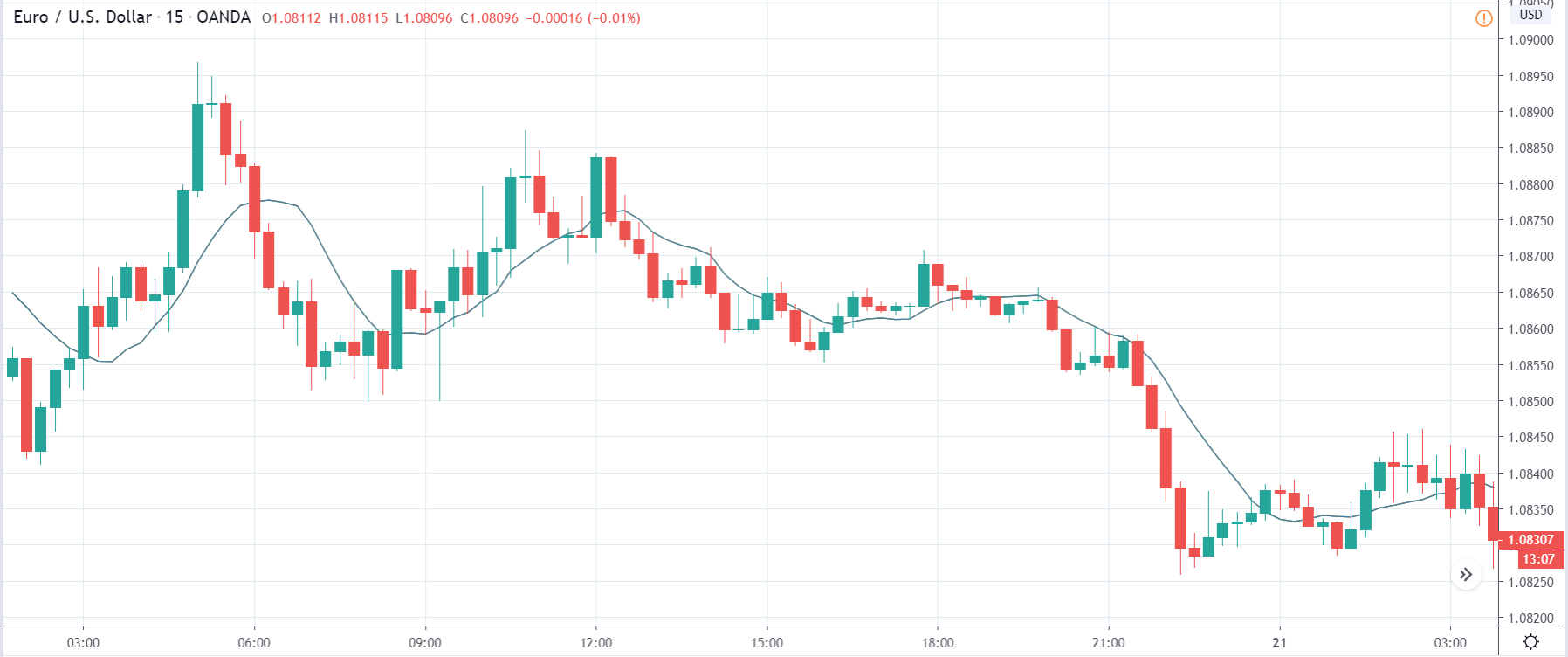
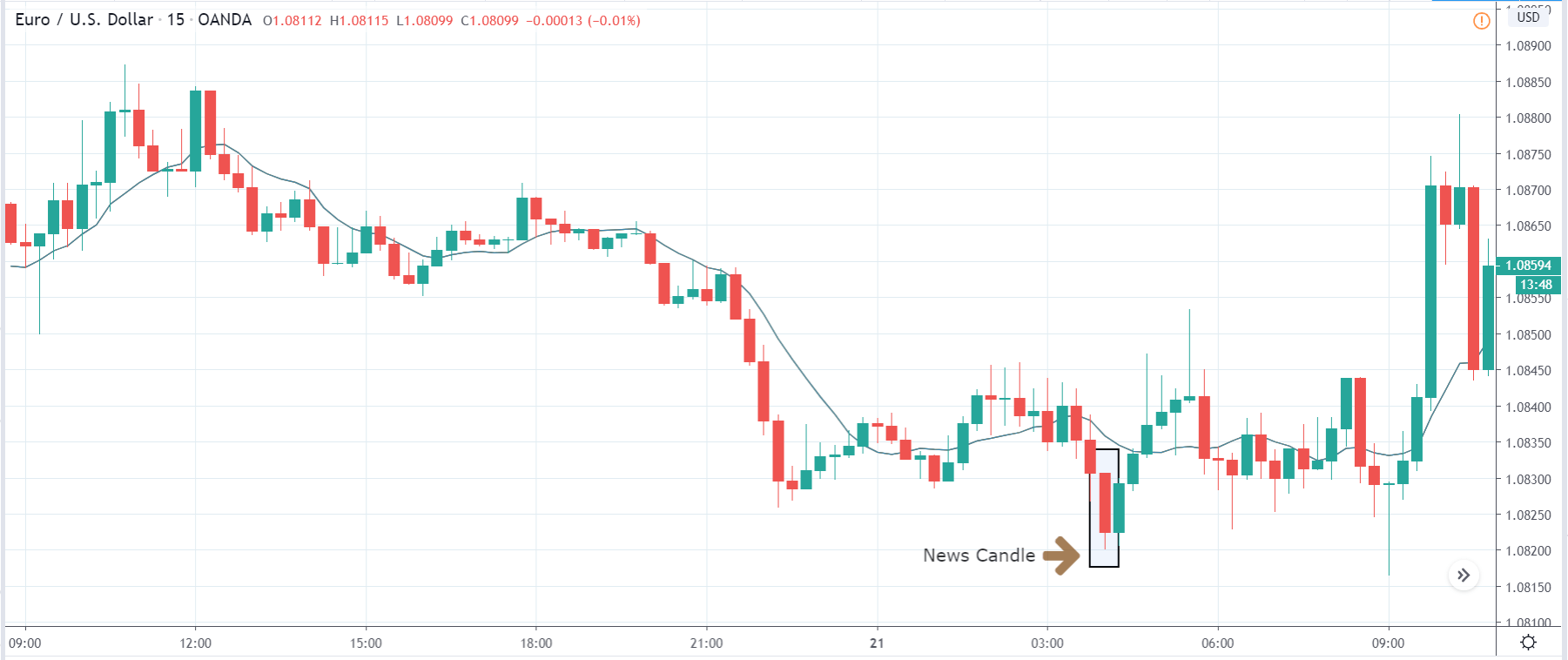
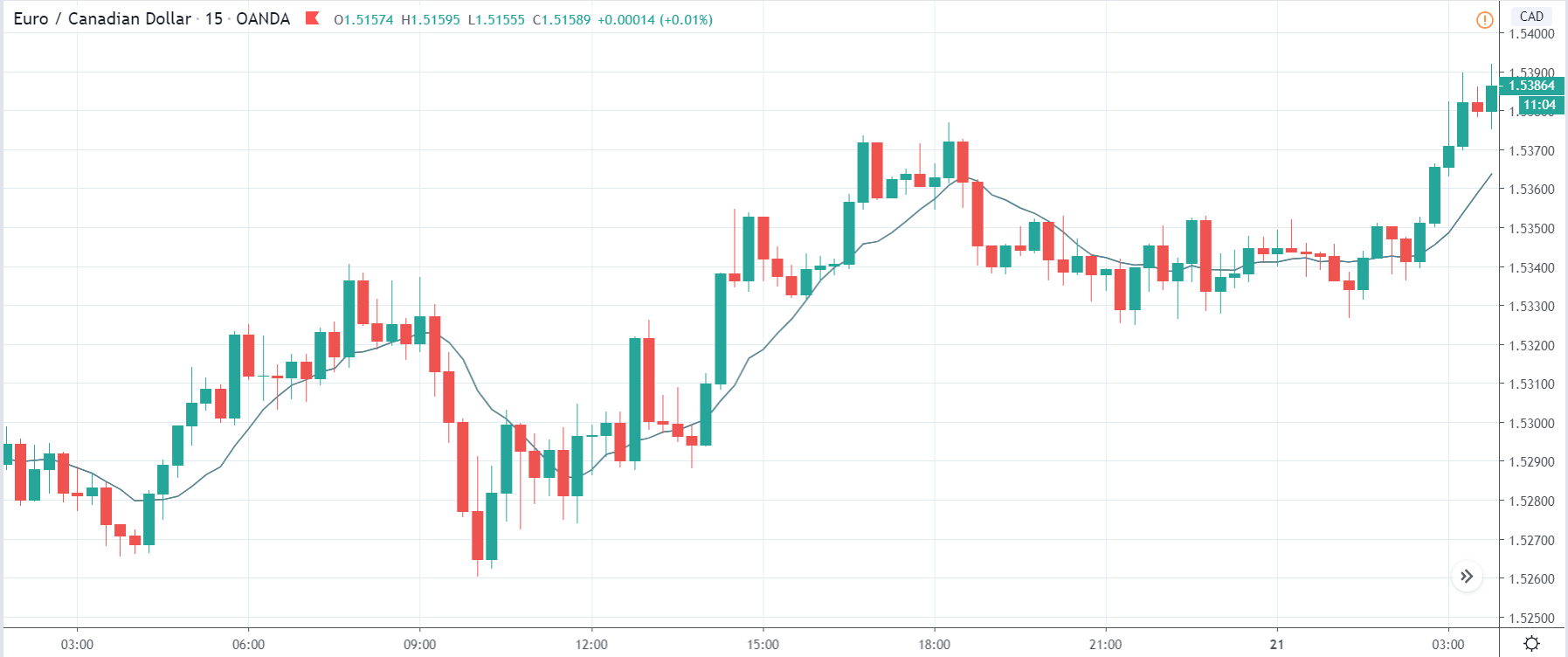
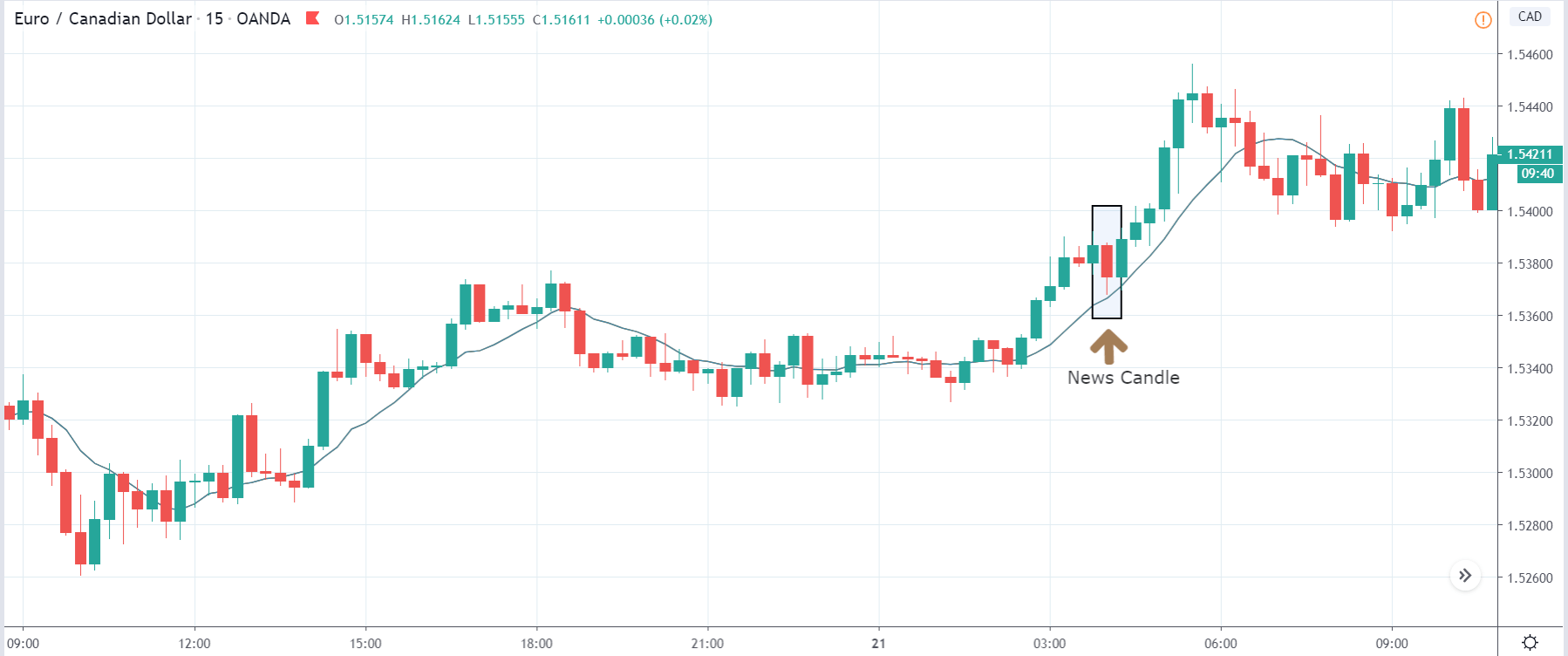
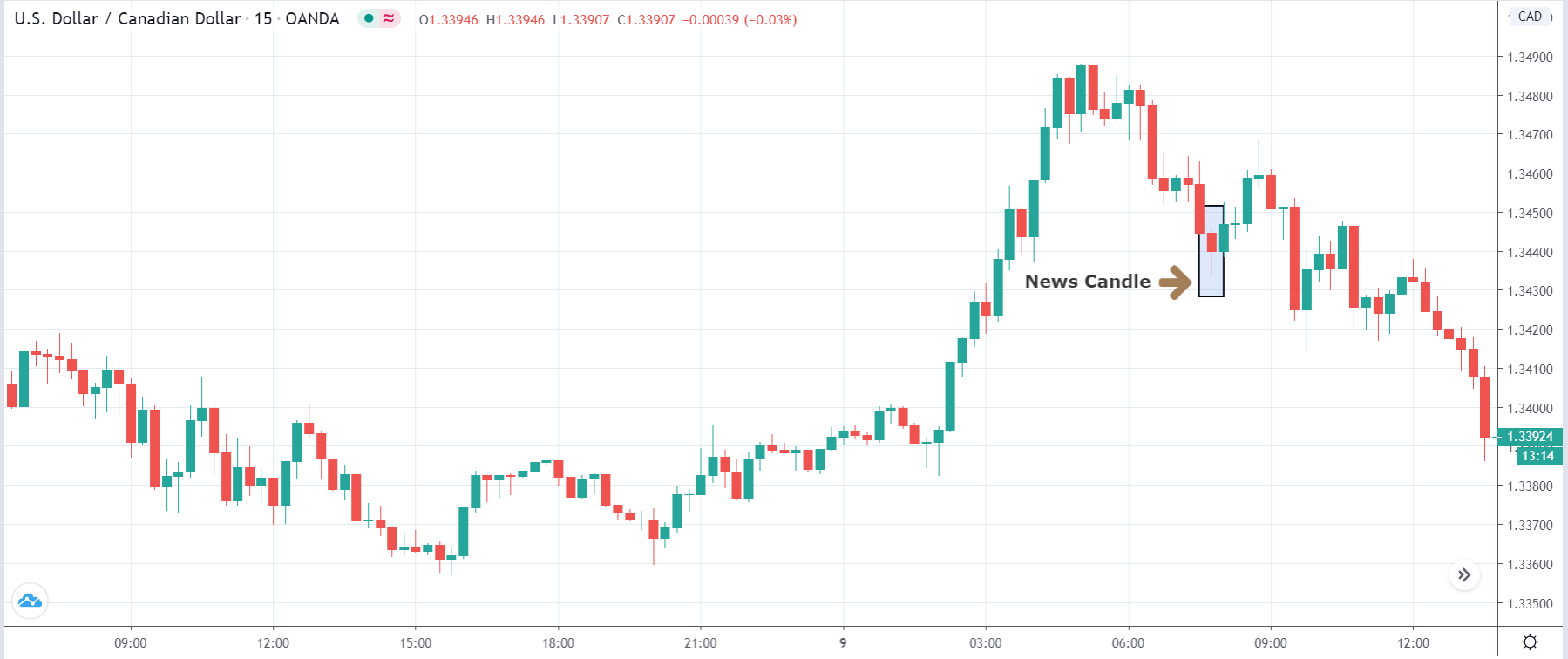
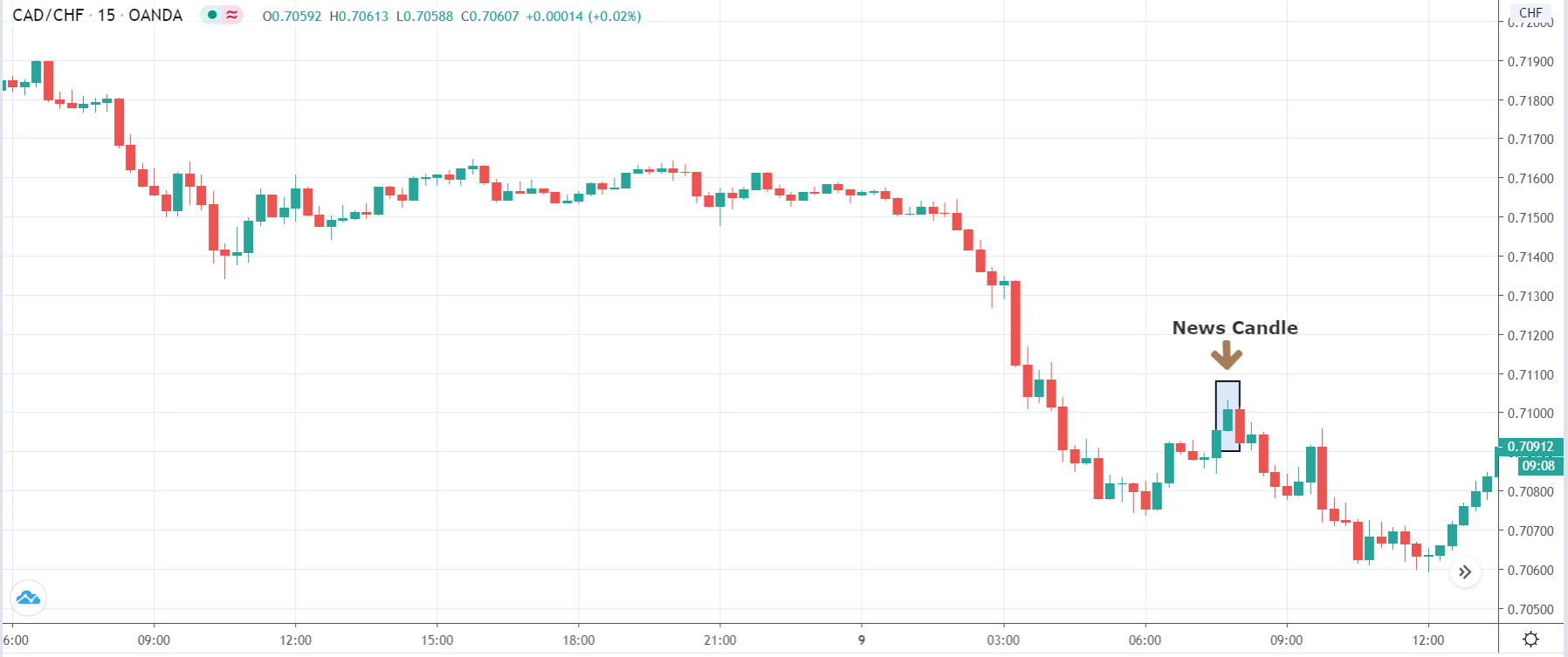
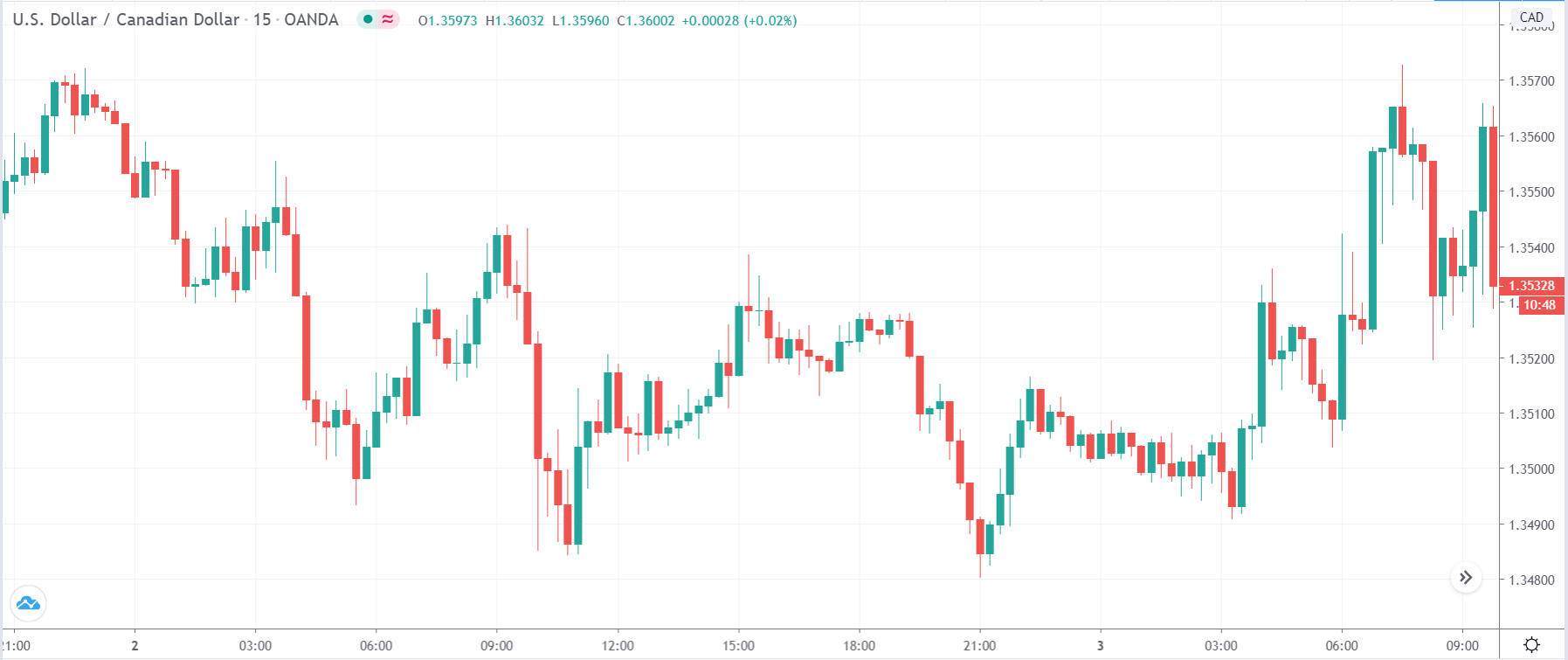
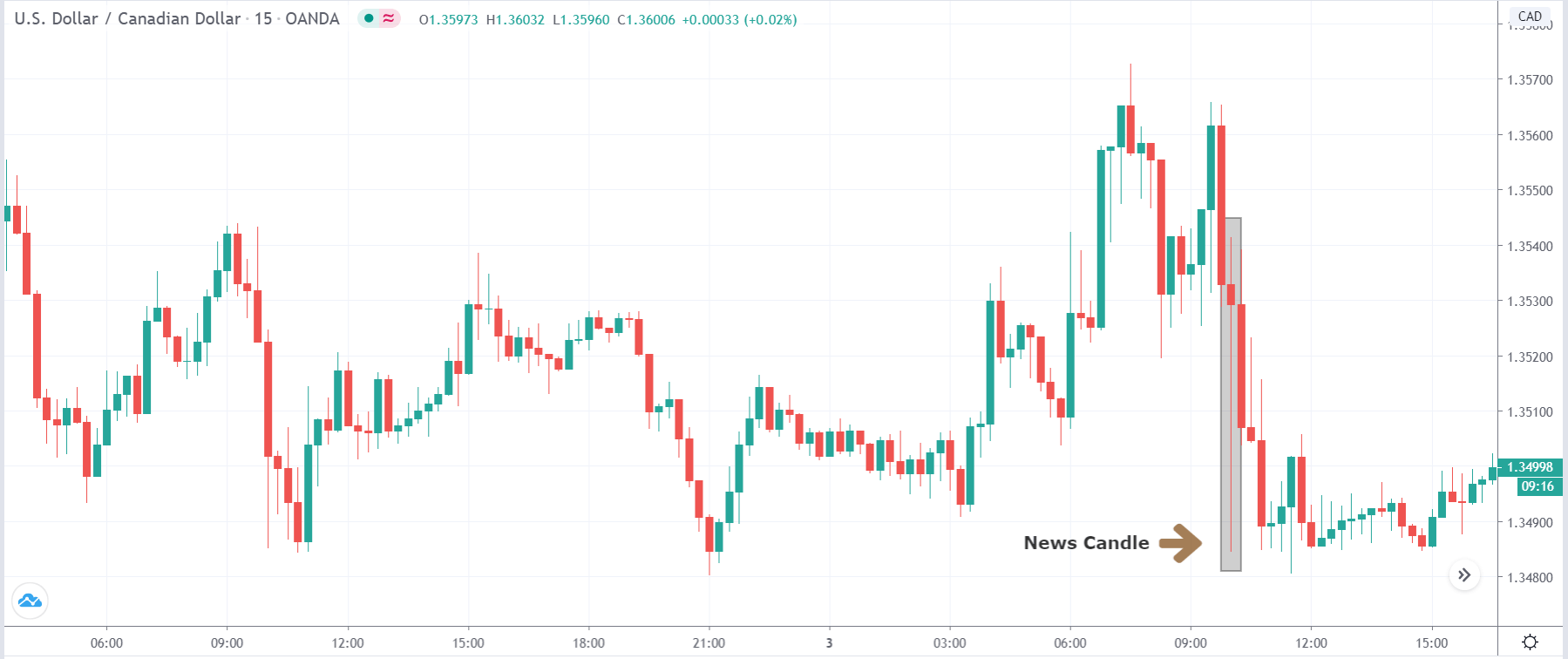
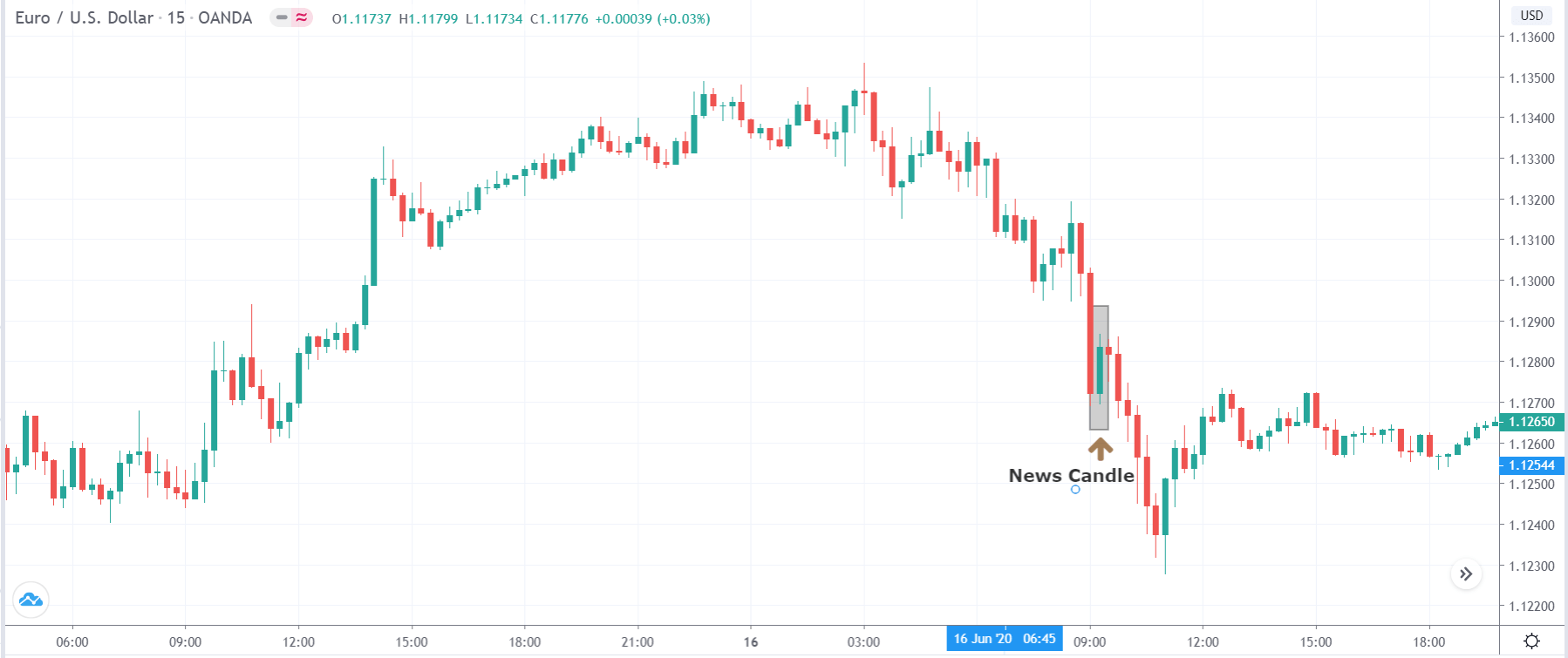
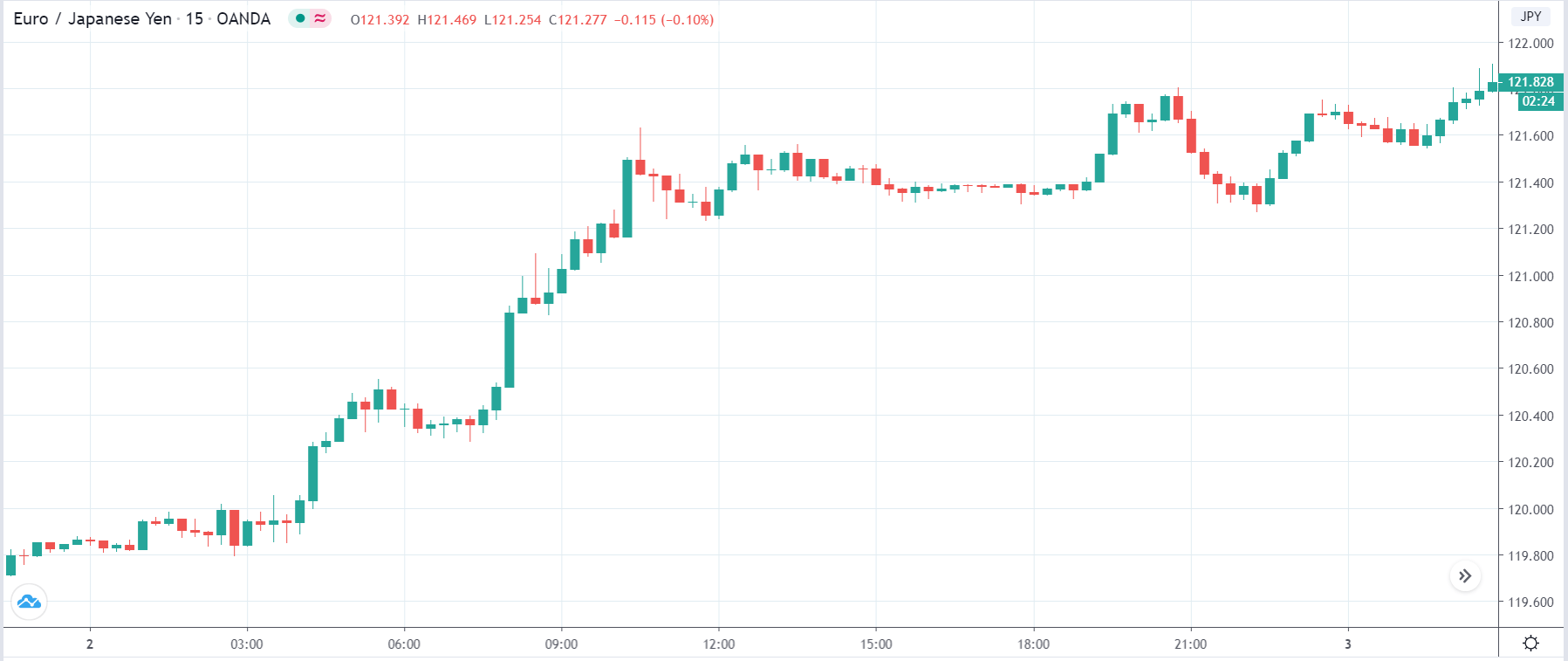
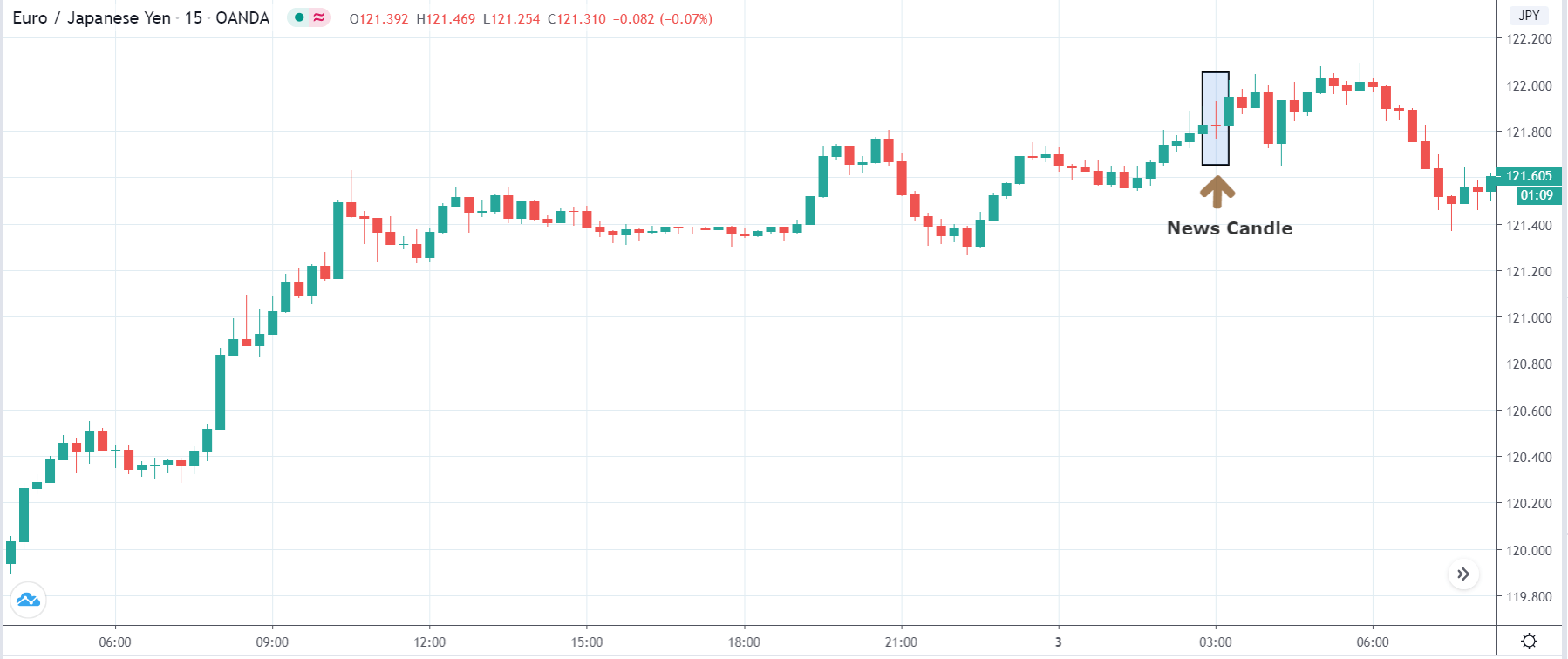
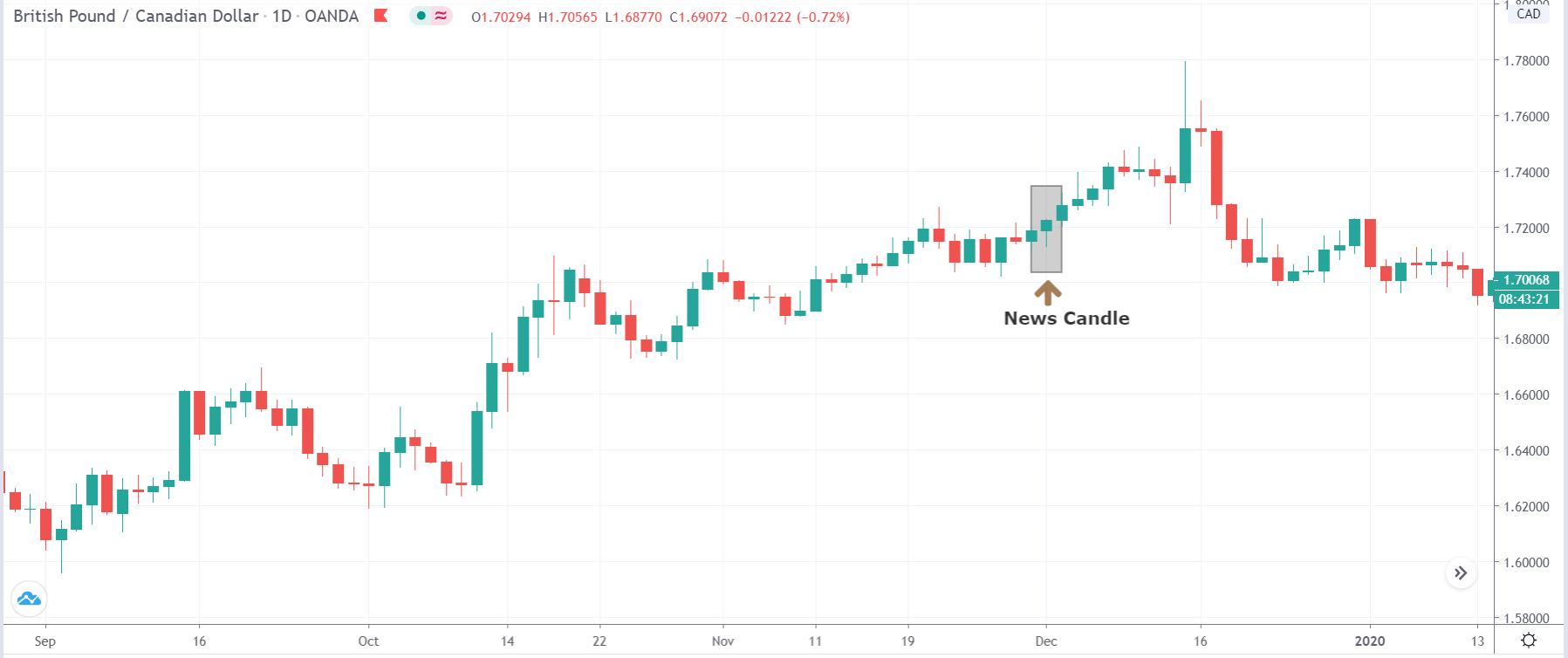
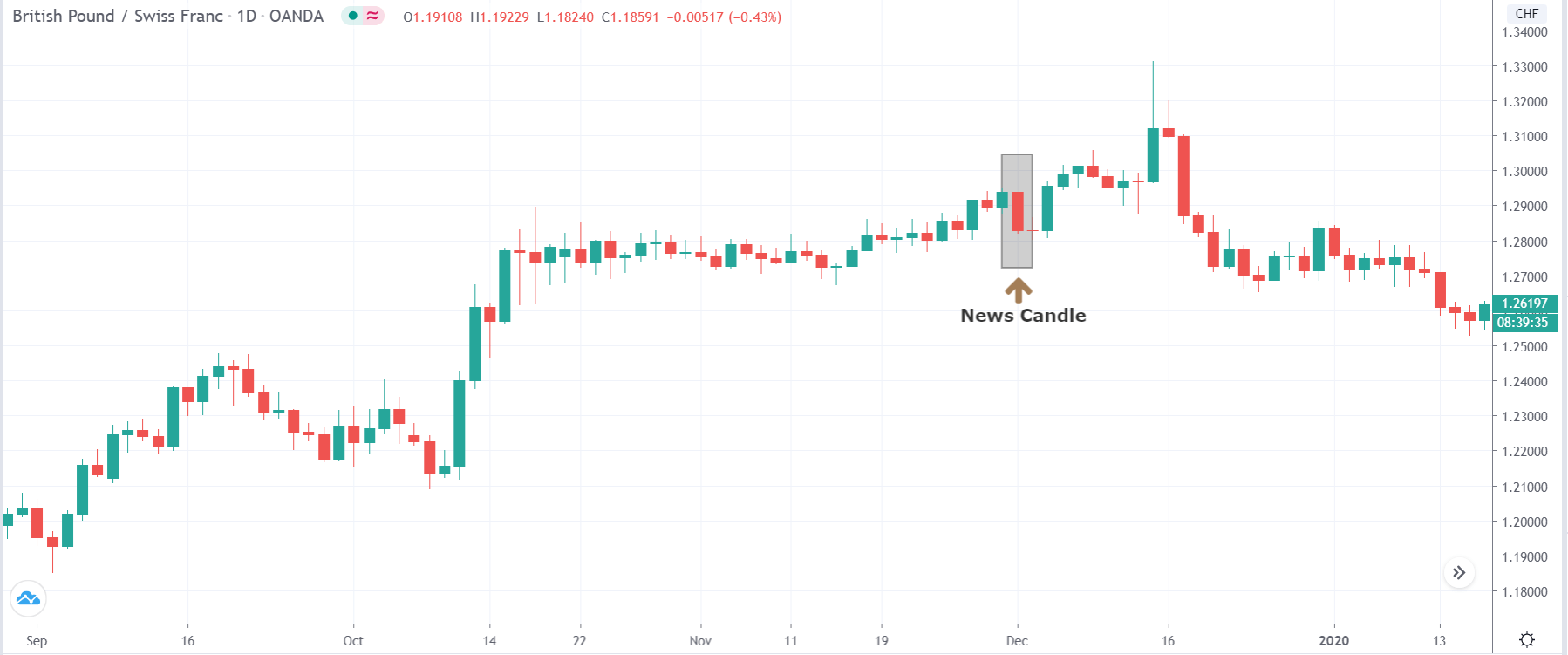
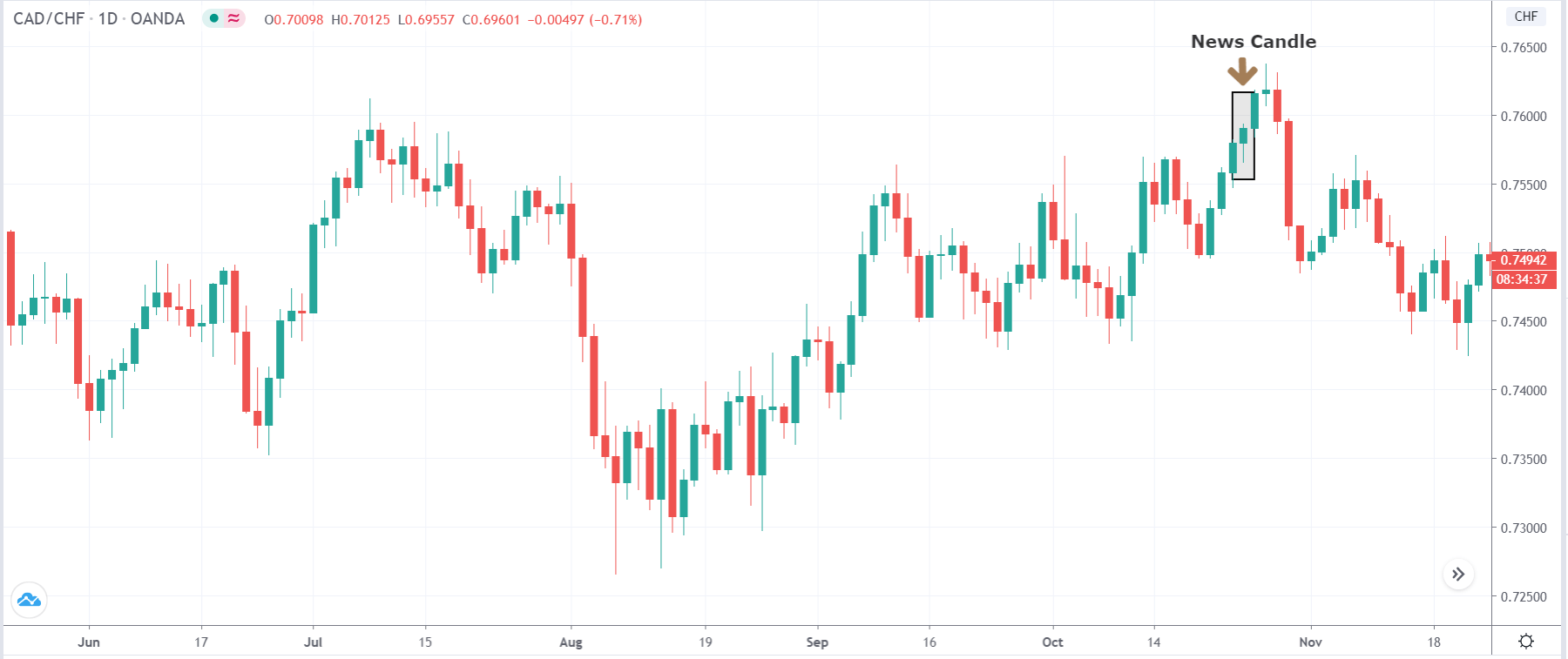
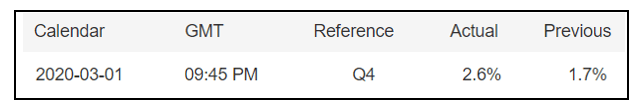
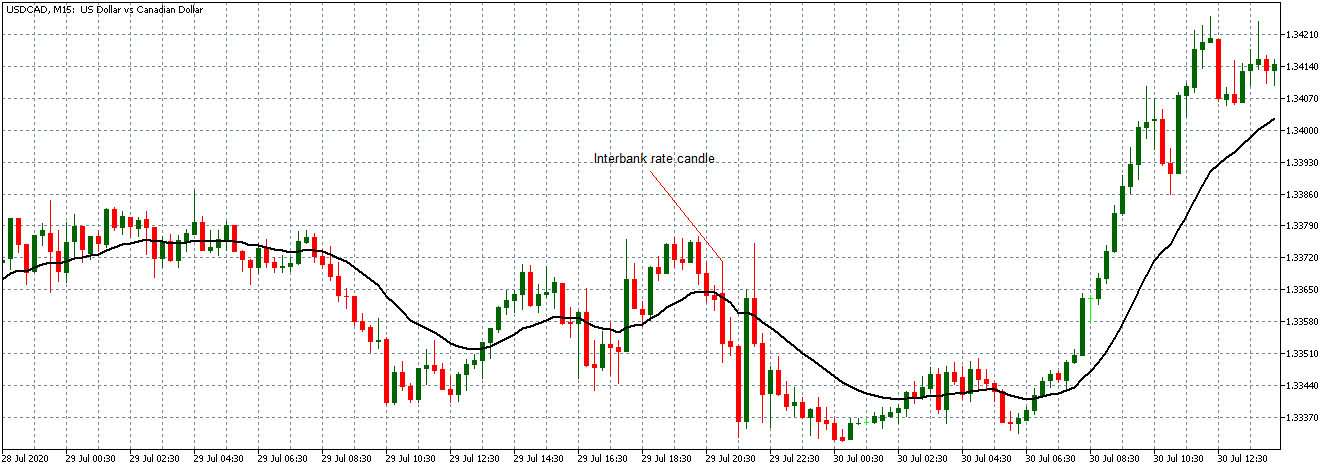
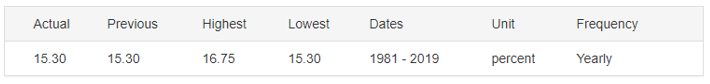
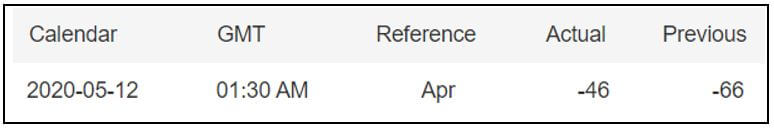
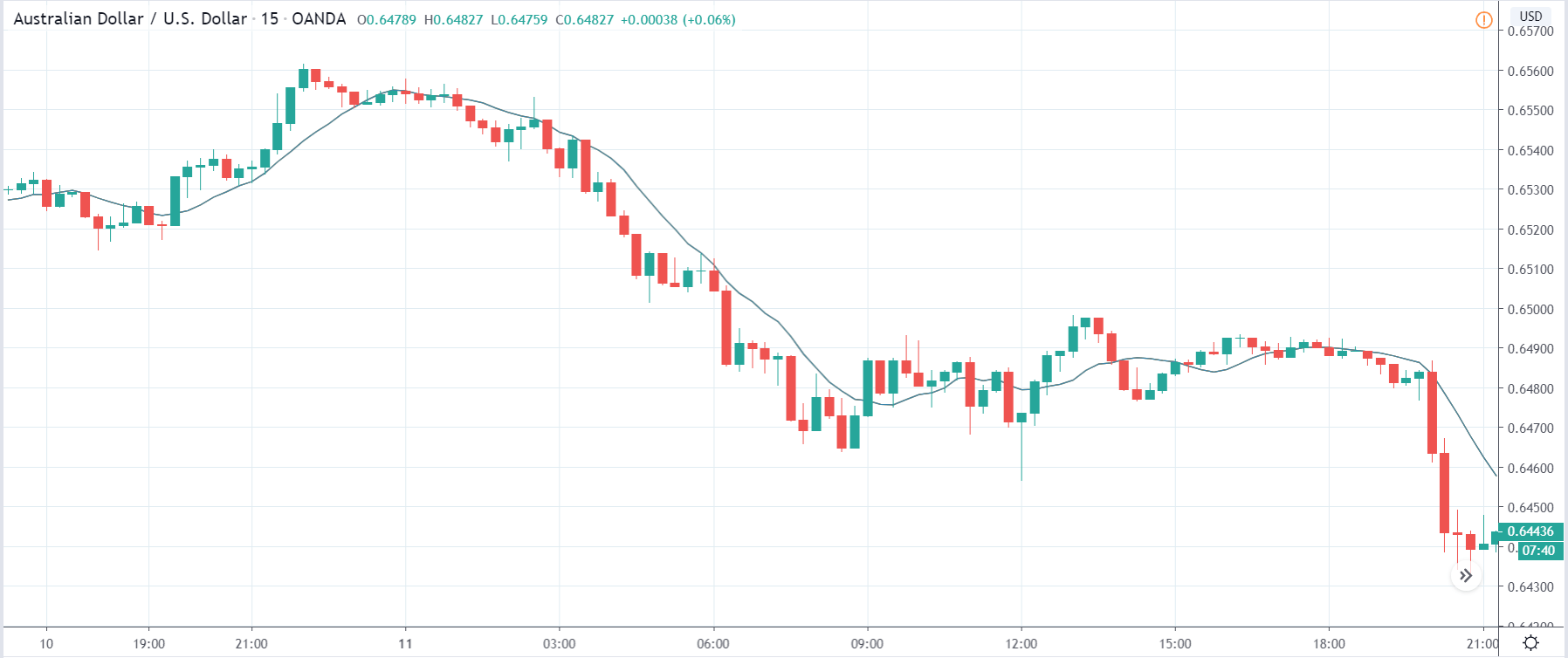
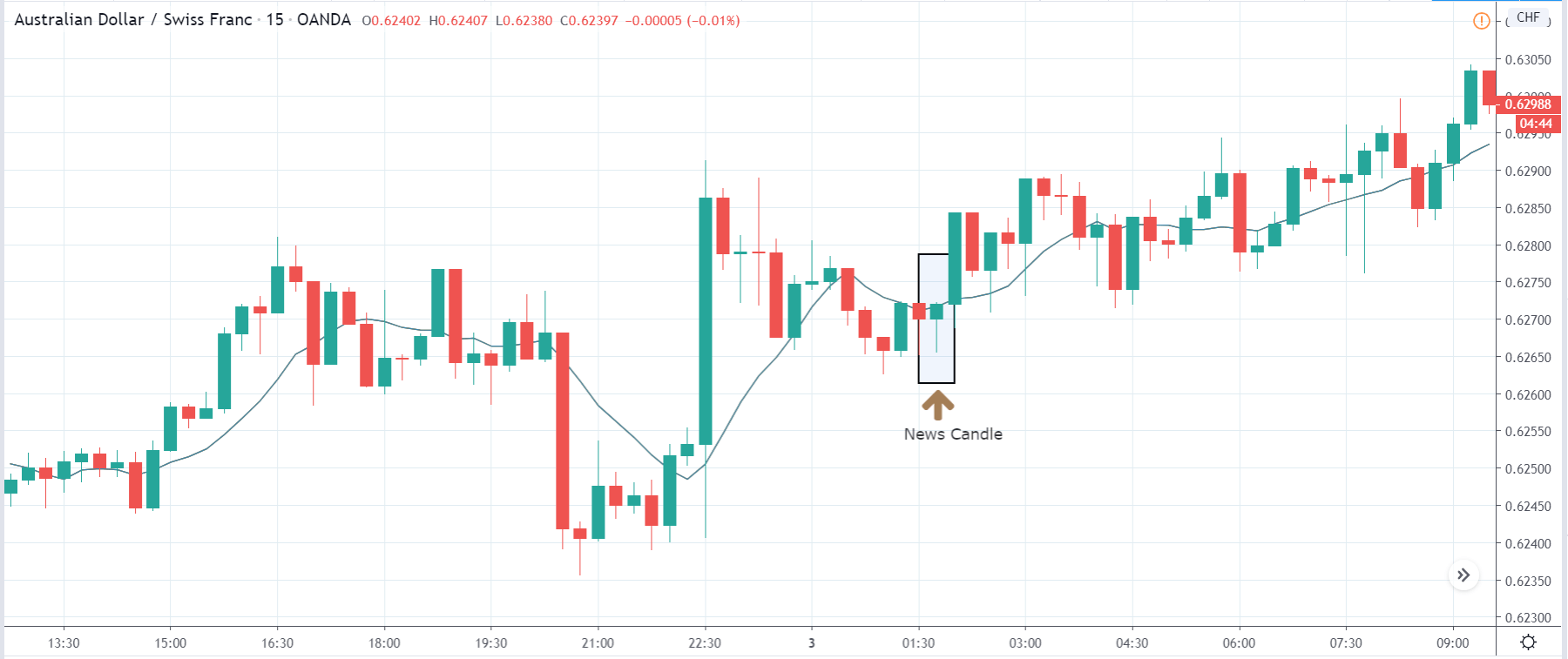
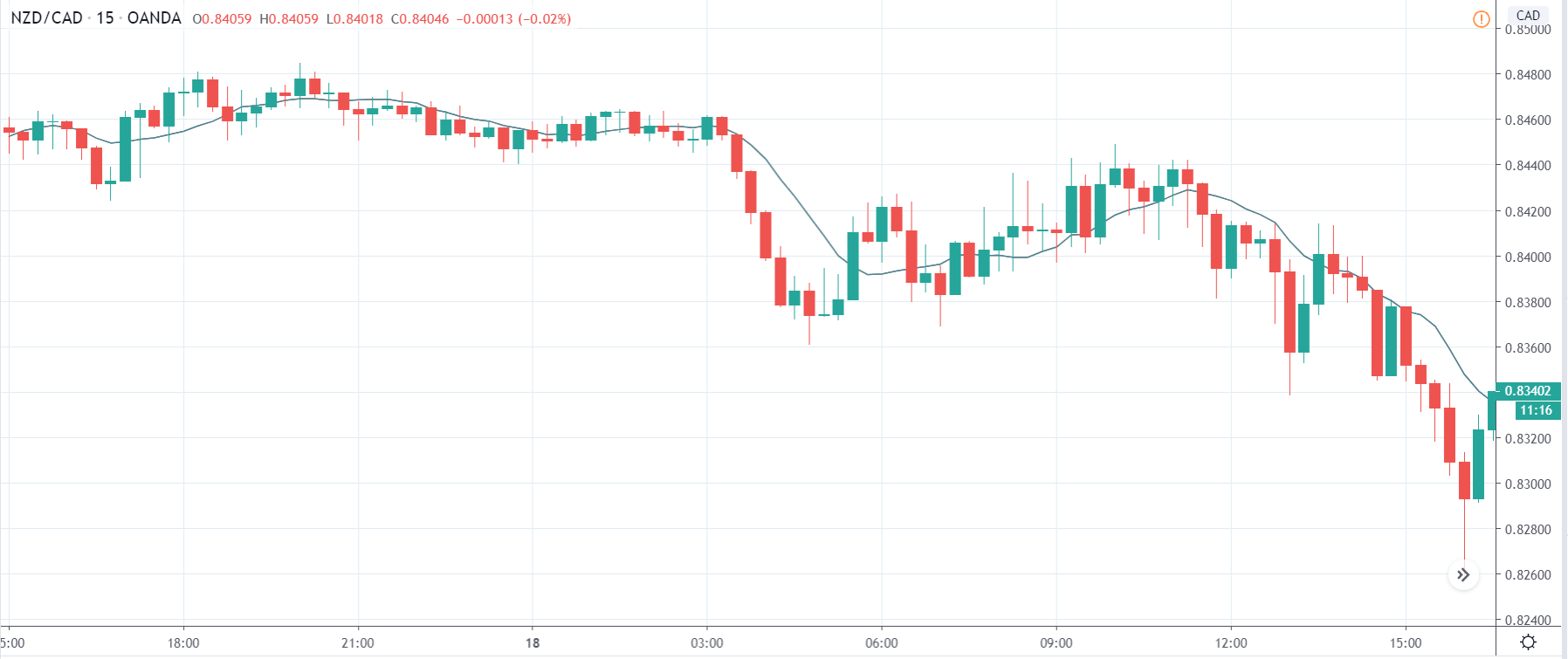
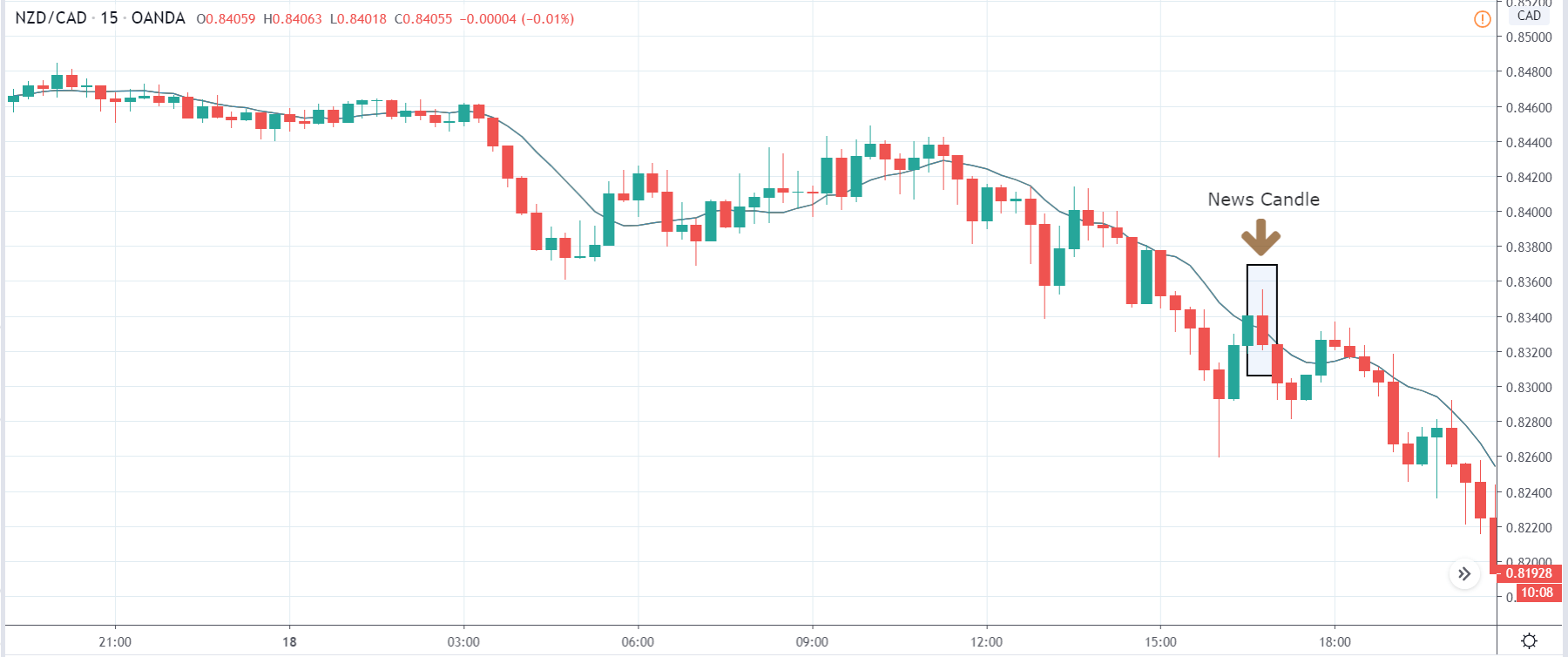
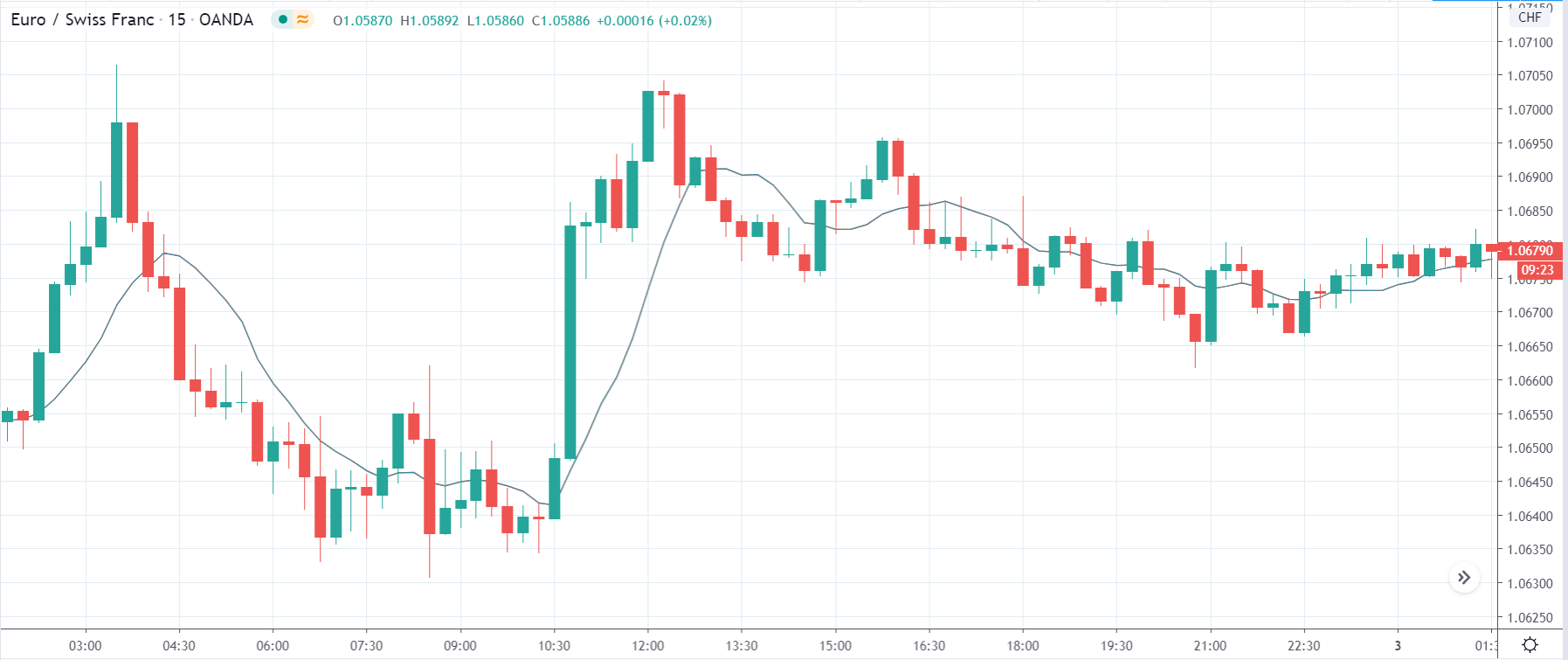
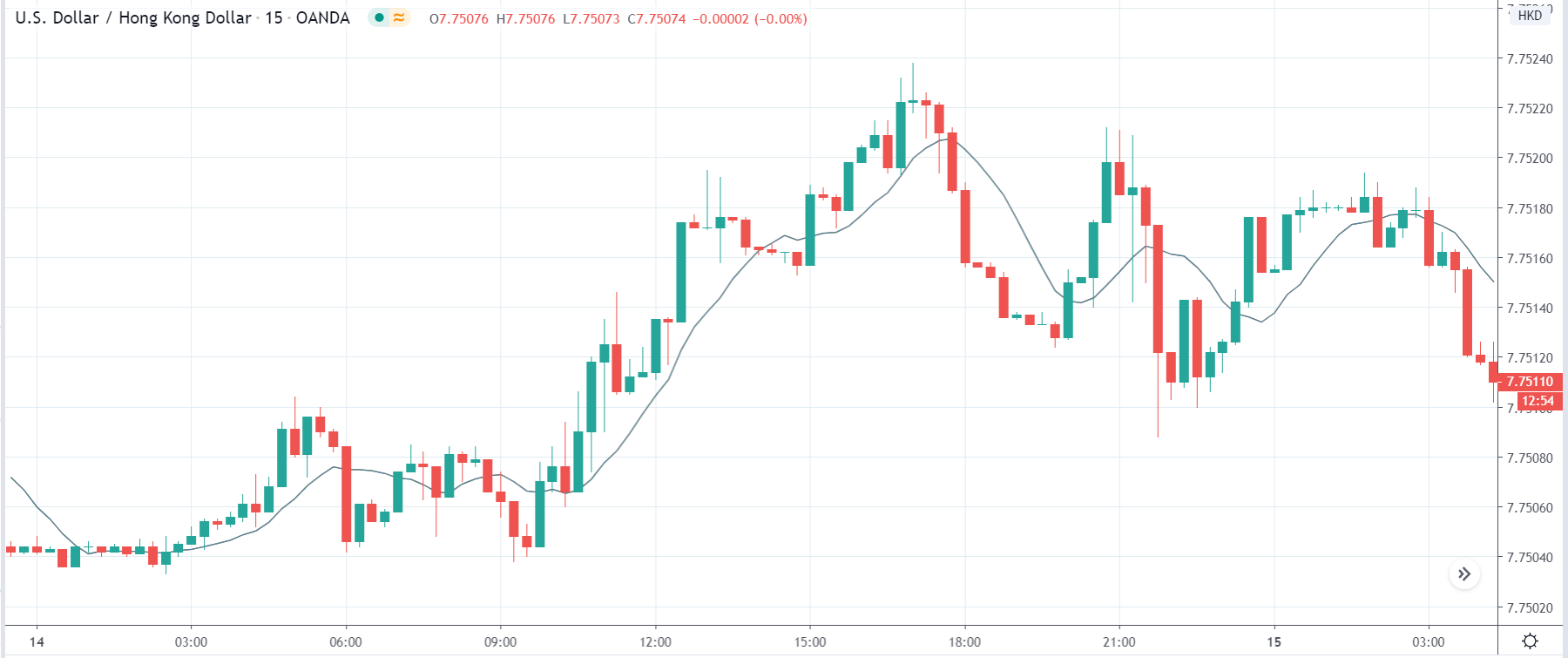
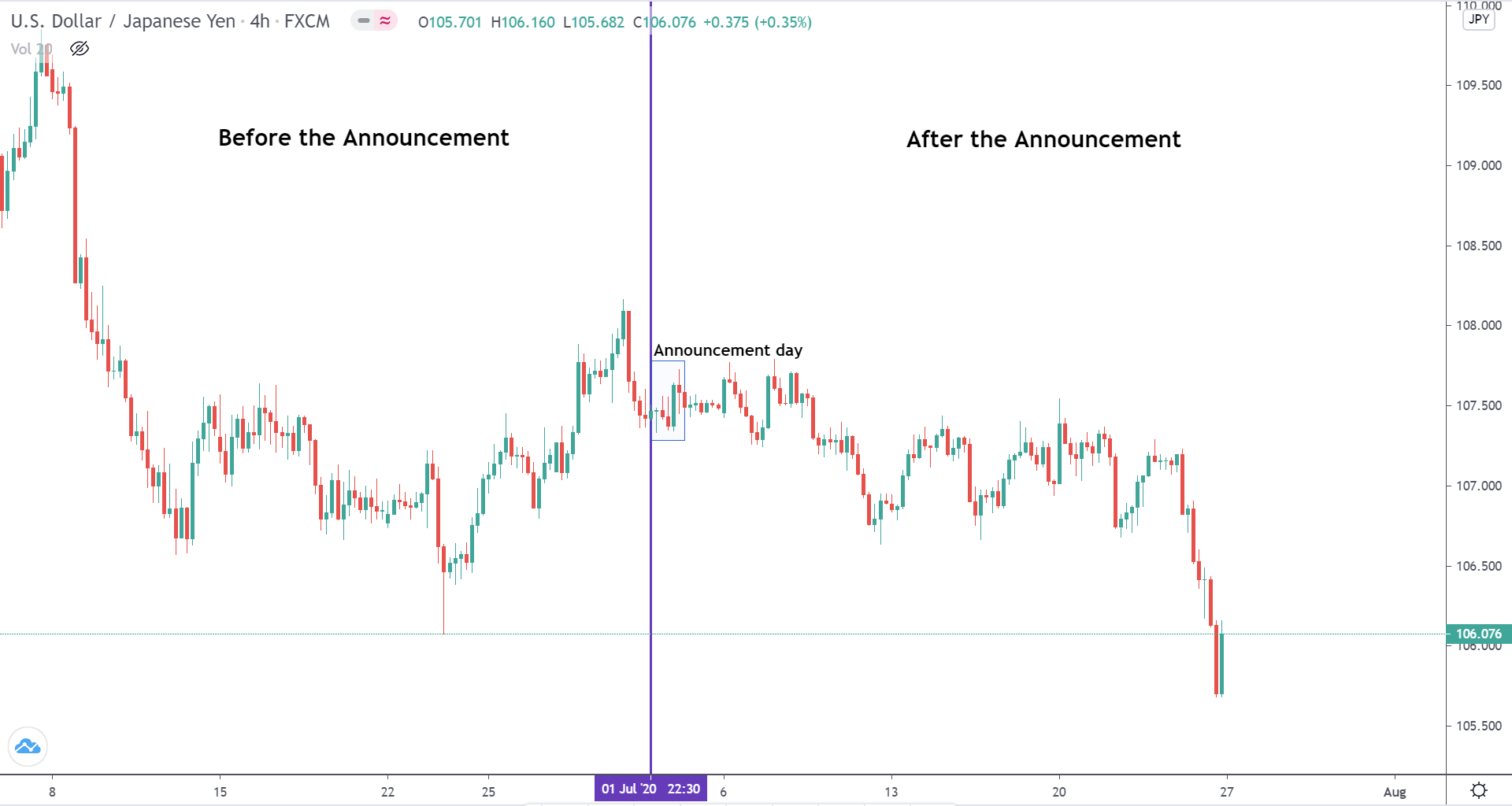
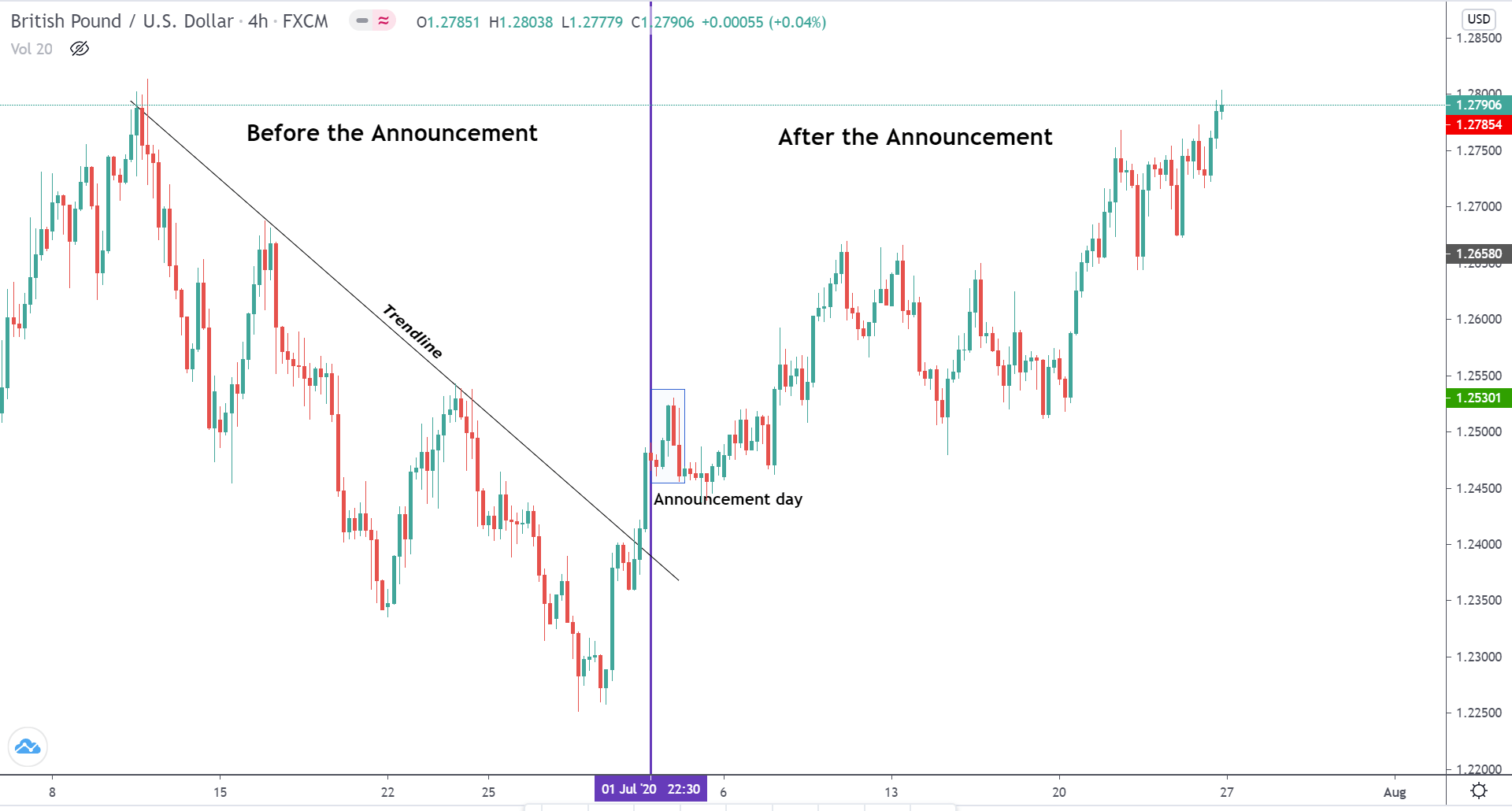
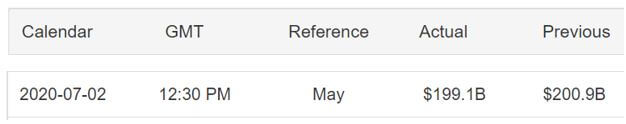
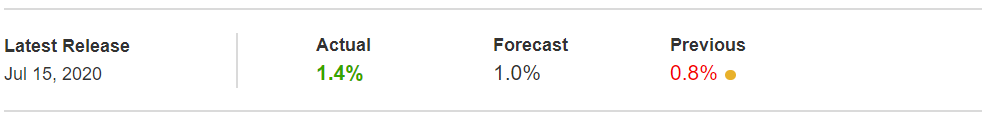
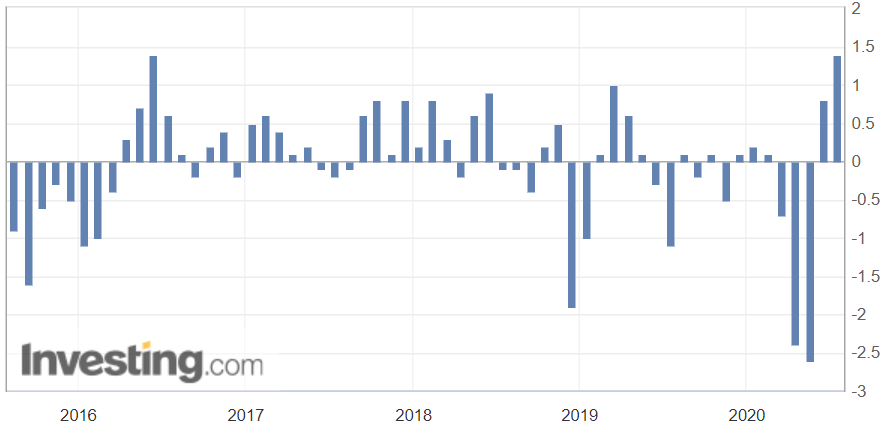
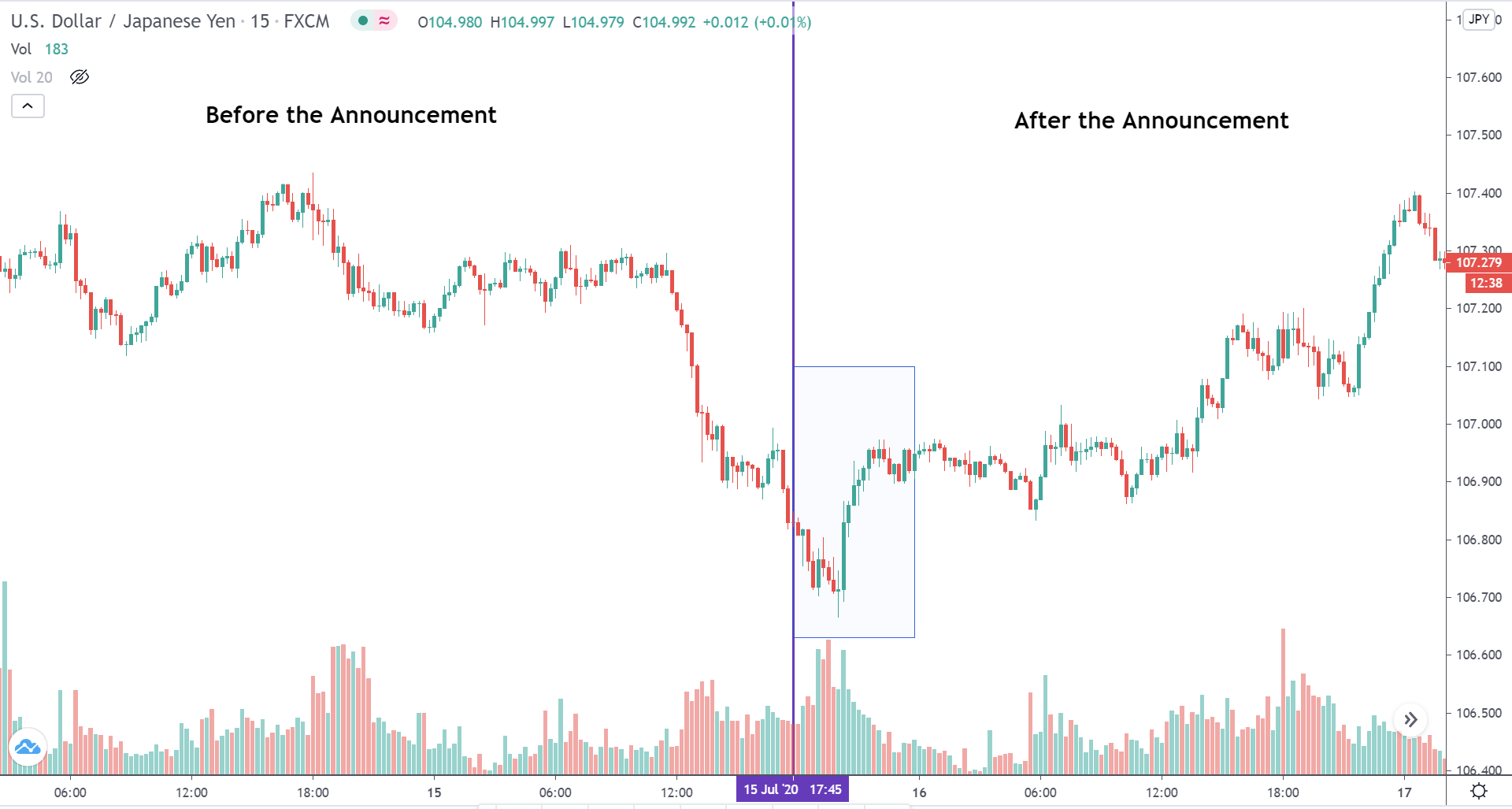
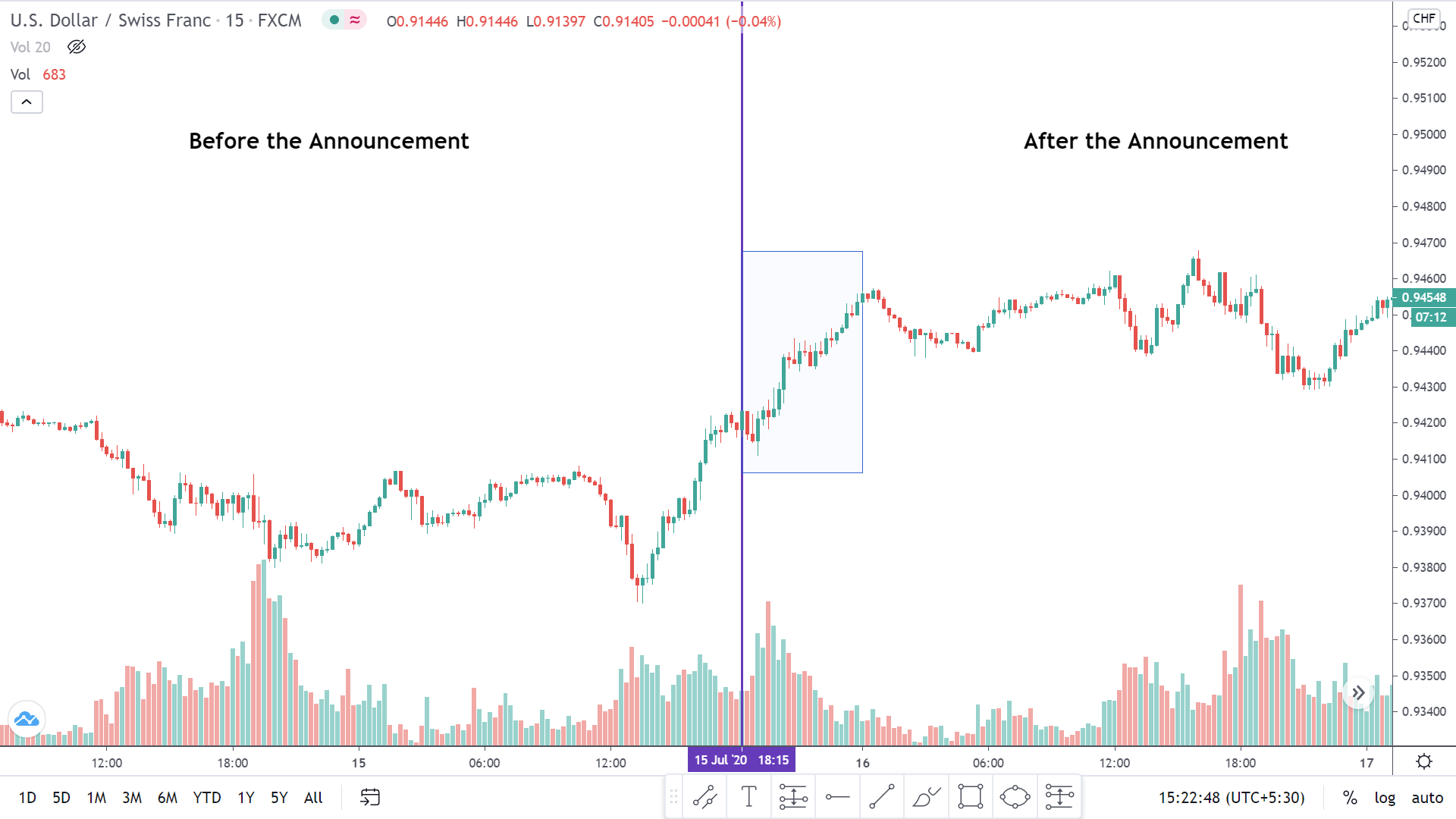
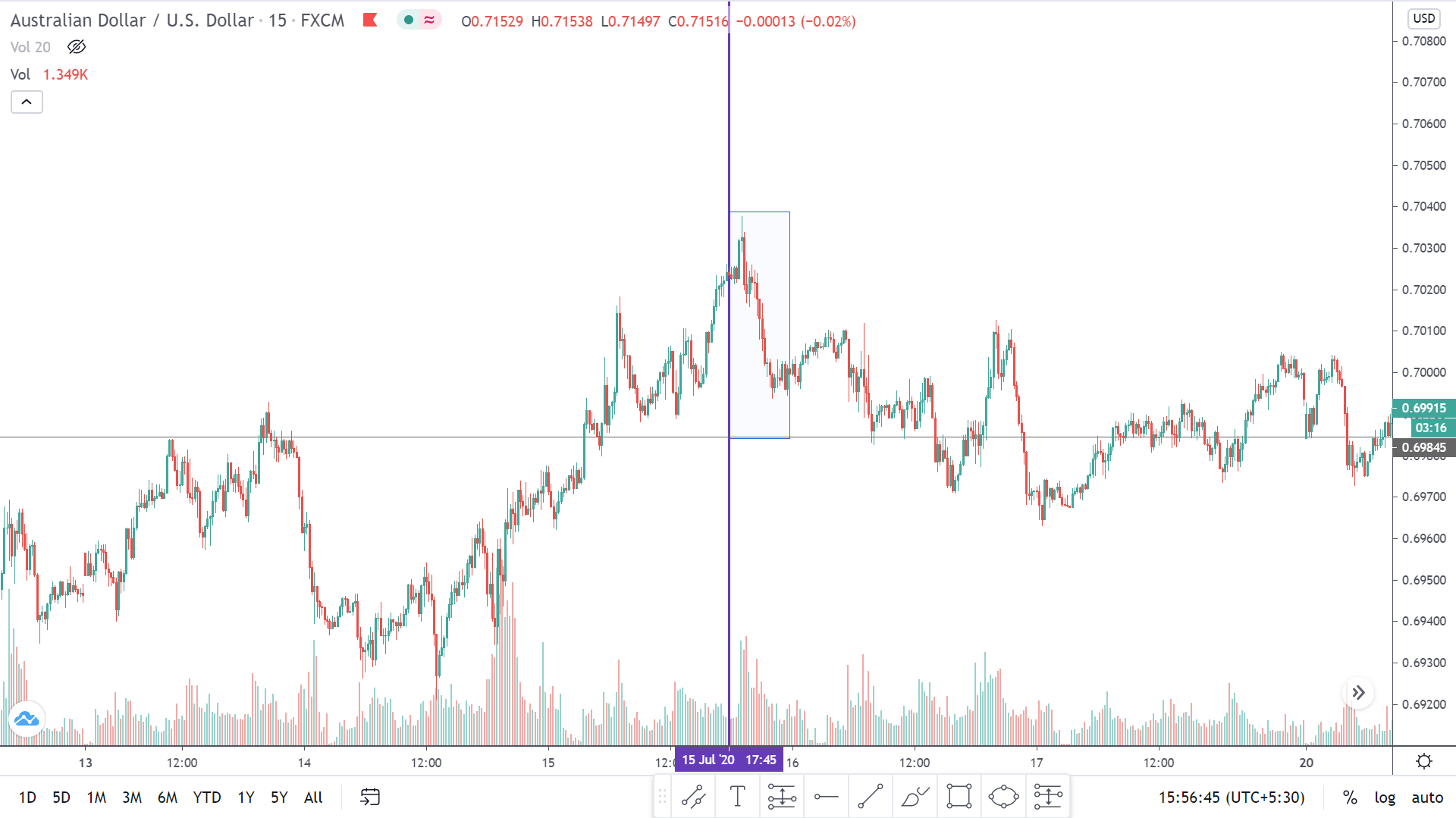
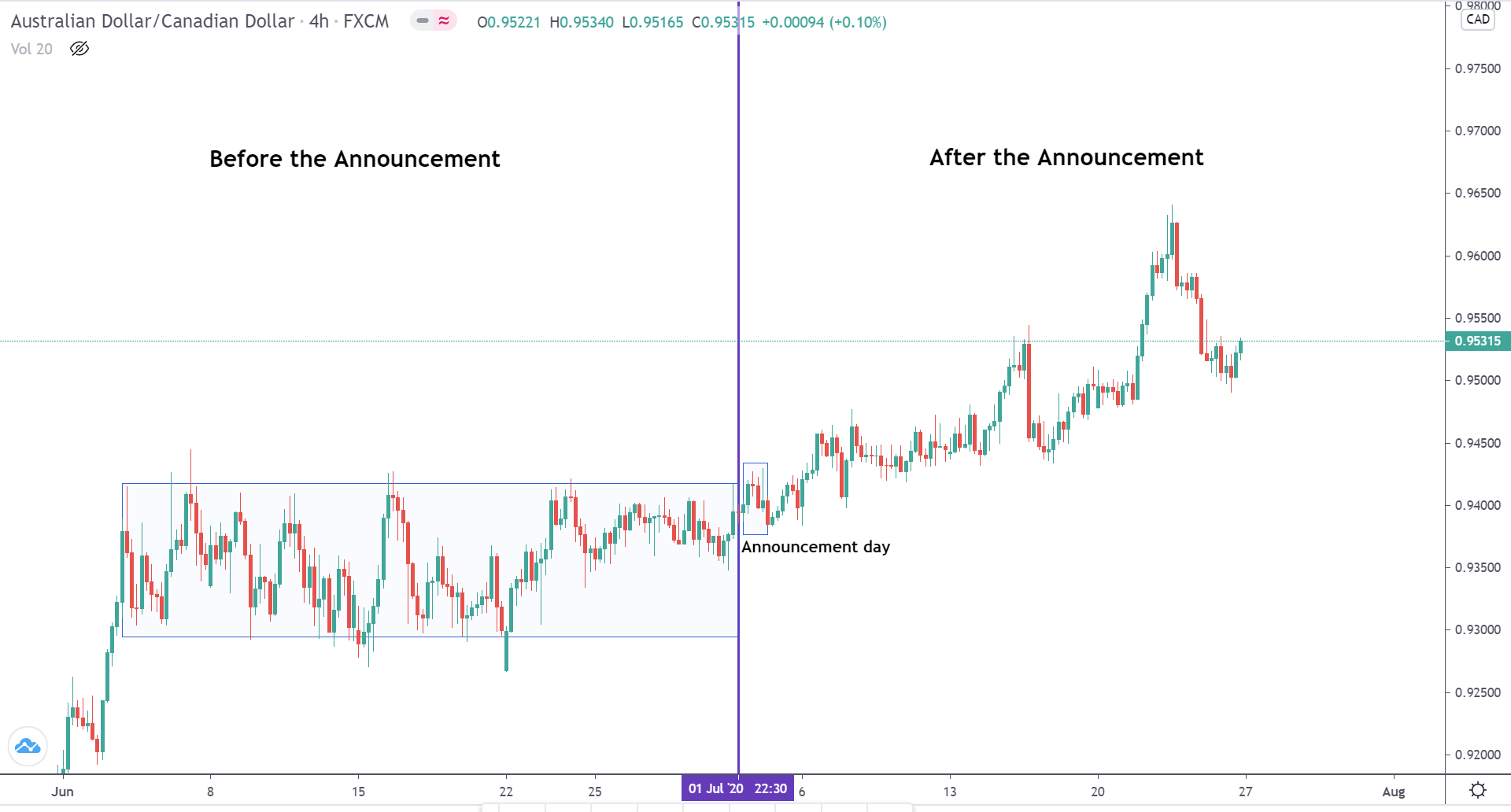
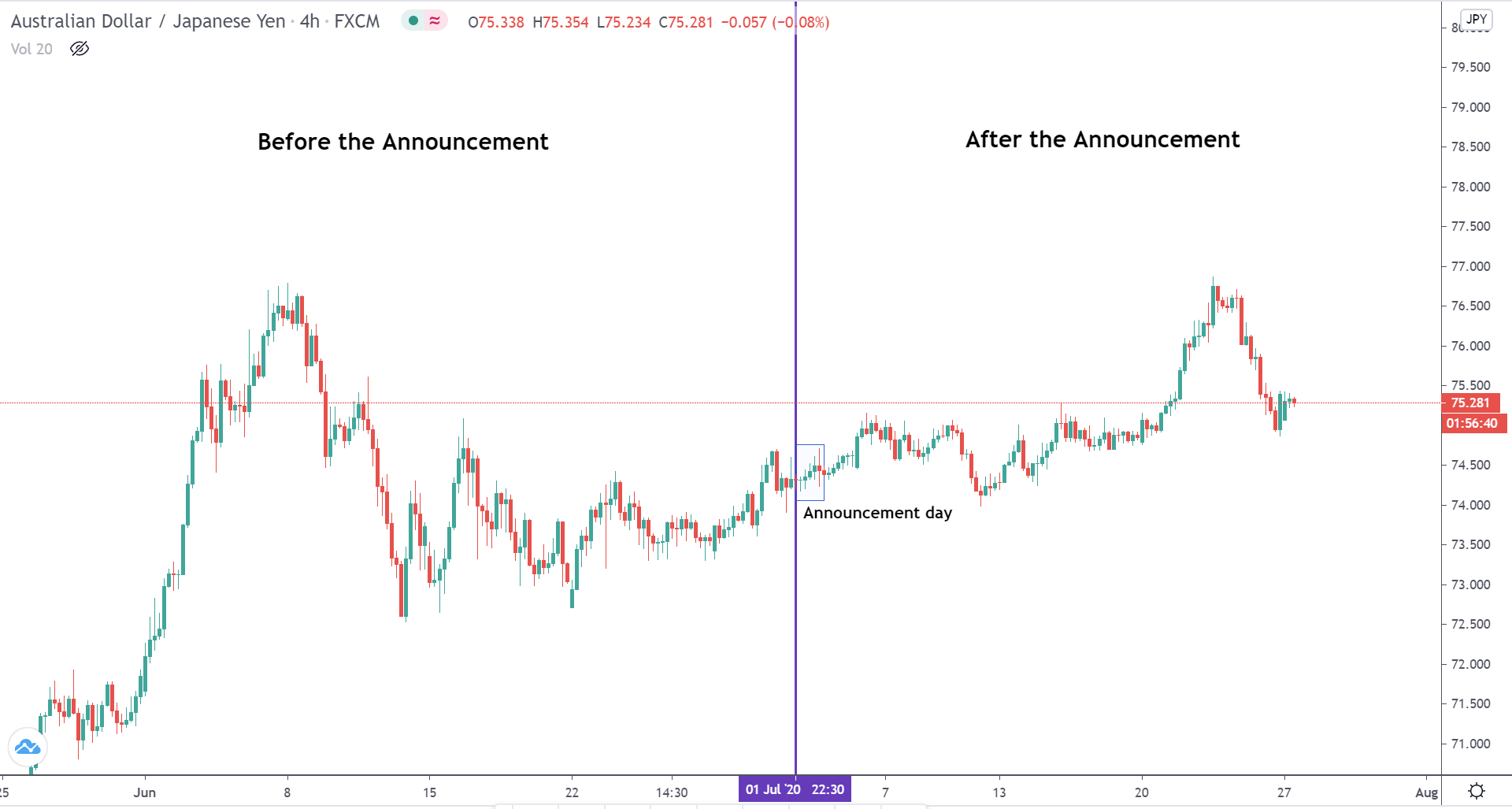
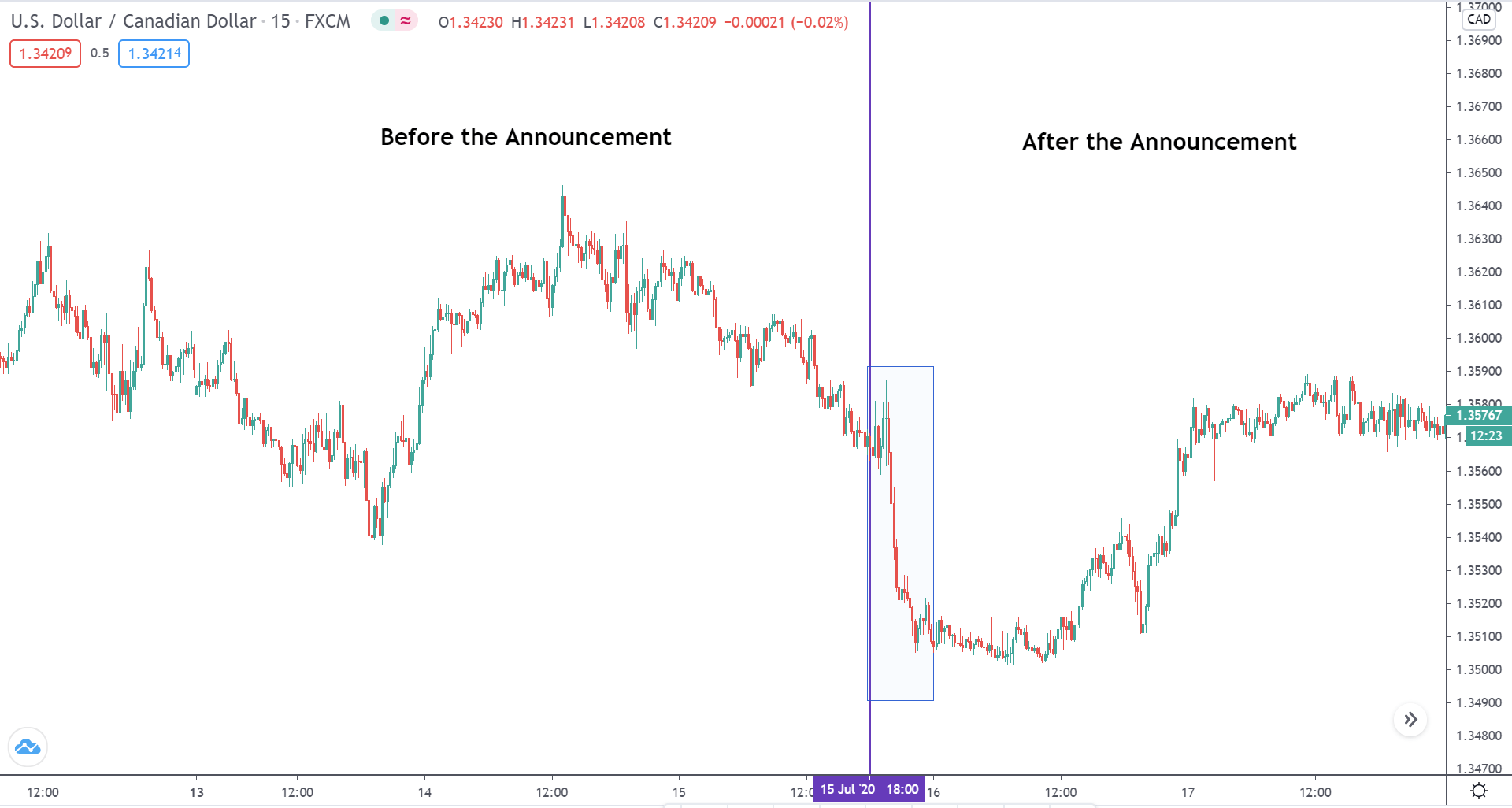
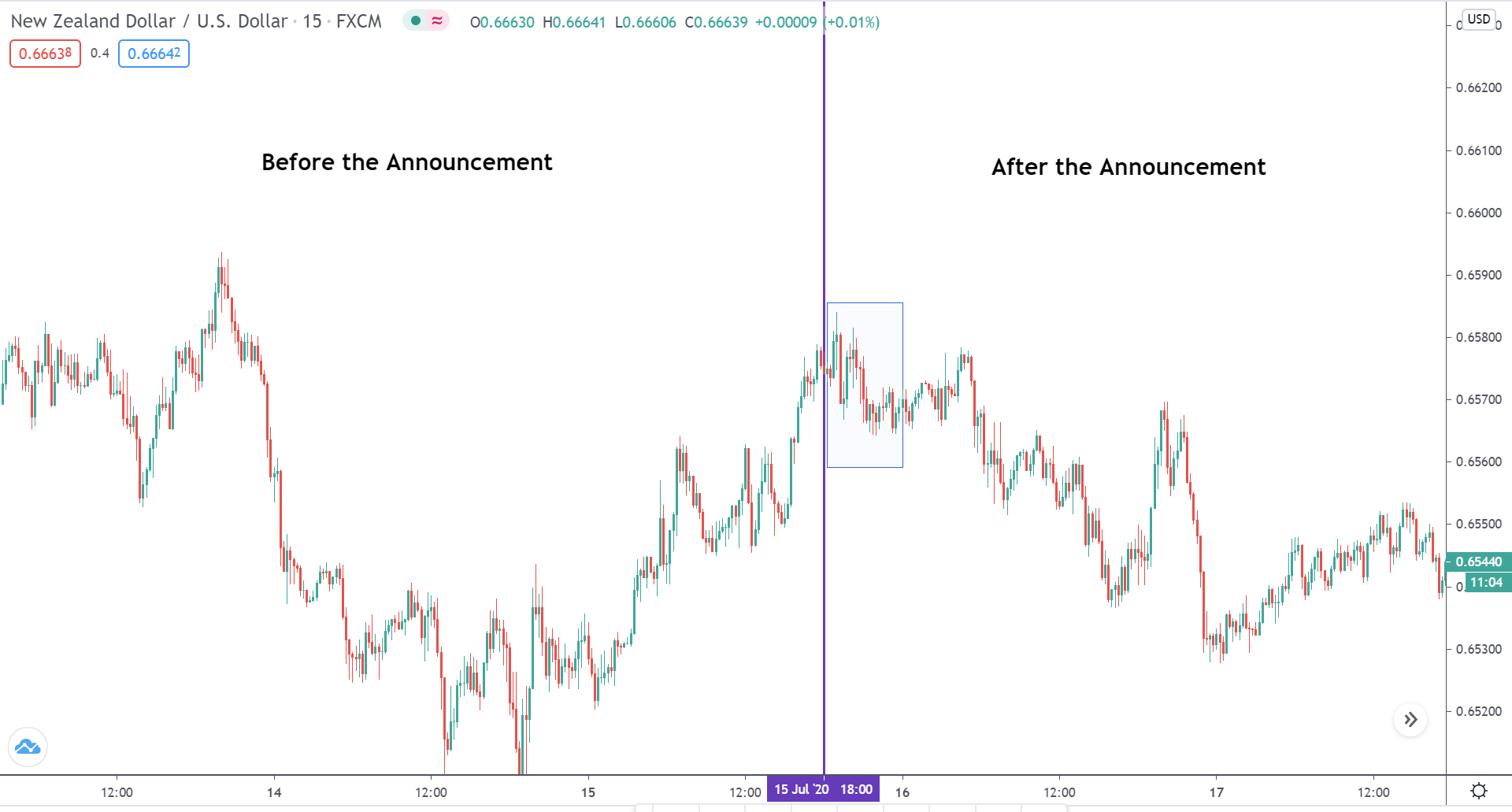
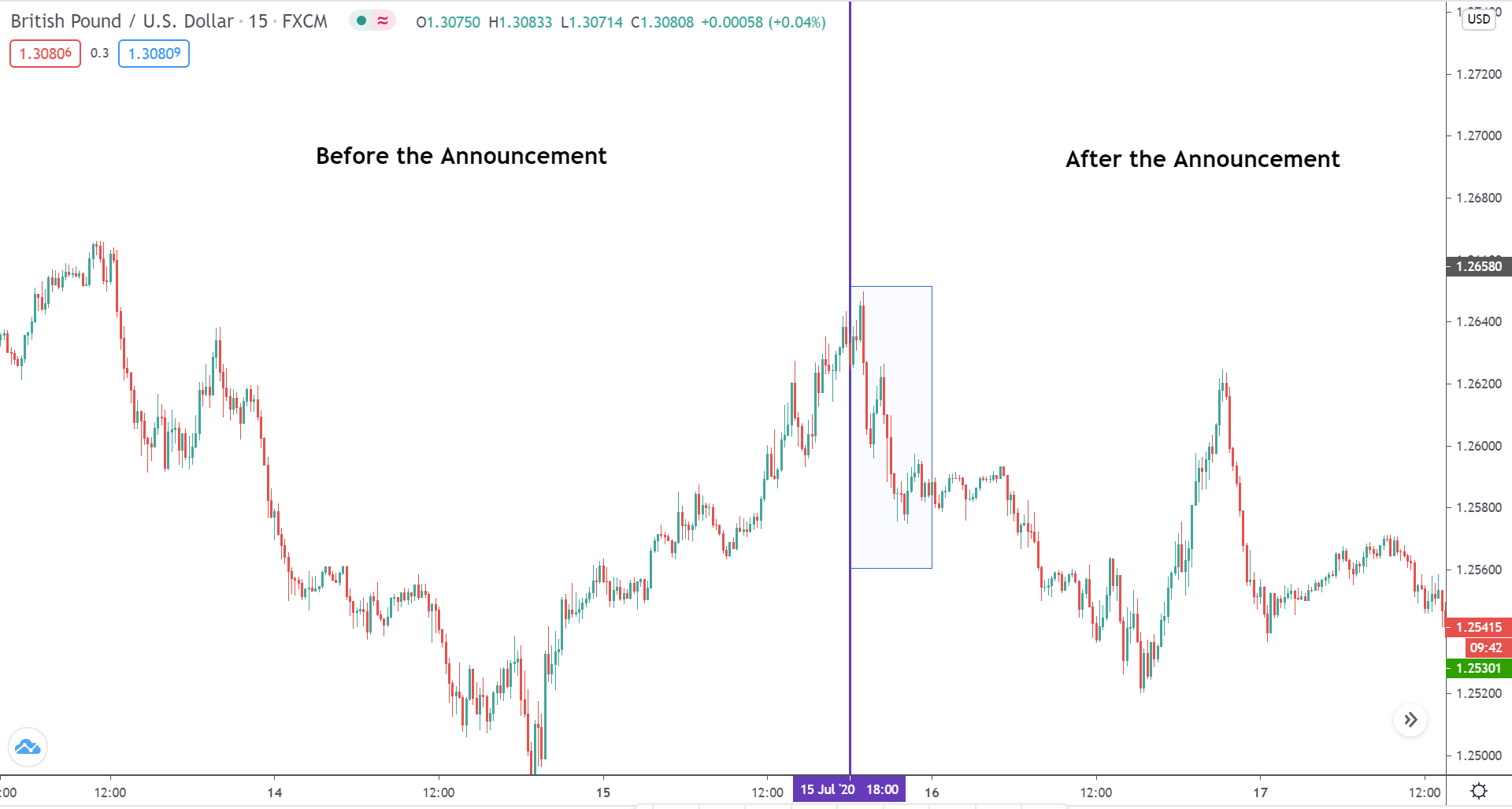
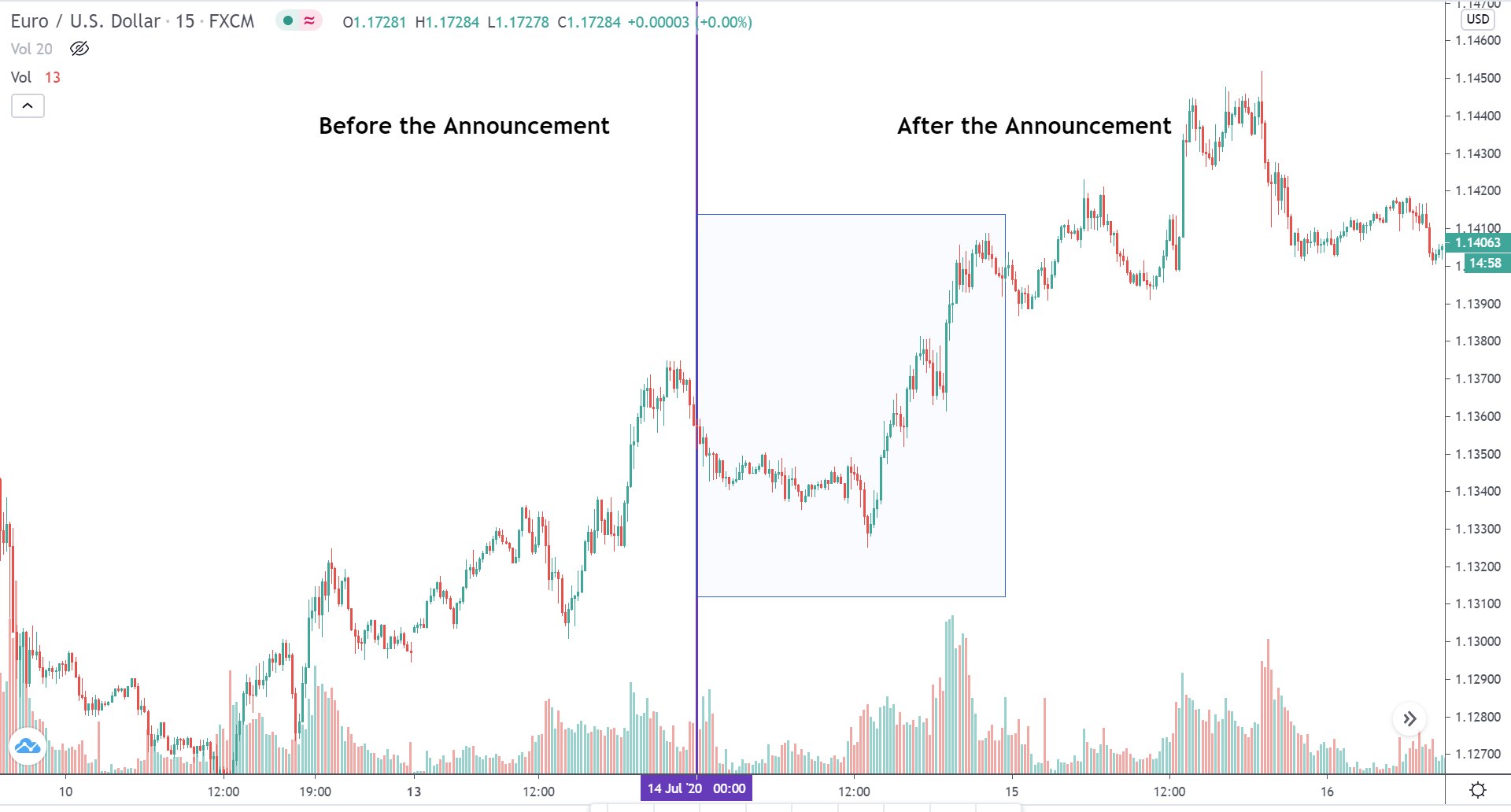
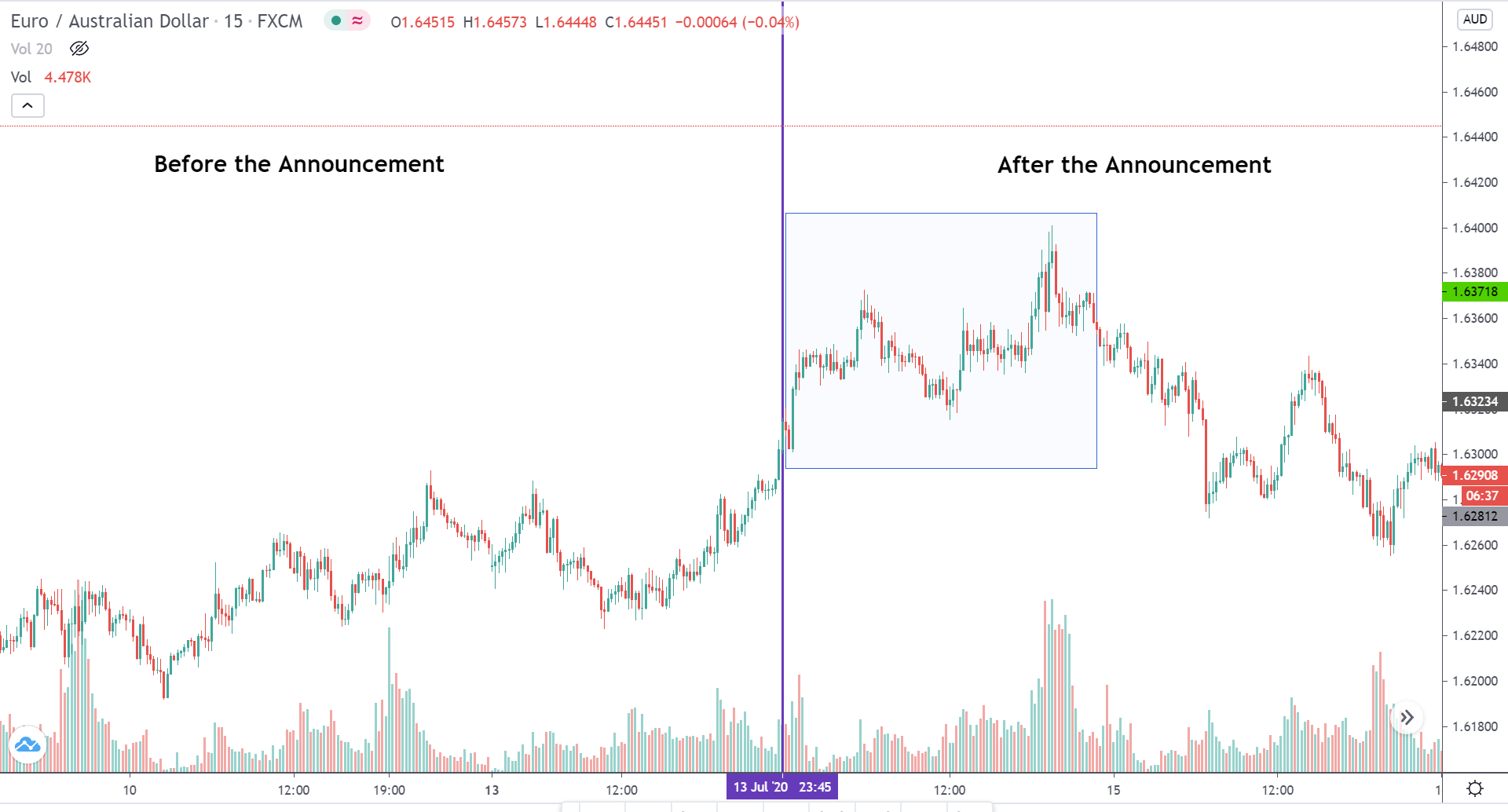
 In today’s lesson, we will analyze the impact of GDP on various currency pairs by observing the change in volatility before and after the news announcement. For that purpose, we have collected the GDP data of Canada, where the below image shows the month-on-month GDP data released recently. Let us find out the market’s reaction to this data.
In today’s lesson, we will analyze the impact of GDP on various currency pairs by observing the change in volatility before and after the news announcement. For that purpose, we have collected the GDP data of Canada, where the below image shows the month-on-month GDP data released recently. Let us find out the market’s reaction to this data.